CHARACTERIZATION, EXPRESSION PATTERN AND PROMOTER ACTIVITY ANALYSIS OF INTERFERON-GAMMA IN JAPANESE EEL, ANGUILLA JAPONICA
-
摘要: 为揭示鱼类IFN-γ的生物学功能, 研究从日本鳗鲡(Anguilla japonica)中克隆获得了IFN-γ基因, 命名为AjIFN-γ。AjIFN-γ具有脊椎动物IFN-γ的典型特征: 包括4外显子/3内含子的基因结构、C端的IFN-γ特征性氨基酸基序和1个核定位信号, 以及6个α-螺旋反向平行构成的二级结构。AjIFN-γ在日本鳗鲡所有组织中均低水平转录表达, 其中肝脏中表达量最高, 其次是皮肤和头肾。Poly I:C刺激和迟缓爱德华氏菌感染均可显著诱导AjIFN-γ在鳃、头肾、体肾和(或)脾脏中的转录表达, 表明AjIFN-γ能够参与日本鳗鲡抗菌和抗病毒的免疫过程。此外, 研究还克隆了AjIFN-γ基因的5′调控区序列共1536 bp, 并构建了一系列Aj IFN-γ 5′调控区删节突变体, 分析其启动子活性, 结果表明, 上游–240/+136区域中含有起始AjIFN-γ转录的关键启动子调控元件, –1062/–814区域存在转录的正调控元件, 而–1252/–1062区域存在转录的负调控元件。上述结果进一步丰富了鱼类IFN-γ的基础知识。Abstract: IFN-γ is a cytokine that is critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral, some bacterial and protozoal infections. In this study, an interferon-γ gene, named AjIFN-γ, was cloned and characterized from Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. The AjIFN-γ shared some common features with its vertebrate homologues including a 4-exon/3-intron gene structure, a typical IFN-γ characteristic motif and a predicted nuclear localization site in the predicted protein. AjIFN-γ mRNA could be detected in all the tested tissues from healthy Japanese eel with the highest in liver, followed by skin and head kidney by real-time RT-PCR. A significantly increased expression of AjIFN-γ could be found in gill, head kidney, trunk kidney and (or) spleen post intraperitoneal injection with Poly I:C or Edwardsiella tarda, which indicated a role in defense of Japanese eel against both viruses and bacteria. Furthermore, luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that the sequence from –240 bp to +136 bp in the 5′ flanking region of AjIFN-γ gene was essential for initiating the transcription of AjIFN-γ, and the sequence form –1062 bp to –814 bp may contain some positive transcriptional regulatory elements while the sequence from –1252 bp to –1062 bp may contain negative transcriptional regula-tory elements. This study provided the basis for further investigation of the expanding functions of IFN-γ molecules in immunity and other physiological processes in teleost and other animals.
-
Keywords:
- IFN-γ /
- Anguilla japonica /
- Transcriptional expression /
- Promoter
-
-
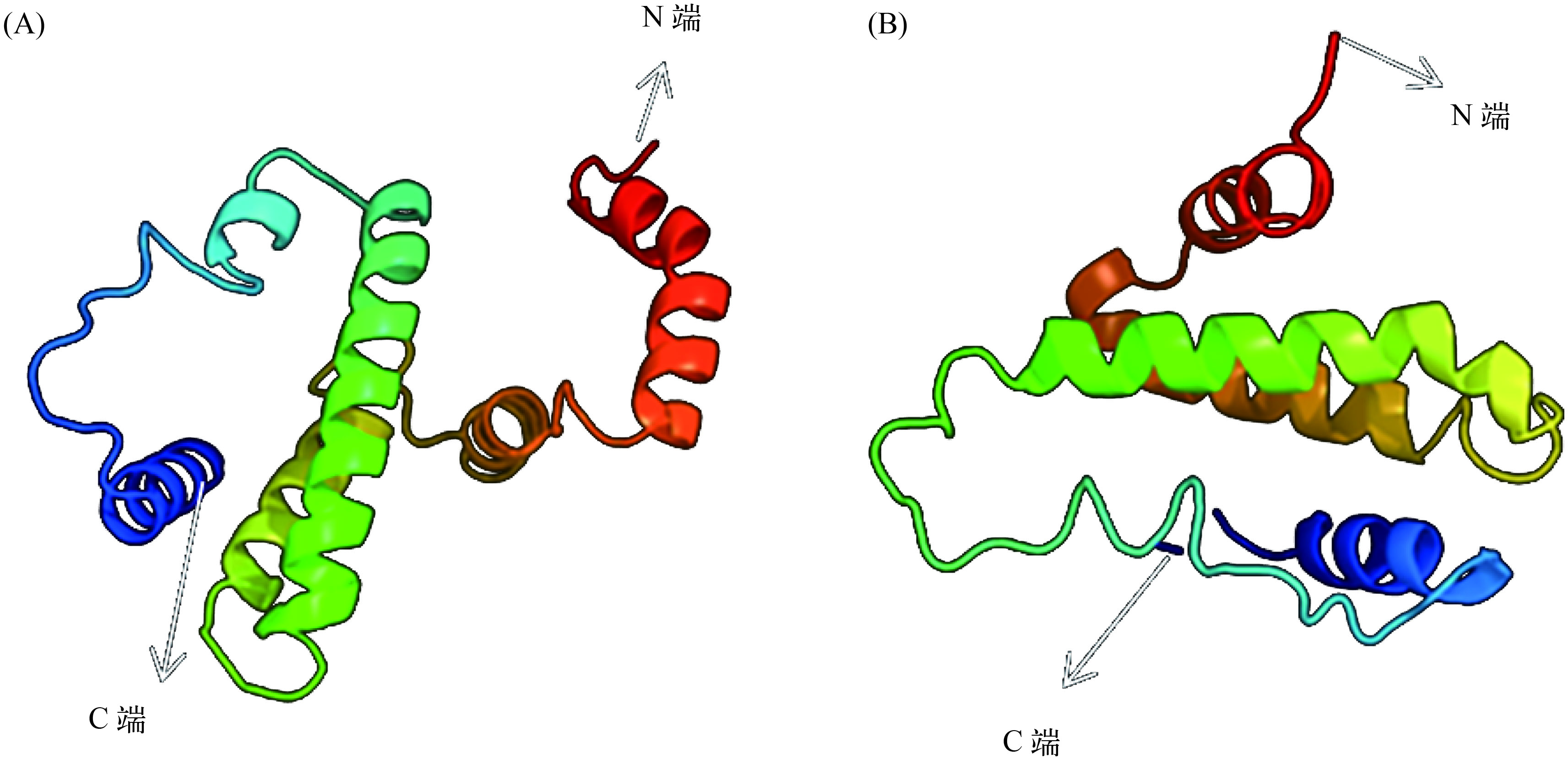
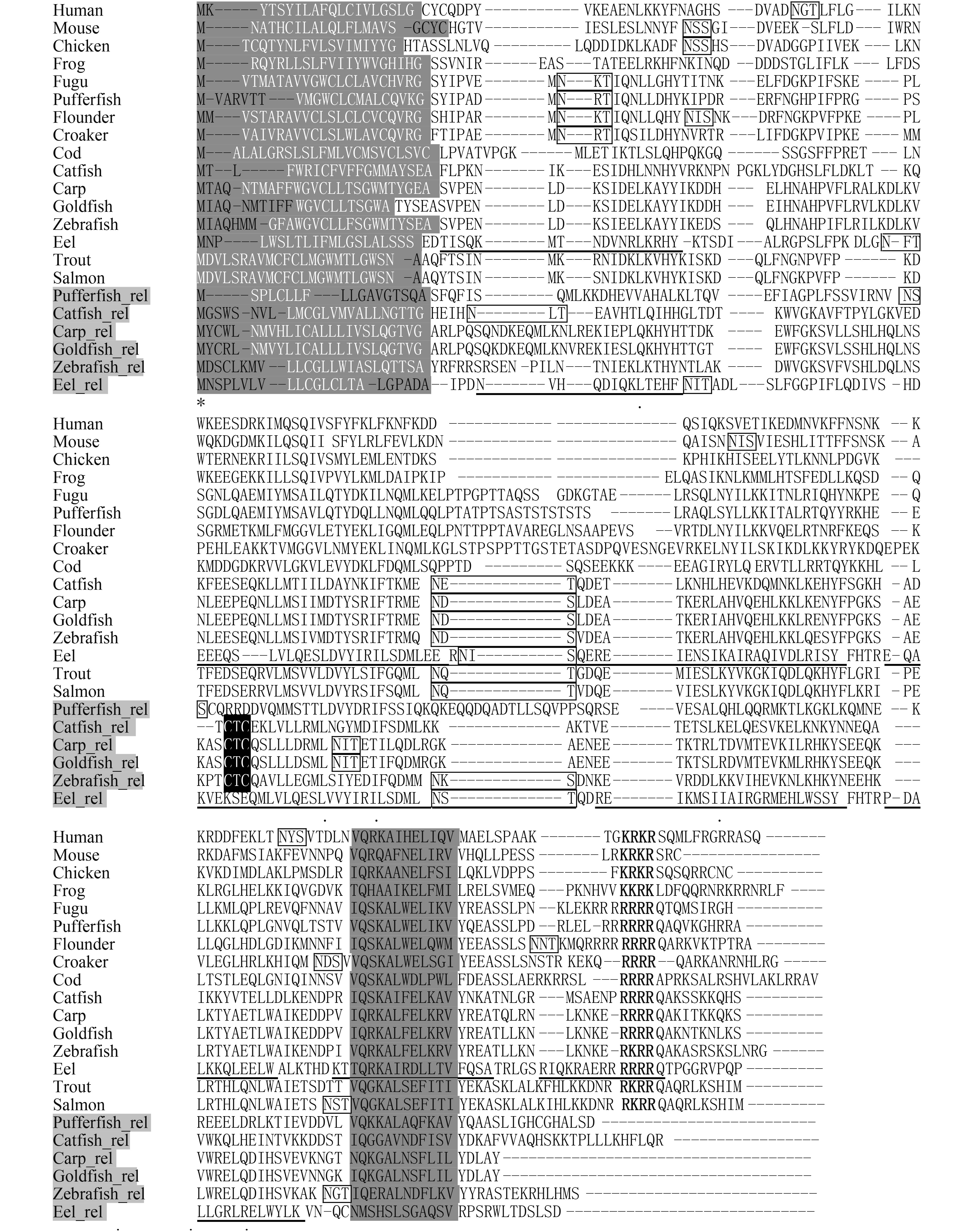
图 1 氨基酸序列多重比对
“–”表示空缺; “*”表示一致, “.”或“:”表示相似; 粗体为NLS; 灰底黑字为IFN-γ特征基序, 灰色名称为IFN-γrel; 下划线为预测的α-螺旋; 灰底白字为信号肽序列; 方框内为预测的N-糖基化位点; 黑色背景为鲤科鱼类中保守的“CTC”基序”
Figure 1. Multiple alignment of deduced amino acid sequence of IFN-γs and IFN-γrels
