THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE ABSORPTION EFFICIENCY OF NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS AND PHOTOSYNTHETIC PHYSIOLOGICAL CHARATERISTICS IN FOUR MACROALGAE SPECIES
-
摘要: 研究以裂片石莼(Ulva fasciata)、肠浒苔(Ulva intestinalis)、龙须菜(Gracilaria lemaneaformis)、坛紫菜(Pyropia haitanensis)为实验材料, 分析了不同温度(15、20、25、30℃)下4种大型海藻对海水中N、P元素的吸收效率和光合特性的特点。结果显示: (1)4种大型海藻对水体N、P均有明显的吸收效果, 吸收能力高低依次为肠浒苔>裂片石莼>坛紫菜>龙须菜; (2)温度过高或过低都会限制藻类对N、P的吸收和正常生长, 同时降低4种藻的相对电子传递速率及光化学效率; (3)裂片石莼与肠浒苔的N、P吸收能力强, 且光合系统对温度耐受性高, 是实施养殖污水生物净化的良好材料; (4)4种海藻对水体中N、P营养盐的吸收在48h内基本完成, 实地应用中可考虑24—48h周期换水或采用流通循环式的培养模式, 以达到既促进藻类的生长又提高营养盐吸收效率的目的, 以避免藻体因营养缺乏引起负生长而造成二次污染。