Dashes (–) indicate gaps in the alignment, asterisks (*) indicate identity and dots (or :) indicate similarity. Nuclear localization signals are in bold and the conserved IFN-γ family signatures are depicted in dark grey. Sequences underlined represent the predicted α-helices. The predicted signal peptides are in italic. The predicted N-glycosylation sites are showed in boxes. The conserved “CTC” motif is shaded in black
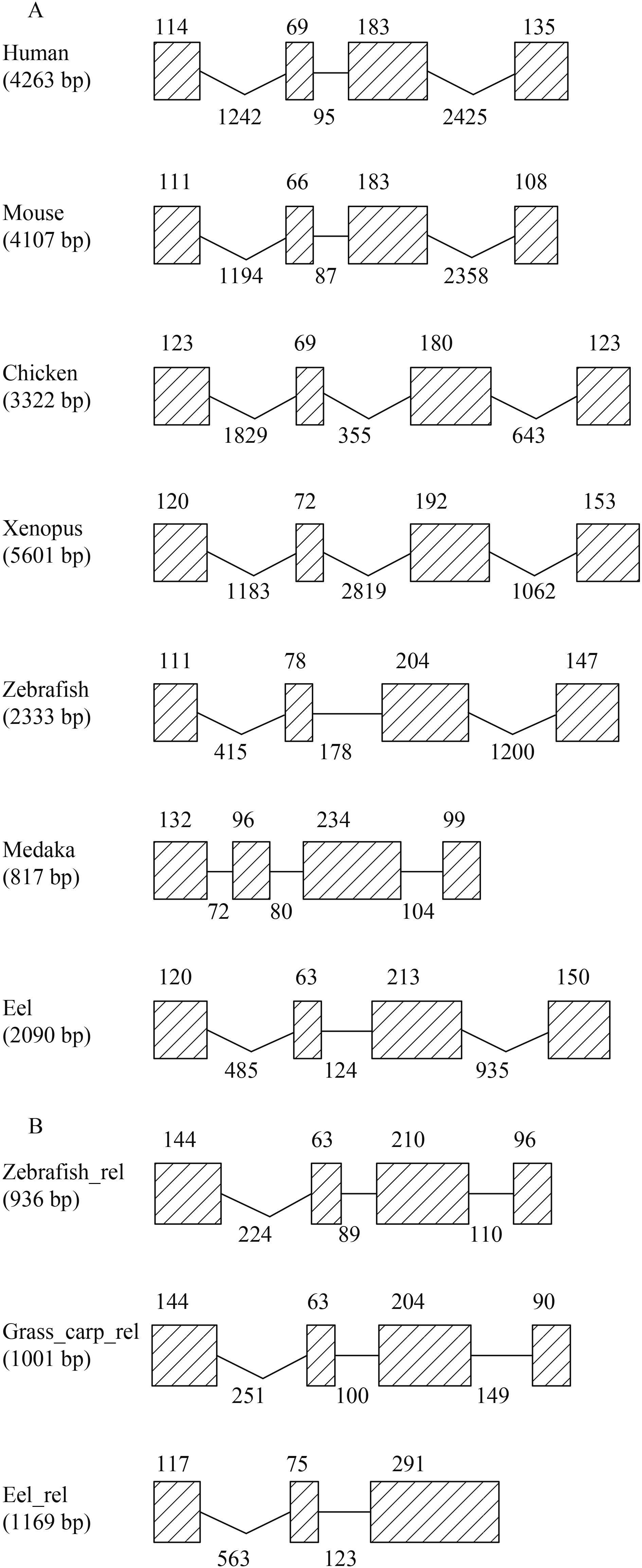
图 3 IFN-γ(A)和IFN-γrel (B)基因结构比较分析
线条表示内含子, 斜线框表示外显子, 数字表示内含子或外显子的碱基数; 基因结构数据来源于Ensembl基因组数据库
Figure 3. Comparative analysis of IFN-γ(A) and IFN-γrel(B) genomic structures
Exons are showed as slash boxes and introns are presented as lines. Numbers above boxes and below lines indicate the size of exons and introns, respectively. The data are derived from Ensembl database
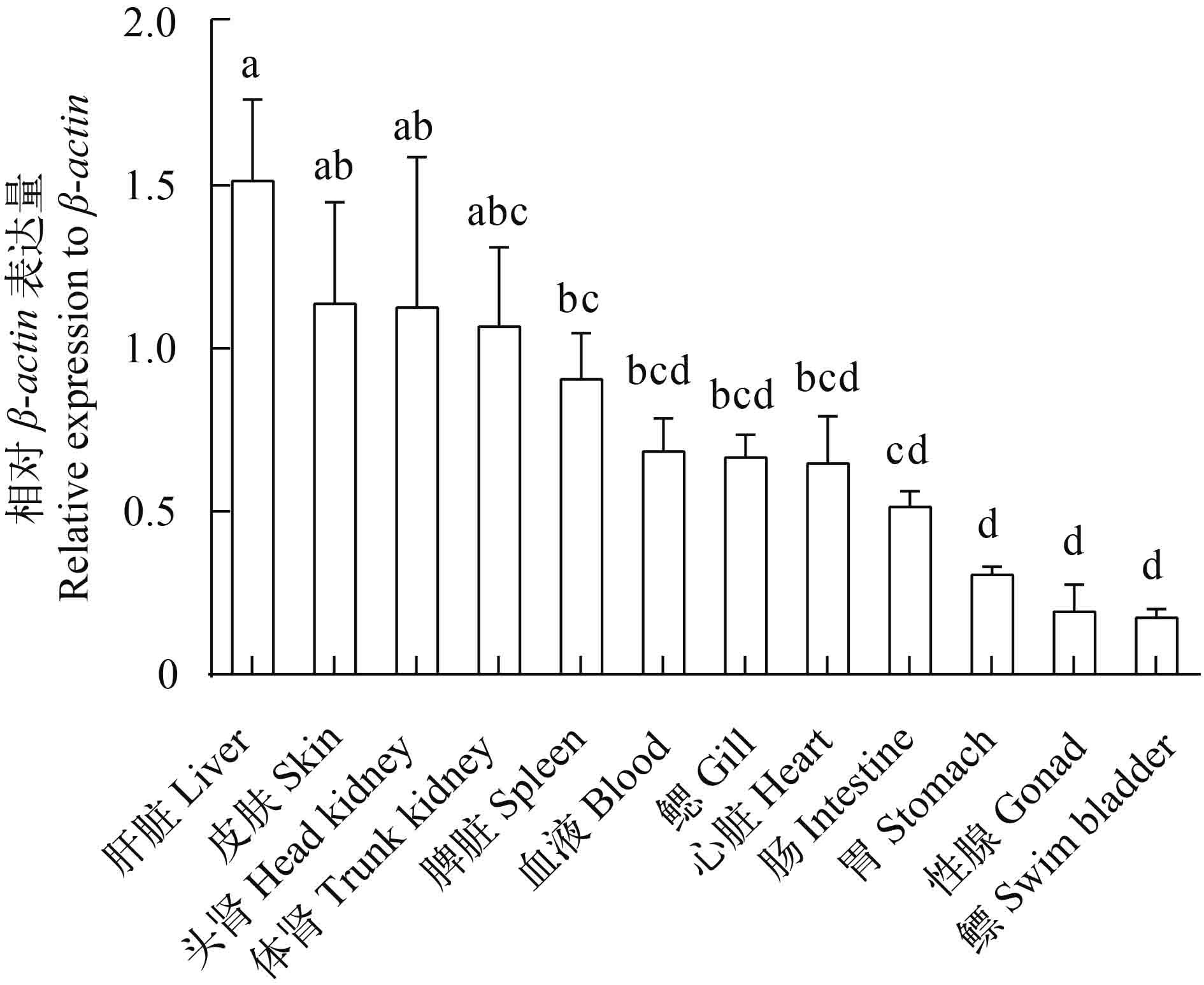
图 5 健康日本鳗鲡不同组织/器官中AjIFN-γ相对β-actin的表达量
数值通过1000×(AjIFN-γ/β-actin)公式计算; 纵轴表示平均值±SEM, N=6; 相同字母表示没有显著性差异, P>0.05
Figure 5. Relative expressions of AjIFN-γ in various tissues of healthy Japanese eel relative to β-actin
The value is present by 1000×(AjIFN-γ/β-actin). Vertical bars represent mean±SEM, N=6. Same letter above the bars means no significant difference. P>0.05
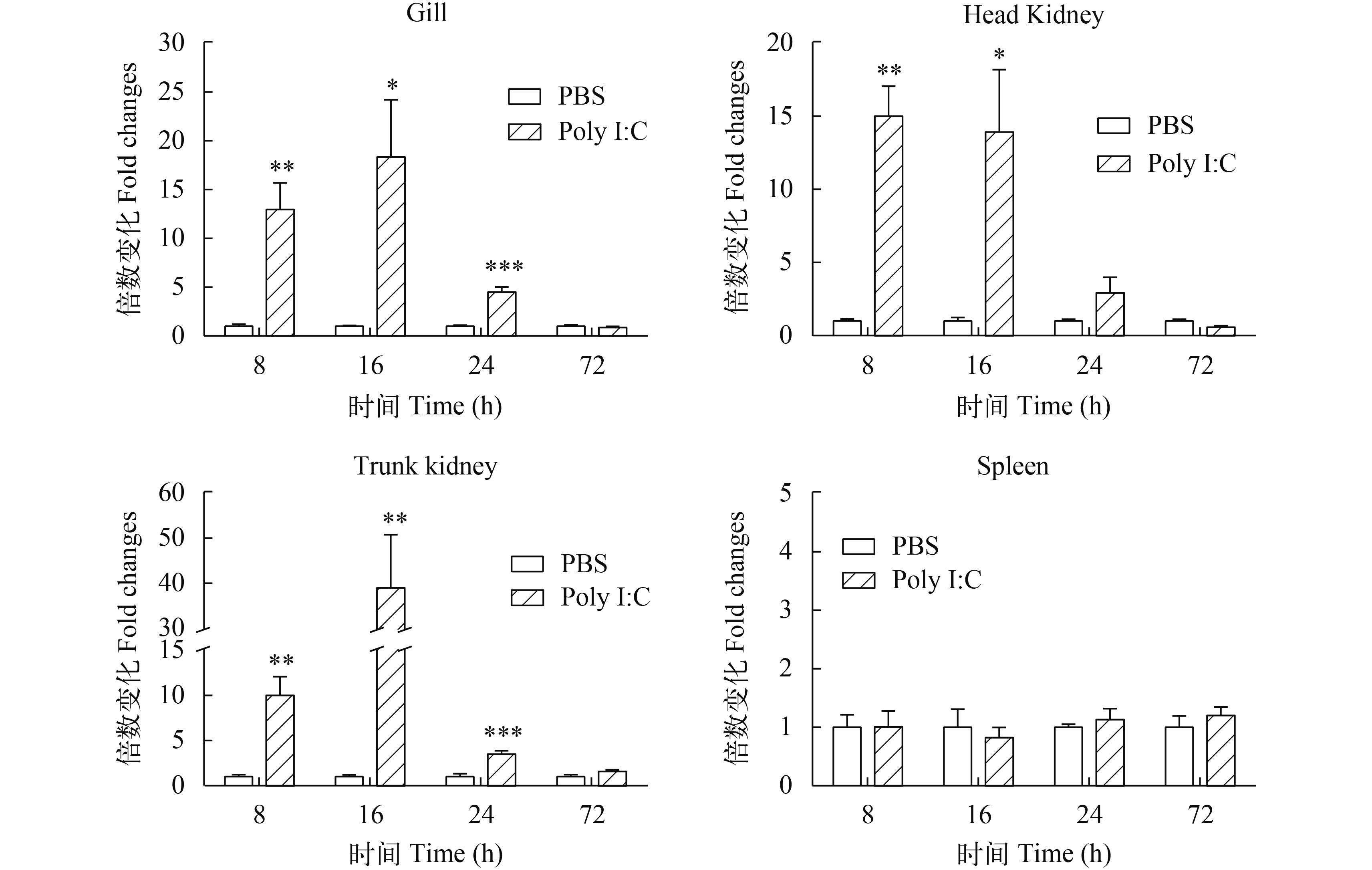
图 6 腹腔注射Poly I:C后AjIFN-γ相对表达量
Poly I:C刺激后8h、16h、24h、72h时, 采用real-time PCR分析不同组织中AjIFN-γ的转录本数量; 以每个组织中β-actin作为内参比; 纵轴表示平均值± SEM, N=6 (鳃16h组, N=5); *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, t-test; 下同
Figure 6. The relative expression of AjIFN-γ in various tissues after intraperitoneal injection with Poly I:C
Real-time PCR was used to analyze the amount of AjIFN-γ transcript in different tissues at 8h, 16h, 24h, 72h after being stimulated by Poly I:Cin vivo. Copies of β-actin in each tissue was used as an internal control for normalized different samples. Vertical bars represented the mean±SEM, N=6 (for gill at 16h, N=5) *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, t-test; the same applies below
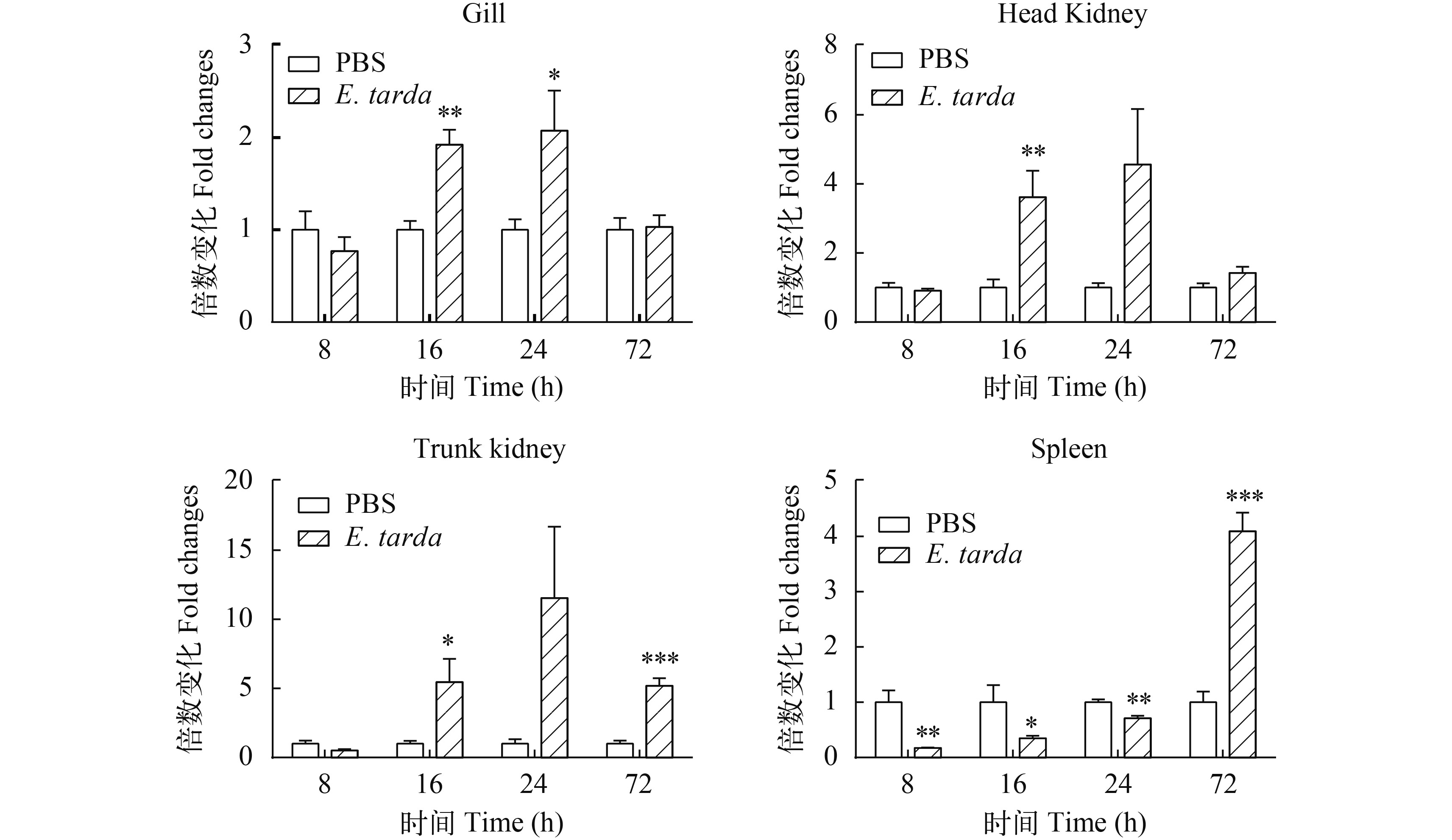
图 7 腹腔注射E. tarda后AjIFN-γ的相对表达量
E. tarda 刺激后8h、16h、24h、72h时, 采用real-time PCR分析不同组织中AjIFN-γ的转录本数量
Figure 7. The relative expression of AjIFN-γ after intraperitoneal injection with E. tarda
Real-time PCR was used to analyze the amount of AjIFN-γ transcript in different tissues at 8h, 16h, 24h and 72h after being challenged by E. tardain in vivo
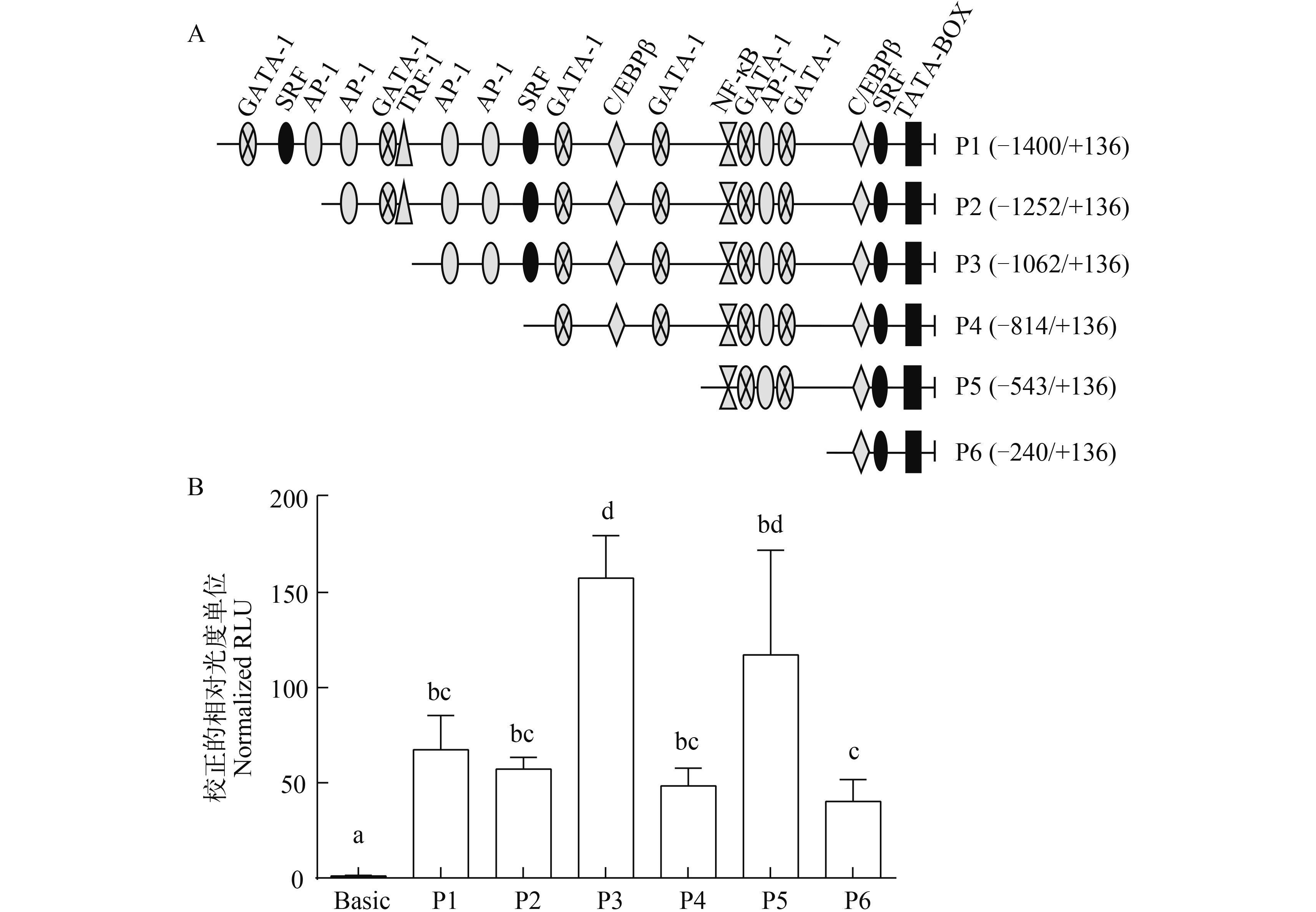
图 8 AjIFN-γ启动子删节突变体的相对活性
A. 用于构建AjIFN-γ启动子5′-端删节突变体的插入序列及其预测的转录因子结合位点示意图; B. AjIFN-γ启动子5′-端删节突变体在AJSB细胞中的相对活性; 启动子活性以经海肾荧光素酶活性校正的相对光度单位(RLU)表示
Figure 8. Relative luciferase activities of promoter 5′-deletion mutants of AjIFN-γ
A. Schematic diagram of the promoter deletion mutants in different length and the TFBSs on them; B. Relative luciferase activities of promoter 5′-deletion mutants of AjIFN-γ in AJSB cells
表 1 本文中所用引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in the present study
引物名称 Primer name 引物序列Primer Sequence (5′-3′) 退火温度Tm (℃) 用途Application AjIFN-gF ATAAAACCAGTGACATCGCCC 62 Internal fragments cloning 克隆中间片段 AjIFN-gR GACTGGAACACCGTCAGCAAG AjIFN-gR1 GGGCTCTGATTGCCTTGATGC 60 5′RACE AjIFN-gR2 CAGGGCGATGTCACTGGTTTTAT 56 AjIFN-gF3 GTACATCAGAATCCTGTCG 60 3′RACE AjIFN-gF4 GATCAGCTACTTCCACAC 55 AjIFN-gFL-F ACGAGGACCTGAGATCCGAAG 60 Sequence confirmation 序列验证 AjIFN-gFL-R CAGAACTTACAGAGCACAGAGC AjIFN-g relFL-F GCTAACGCTCGACAAGCTCAGA 60 AjIFN-g relFL-R CGACTGGTCTATGAATCGCAATCT qAjIFN-gF GCATTAT AAAACCAGTGACA 58 Real time-qPCR 实时荧光定量分析 qAjIFN-gR TCTTGTCGTGCGTCT TCAGG qAj-actinF TCACCACCACAGCCGAAAGG 62 qAj-actinR CGCAGGATTCCATTCCCAGGA AjIFN-gProF CTGACAGAGGTGCAGGTGATGC 64 Promoter amplification 启动子扩增 AjIFN-gProR CTTCGGAGGAGCTGAGAGCC AjIFN-gP1F CGACGCGTCTGACAGAGGTGCAGGTGATGC 67 Truncated regulatory sequence 调控区删节片段扩增 AjIFN-gP2F CGACGCGTCACGTCGCGCTGATGTCACT AjIFN-gP3F CGACGCGTCTCGGAAGACTTGAGGTGAGGAAC AjIFN-gP4F CGACGCGTAGTATGGCTCTGTGGCGATGTC AjIFN-gP5F CGACGCGTAGCGTTCGACATGCACTGGTATC AjIFN-gP6F CGACGCGTGTACCTCCAAATCTCAGCTCACCC AjIFN-gP1R GGAAGATCTAAGGGAGAAGTTTGGTGAAGCAGAG 注: qAjIFN-gF和qAjIFN-gR跨内含子, 直下划线与波浪线分别表示不同外显子的核苷酸序列; AjIFN-gP1F-P6F以及AjIFN-gP1R中, 5′-端粗体为保护性碱基, 灰色为酶切位点 Note: qAjIFN-gF and qAjIFN-gR are cross-intron primers, the nucleotide sequences with underline and wave line are from different exons. The bold and grey shade in the 5′-terminal of AjIFN-gP1F-P6F and AjIFN-gP1R are protective bases and restriction enzyme cutting sites, respectively 表 2 日本鳗鲡 Ⅱ型IFN与其他脊椎动物 Ⅱ型IFN的同源性
Table 2 Protein homology between type Ⅱ IFN from Japanese eel and other vetebrates
分类 Classification 物种名称 Species 登录号 Accession number 信号肽 Signal peptide (aa) 一致性/相似性 Identity/Similarity (%) N-糖基化位点(个) N-glocosylation site AjIFN-γ AjIFN-γrel IFN-γ 哺乳类 人类Homo sapiens P01579 20 15.1/39.1 13.1/34.5 2 小鼠Mus musculus ABN80441 22 14.3/36.0 13.5/41.6 2 鸟类 鸡Gallus gallus ABI83735 19 20.0/38.6 17.5/40.6 0 两栖类 爪蟾Xenopus tropicalis ABU54059 21 15.8/42.6 15.3/36.0 2 鲀形目 红鳍东方鲀Takifugu rubripes CAE82301 22 23.1/39.6 21.2/35.0 1 绿河鲀Tetraodon nigroviridis AHZ62714 22 23.1/41.8 19.0/36.8 1 鲽形目 牙鲆Paralichthys olivaceus BAG50576 23 21.9/37.6 21.2/34.5 3 鲈形目 大黄鱼Larimichthys crocea AIZ77177 22 20.0/35.5 16.8/30.5 2 鳕形目 大西洋鳕Gadus morhua ACN41957 24 23.1/42.1 17.5/31.0 0 鲤形目 鲤Cyprinus carpio CAJ51088 26 25.0/45.7 19.7/41.6 1 斑马鱼Danio rerio NP_998029 26 25.2/44.7 23.4/42.1 1 金鱼Carassius auratus ACG68885 21 26.3/44.7 21.2/39.6 1 鲇形目 斑点叉尾鲙Ictalurus punctatus AAZ40505 20 29.7/50.3 24.8/45.7 1 鳗鲡目 日本鳗鲡Anguilla japonica KU950362 21 —— 40.9/51.8 2 鲑形目 大西洋鲑Salmo salar ACN37863 24 30.7/53.8 27.0/45.2 2 虹鳟Oncorhynchus mykiss CAE82300 24 30.1/53.3 27.0/45.2 1 IFN-γrel 鲀形目 绿河鲀Tetraodon nigroviridis AHZ62713 18 17.5/33.8 16.1/36.3 1 鲤形目 鲤Cyprinus carpio CAJ98867 25 17.7/35.5 17.5/43.7 1 金鱼Carassius auratus ACV41807 26 17.9/36.0 18.2/44.2 1 草鱼Ctenopharyngodon idella ACN56579 23 20.3/36.0 16.1/43.7 0 斑马鱼Danio rerio NP_001018629 24 20.5/40.1 18.2/46.2 2 鲇形目 斑点叉尾鲙Ictalurus punctatus AAZ40504 24 28.6/46.7 20.4/44.7 1 鳗鲡目 日本鳗鲡Anguilla japonica KU950363 23 40.9/51.8 —— 2 -