Abstract: Purifying wastewater with biological methods is highly important in the field of ecological recirculating aquaculture. To study the effects of temperature on the absorption of nitrogen and phosphorus and photosynthetic performance of macroalgae in sea water, four species including Ulva fasciata, Ulva intestinalis, Gracilaria lemaneaformis and Pyropia haitanensis were cultured under four temperature conditions (15, 20, 25 and 30℃). The results showed that: (1) most N and P had been absorbed by the four macroalgae species, and the absorbing ability from high to low is Ulva intestinalis>Ulva fasciata>Pyropia haitanensis>Gracilaria lemaneaformis; (2) extremely high and low temperature will limit the absorbing of N and P, growth, relative electron transfer rate, and chlorophyll fluorescence in four macroalgae species; (3) U. fasciata and U. intestinalis were the best choices due to their high absorption rates of N and P and the tolerance of a wide temperature range; (4) nitrogen and phosphorus could be completely absorbed within 48h by the four macroalgae species. To promote algal growth, improve the removal efficiency of nutrients, as well as prevent secondary pollution caused by nutrition limited negative growth of macroalgae, it’s better to replace the wastewater within 24—48h, or apply the circulation mode in the process of wastewater treatment.
-
Keywords:
- Macroalgae /
- Temperature /
- Nutrient /
- Absorbing ability /
- Fluorescence parameters
-
近年来, 海水养殖业发展迅猛, 沿海养殖场中池塘养殖的废水排放量与日俱增, 导致近岸海水的富营养化日益严重[1], 其主要污染指标为无机氮和活性磷酸盐[2]。水体恶化导致更多灾难性环境事件发生[3], 严重影响了海水养殖业的可持续发展及海洋生态安全[4]。富营养化水体的治理已成为当今世界性难题[5]。国内外学者一致认为, 大型海藻具有极佳的水体净化能力, 并具有较高经济价值, 是进行养殖污水处理和富营养化水体修复的有效方式[6—9]。20世纪70年代大型海藻作为生物滤器净化水体开始发展, 后来被很多专家学者所重视, 逐渐发展并完善了大型海藻与鱼、虾、贝等混养的综合生态养殖模式, 筛选合适的藻类和净水处理工艺是利用大型海藻进行污染水体的生物修复亟待解决的问题[10]。
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