[1] Schroder K, Hertzog P J, Ravasi T, et al. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions [J]. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2004, 75(2): 163—189
[2] Frucht D M, Fukao T, Bogdan C, et al. IFN-gamma production by antigen-presenting cells: mechanisms emerge [J]. Trends in Immunology, 2001, 22(10): 556—560 doi: 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)02005-1
[3] Shtrichman R, Samuel C E. The role of gamma interferon in antimicrobial immunity [J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2001, 4(3): 251—259 doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(00)00199-5
[4] Arts J A, Tijhaar E J, Chadzinska M, et al. Functional analysis of carp interferon-gamma: evolutionary conservation of classical phagocyte activation [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(5): 793—802
[5] Zou J, Yoshiura Y, Dijkstra J M, et al. Identification of an interferon gamma homologue in Fugu, Takifugu rubripes [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2004, 17(4): 403—409
[6] Igawa D, Sakai M, Savan R. An unexpected discovery of two interferon gamma-like genes along with interleukin (IL)-22 and -26 from teleost: IL-22 and -26 genes have been described for the first time outside mammals [J]. Molecular Immunology, 2006, 43(7): 999—1009 doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.05.009
[7] Milev-Milovanovic I, Long S, Wilson M, et al. Identification and expression analysis of interferon gamma genes in channel catfish [J]. Immunogenetics, 2006, 58(1): 70—80 doi: 10.1007/s00251-006-0081-x
[8] Stolte E H, Savelkoul H F J, Wiegertjes G, et al. Differential expression of two interferon-gamma genes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2008, 32(12): 1467—1481
[9] Grayfer L, Belosevic M. Molecular characterization, expression and functional analysis of goldfish (Carassius aurutus L.) interferon gamma [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2009, 33(2): 235—246
[10] Chen W Q, Xu Q Q, Chang M X, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the IFN-gamma related gene (IFN-gamma rel) in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella [J]. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 2010, 134(3—4): 199—207 doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.09.007
[11] Yang K, Zhang S, Chen D, et al. IFN-gamma-activated lymphocytes boost nitric oxide production in grass carp monocytes/macrophages [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2013, 35(5): 1635—1641
[12] Shibasaki Y, Yabu T, Araki K, et al. Peculiar monomeric interferon gammas, IFNgammarel 1 and IFNgammarel 2, in ginbuna crucian carp [J]. The FEBS Journal, 2014, 281(4): 1046—1056 doi: 10.1111/febs.12666
[13] Zou J, Carrington A, Collet B, et al. Identification and bioactivities of IFN-γ in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: the first Th1-type cytokine characterized functionally in fish [J]. The Journal of Immunology, 2005, 175(4): 2484—2494 doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.4.2484
[14] Furnes C, Seppola M, Robertsen B. Molecular characte-risation and expression analysis of interferon gamma in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2009, 26(2): 285—292
[15] Chen R N, Su Y Q, Wang J, et al. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of interferon-gamma in the large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 46(2): 596—602
[16] Sunarto A, Mccoll K A. Expression of immune-related genes of common carp during cyprinid herpesvirus 3 infection [J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2015, 113(2): 127—135 doi: 10.3354/dao02824
[17] Robertsen B, Zou J, Secombes C, et al. Molecular and expression analysis of an interferon-gamma-inducible guanylate-binding protein from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2006, 30(11): 1023—1033 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7273952_Molecular_and_expression_analysis_of_an_interferon-gamma-inducible_guanylate-binding_protein_from_rainbow_trout_Oncorhynchus_mykiss
[18] Sun B, Skjaeveland I, Svingerud T, et al. Antiviral acti-vity of salmonid gamma interferon against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and salmonid alphavirus and its dependency on type I interferon [J]. Journal of Virology, 2011, 85(17): 9188—9198 doi: 10.1128/JVI.00319-11
[19] Peng W, Lu D Q, Li G F, et al. Two distinct interferon-gamma genes in Tetraodon nigroviridis: Functional analysis during Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection [J]. Molecular Immunology, 2016, 70: 34—46 doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.12.004
[20] Robertsen B, Bergan V T, Larsen R, et al. Atlantic salmon interferon genes: cloning, sequence analysis, expression, and biological activity [J]. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, 2003, 23(10): 601—612
[21] Grayfer L, Garcia E G, Belosevic M. Comparison of macrophage antimicrobial responses induced by type II interferons of the goldfish (Carassius auratus L. ) [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 285(31): 23537—23547 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.096925