裂片石莼、肠浒苔、龙须菜、坛紫菜于2016年采于温州市平阳县鳌江镇附近海域(120°20′E, 27°35′N)。挑选鲜活健康的藻体, 用消毒海水清洗, 软毛刷除净表面附着物, 并用0.7%的KI溶液浸泡10min, 除去杂藻和细菌, 然后用灭菌海水冲洗两次备用。实验开始前, 每种藻取3 g至1000 mL烧杯中在光照培养箱中充气预培养1d(培养光强100 μmol/(m2·s), 光周期为12h L﹕12h D), 温度与实验温度一致。预培养海水为人工配制[19], 盐度为30。
1.2 实验方法
将裂片石莼、龙须菜、肠浒苔、坛紫菜放置在富营养化水体中, 分别在15、 20、 25、 30℃条件下光照培养48h。培养过程中于0、6、12、24、36、48h进行水质检测, 培养结束后测定海藻生长速率及叶绿素荧光参数。
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
生长速率的测定 培养前和培养后进行藻体鲜重的测定。用吸水纸吸干藻体表面的水分, 使用电子天平称量藻体鲜重。相对生长速率计算公式为(RGR, %/d)= 100×(LnWn–LnWn–1)/(tn–tn–1), Wn–1、Wn分别为为tn–1、tn时的藻体鲜重。
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin 7.0和SPSS统计软件进行数据处理和统计分析, 用t检验法(t-tests)方差分析检测平均数之间的差异(P), 以P<0.05作为差异的显著性水平。