[22] 郭松林. 鳗鲡细菌性疾病的研究概况. 科学养鱼, 2011, 263(7): 48—49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXYY201107033.htm Guo S L. The research situation of eel bacterial disease [J]. Scientific Fish Aquaculture, 2011, 263(7): 48—49
郭松林. 鳗鲡细菌性疾病的研究概况. 科学养鱼, 2011, 263(7): 48—49 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXYY201107033.htm[23] 段明珠, 黄贝, 梁英, 等. 日本鳗鲡肝脏表达抗菌肽2基因的克隆与表达. 水生生物学报, 2016, 30(2): 252—260 http://ssswxb.ihb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract3996.shtml Duan M Z, Huang B, Liang Y, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a liver expressed antimicrobial peptide-2 in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2016, 30(2): 252—260
段明珠, 黄贝, 梁英, 等. 日本鳗鲡肝脏表达抗菌肽2基因的克隆与表达. 水生生物学报, 2016, 30(2): 252—260 http://ssswxb.ihb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract3996.shtml[24] Wang T, Gao Q, Nie P, et al. Identification of suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) 6, 7, 9 and CISH in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and analysis of their expression in relation to other known trout SOCS [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2010, 29(4): 656—667
[25] Qi Z T, Nie P. Comparative study and expression analy-sis of the interferon gamma gene locus cytokines in Xenopus tropicalis [J]. Immunogenetics, 2008, 60(11): 699—710 doi: 10.1007/s00251-008-0326-y
[26] 侍建涛, 李志, 桂建芳, 等. 斑马鱼fem-1c cDNA克隆与表达分析. 水生生物学报, 2015, 39(3): 459—467 doi: 10.7541/2015.61 Shi J T, Li Z, Gui J F, et al. The cloning and expression analysis of zebrafish fem-1c, a member of fem-1 family [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2015, 39(3): 459—467
侍建涛, 李志, 桂建芳, 等. 斑马鱼fem-1c cDNA克隆与表达分析. 水生生物学报, 2015, 39(3): 459—467 doi: 10.7541/2015.61[27] Zou J, Clark M S, Secombes C J. Characterisation, expression and promoter analysis of an interleukin 10 homologue in the puffer fish, Fugu rubripes [J]. Immunogenetics, 2003, 55(5): 325—335 doi: 10.1007/s00251-003-0580-y
[28] Yoshiura Y, Kiryu I, Fujiwara A, et al. Identification and characterization of Fugu orthologues of mammalian interleukin-12 subunits [J]. Immunogenetics, 2003, 55(5): 296—306 doi: 10.1007/s00251-003-0582-9
[29] Bird S, Zou J, Kono T, et al. Characterisation and expression analysis of interleukin 2(IL-2) and IL-21 homologues in the Japanese pufferfish, Fugu rubripes, following their discovery by synteny [J]. Immunogenetics, 2004, 56(12): 909—923
[30] Schoenborn J R, Wilson C B. Regulation of interferon-γ during innate and adaptive immune responses [J]. Advances in Immunology, 2007, 96: 41—101 doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(07)96002-2
[31] Zou J, Secombes C J. Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2011, 35(12): 1376—1387