2. 结果
2.1 藻类生长
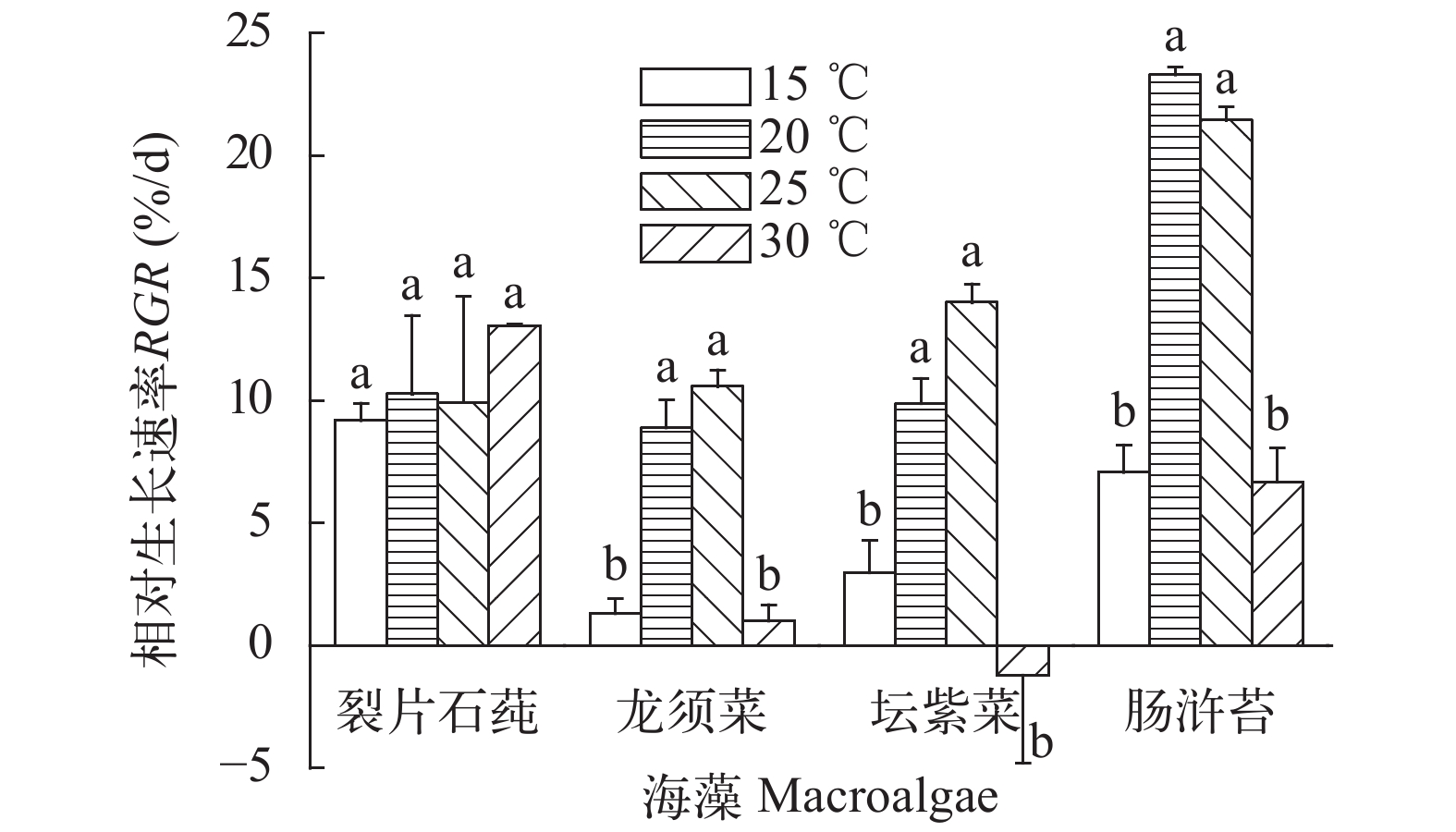
在15—25℃内, 温度变化对裂片石莼生长无显著影响(P>0.05)。龙须菜、坛紫菜和肠浒苔的生长在不同温度下差异显著(P<0.05), 最高相对生长率均出现在20℃与25℃, 温度为15℃和30℃时相对生长率明显降低, 坛紫菜在30℃时甚至出现负增长, 说明高温对坛紫菜的正常生长造成威胁。4种藻中肠浒苔生长得最快, 20℃时每天的相对生长率高达24%, 20℃与25℃时生长情况明显优于其他3种藻类。
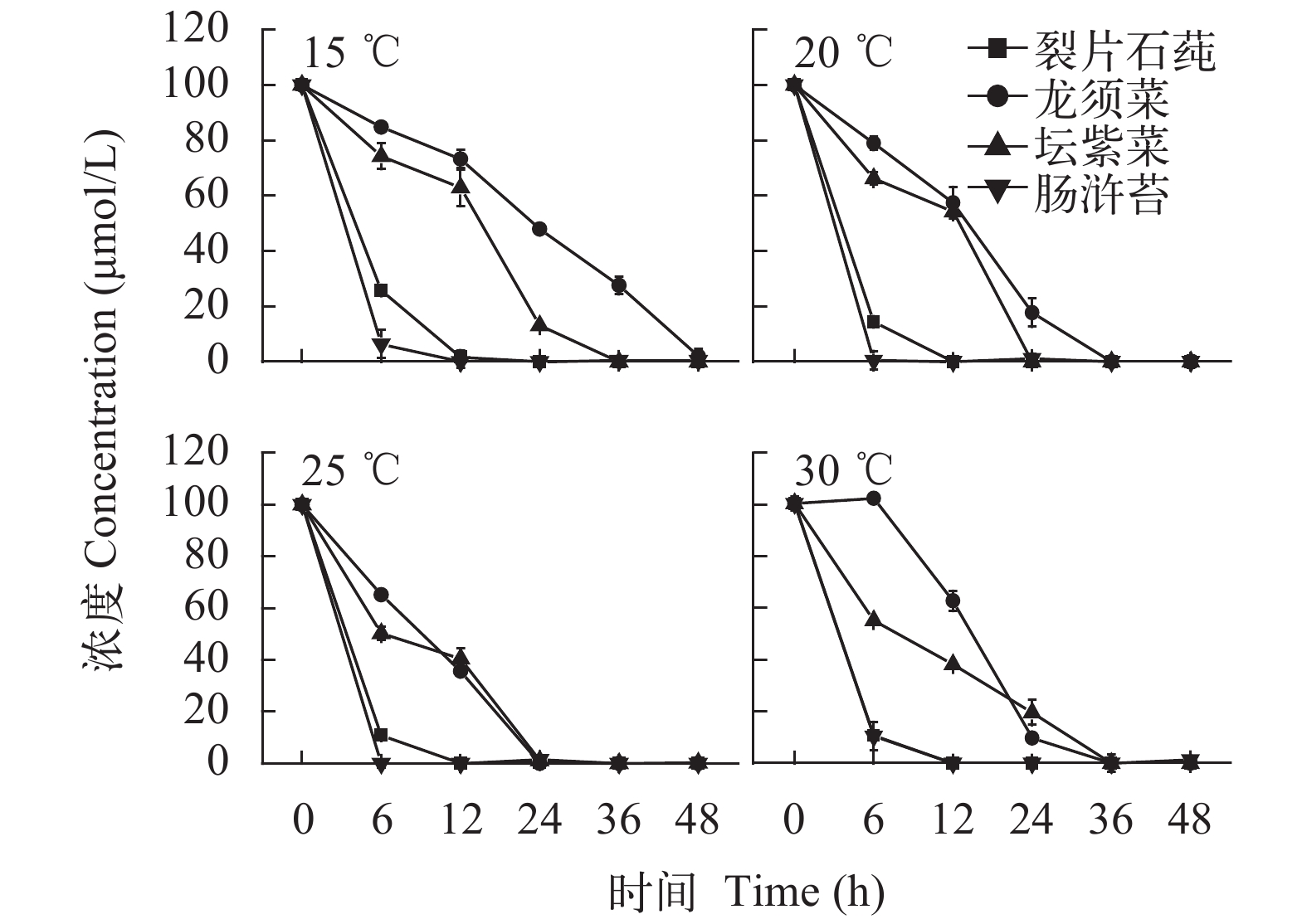
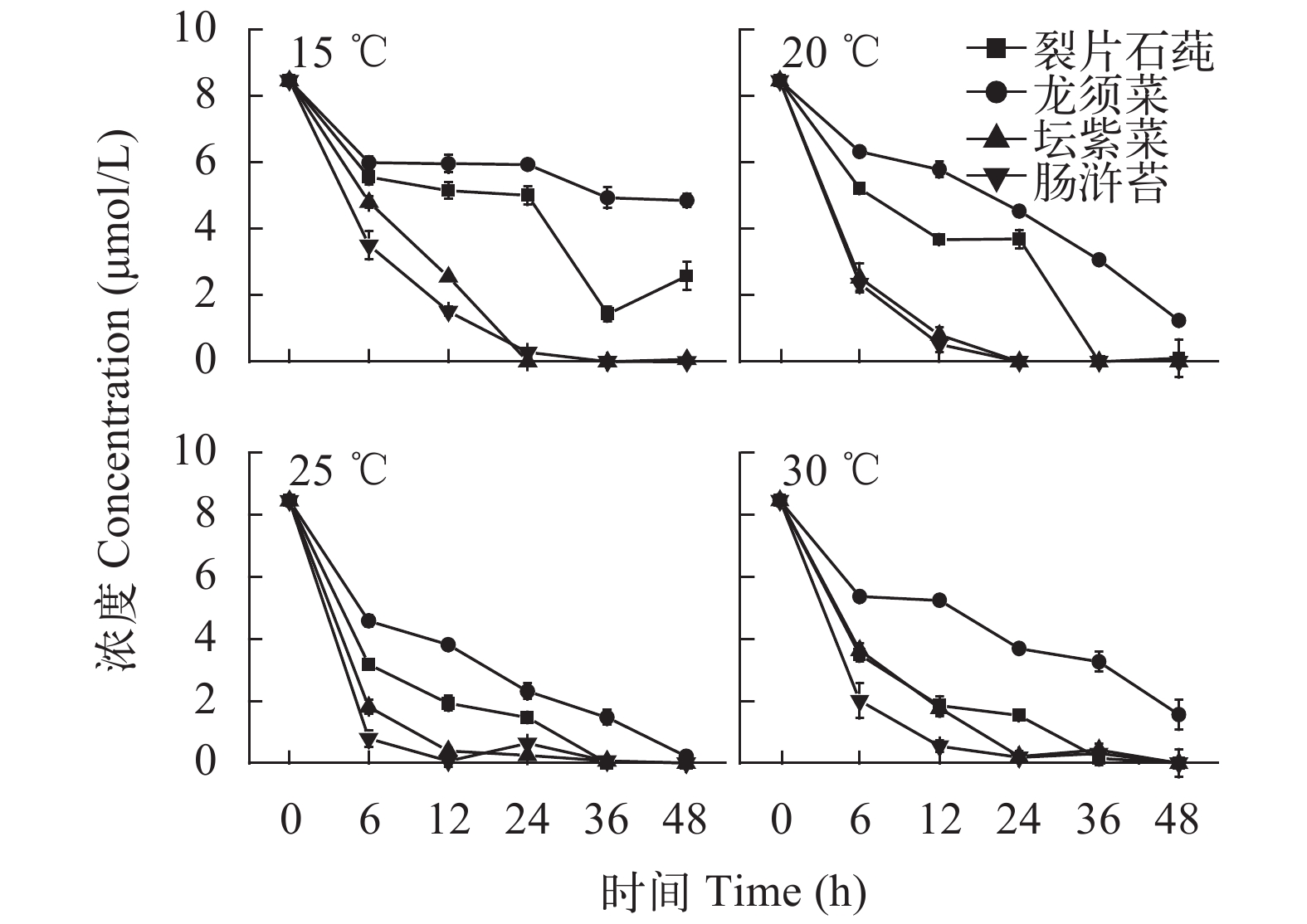
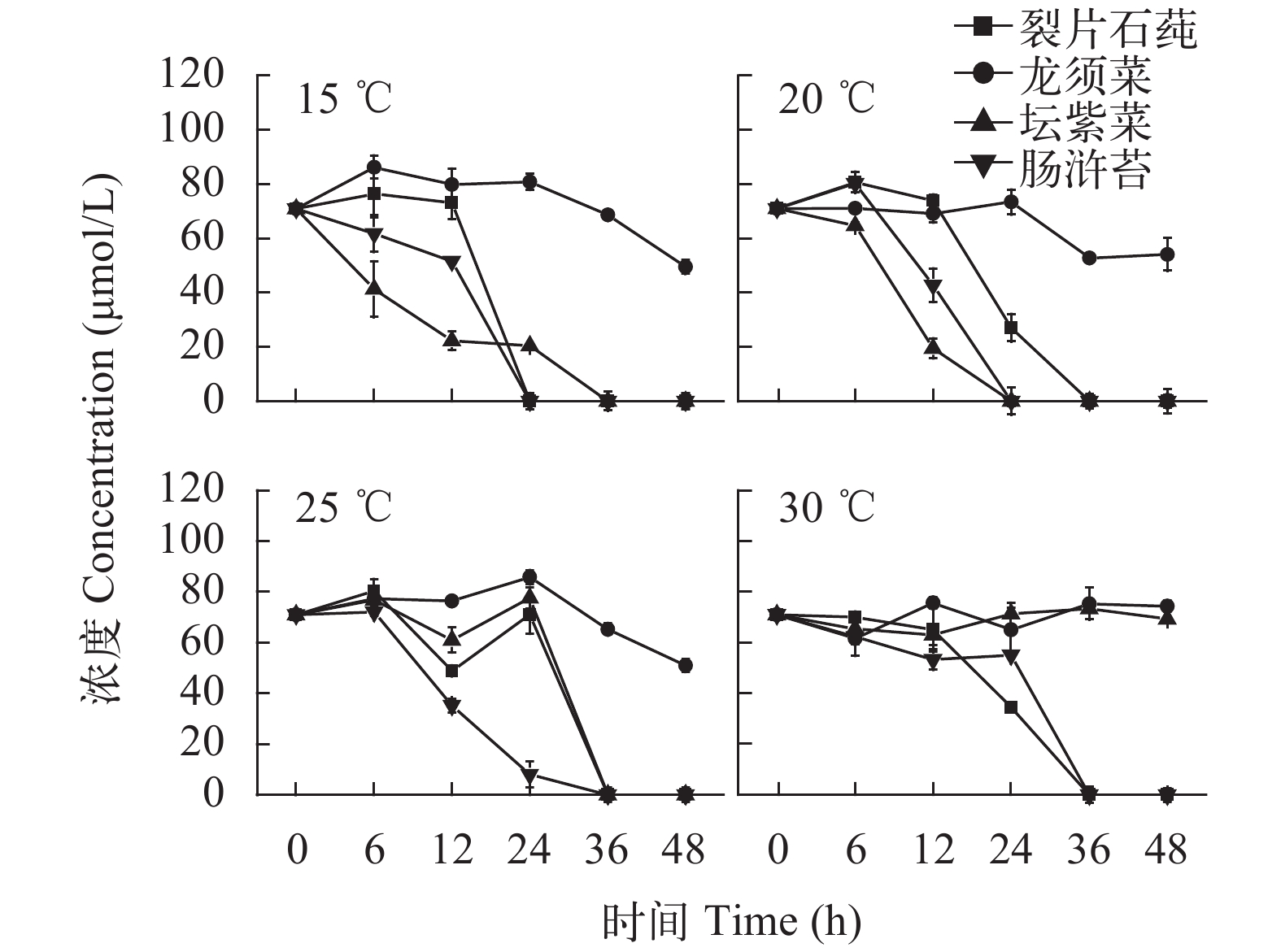
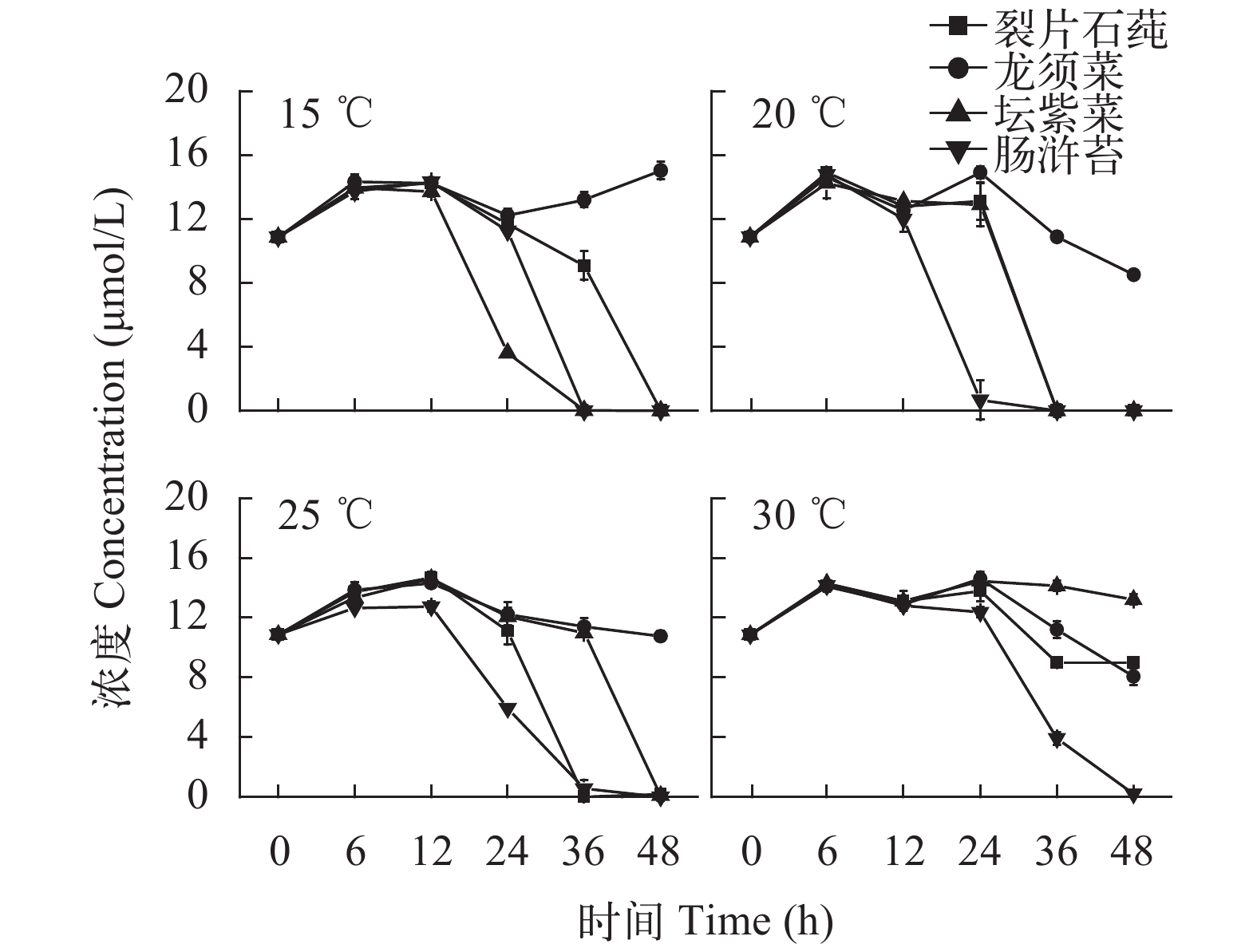
2.2 营养盐吸收情况
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 7 at column 23: Extra content at the end of the documentBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
${\rm{PO}}