[32] Parhi J, Sahoo L, Choudhury J, et al. Molecular characte-rization and expression analysis of interferon γ (IFN-γ) gene in Labeo rohita (Ham. ) [J]. Aquaculture Reports, 2015, 2: 97—105 doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2015.08.007
[33] Zou J, Secombes C J. Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2011, 35(12): 1376—1387
[34] 张永安, 孙宝剑, 聂品. 鱼类免疫组织和细胞的研究概况. 水生生物学报, 2000, 24(6): 648—654 http://ssswxb.ihb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract654.shtml Zhang Y A, Sun B J, Nie P. Immune tissues and cells of fish: a review [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2000, 24(6): 648—654
张永安, 孙宝剑, 聂品. 鱼类免疫组织和细胞的研究概况. 水生生物学报, 2000, 24(6): 648—654 http://ssswxb.ihb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract654.shtml[35] Davidson G A, Lin SH, Secombes C J, et al. Detection of specific and ‘constitutive’ antibody secreting cells in the gills, head kidney and peripheral blood leucocytes of dab (Limanda limanda) [J]. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 1997, 58(3—4): 363—374 doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(97)00017-2
[36] Salinas I, Zhang YA, Sunyer J O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish [J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 2011, 35(12): 1346—1365
[37] Scapigliati G, Romano N, Abelli L. Monoclonal antibo-dies in fish immunology: identification, ontogeny and activity of T- and B-lymphocytes [J]. Aquaculture, 1999, 172(1—2): 3—28 doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00440-2
[38] Ortiz N N, Gerdol M, Stocchi V, et al. T cell transcripts and T cell activities in the gills of the teleost fish sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) [J]. Developmental & Compara-tive Immunology, 2014, 47(2): 309—318
[39] Boschi I, Randelli E, Buonocore F, et al. Transcription of T cell-related genes in teleost fish, and the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) as a model [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 31(5): 655—662
[40] 陈翠珍. 爱德华氏菌及鱼类爱德华氏菌病. 河北科技师范学院学报, 2004, 18(3): 70—76 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNS200403018.htm Chen C Z. Edwardsiella and edwardsiellasis of fish [J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology, 2004, 18(3): 70—76
陈翠珍. 爱德华氏菌及鱼类爱德华氏菌病. 河北科技师范学院学报, 2004, 18(3): 70—76 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNS200403018.htm[41] Jung C Y, Hikima J, Ohtani M, et al. Recombinant interferon-gamma activates immune responses against Edwardsiella tarda infection in the olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2012, 33(2): 197—203
[42] Penix L A, Weaver W M, Pang Y, et al. Two essential regulatory elements in the human interferon gamma promoter confer activation specific expression in T cells [J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 1993, 178(5): 1483—1496 doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1483
[43] Penix L A, Sweetser M T, Weaver W M, et al. The proximal regulatory element of the interferon-γ promoter mediates selective expression in T cells [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996, 271(50): 31964—31972 doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.31964
[44] Aune T M, Penix L A, Rincon M R, et al. Differential transcription directed by discrete gamma interferon promoter elements in naive and memory (effector) [J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1997, 17(1): 199—208 doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.1.199
[45] Sweetser M T, Hoey T, Sun A L, et al. The roles of nuc-lear factor of activated T cells and ying-yang 1 in activation-induced expression of the interferon-γ promoter in T cells [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(52): 34775—34783 doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.52.34775
[46] Kiani A, García-Cózar F J, Habermann I, et al. Regulation of interferon-γ gene expression by nuclear factor of activated T cells [J]. Blood, 2001, 98(5): 1480—1488 doi: 10.1182/blood.V98.5.1480
[47] Tato C M, Villarino A, Caamaño J H, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB activity in T and NK cells results in defective effector cell expansion and production of IFN-γ required for resistance to Toxoplasma gondii [J]. The Journal of Immunology, 2003, 170(6): 3139—3146 doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.6.3139
[48] Young H A, Bream J H. IFN-γ recent advances in understanding regulation of expression, biological functions, and clinical applications [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2007, 316: 97—117
[49] Lai Q, Lin G, Ma M, et al. IRF-1 acts as a positive regulator in the transcription of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) IFN gene [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2013, 34(6): 1432—1438
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 万为民. 配合饲料投喂量和粒径对绿盘鲍稚鲍生长和存活的影响. 渔业现代化. 2022(01): 30-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李琪,刘鉴毅,孙艳秋,邹雄,王妤,庄平,冯广朋,赵峰,黄晓荣,杨俊. 投喂策略对多纹钱蝶鱼幼鱼生长的影响. 海洋科学. 2022(03): 93-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吕云云. 不同投喂水平对皱纹盘鲍生长、体成分及消化酶活性的影响. 海洋湖沼通报. 2022(03): 16-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈云飞,彭慧珍,刘庄鹏,胡毅,吕怡航,李昭林,张德洪. 投喂水平对黄鳝(Monopterus albus)生长、肠道消化酶活性及部分血清生理生化指标的影响. 渔业科学进展. 2017(02): 114-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 段国庆,江河,胡王,凌俊,胡玉婷,潘庭双. 投喂水平对黄鳝幼鱼生长的影响. 广东农业科学. 2015(07): 105-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: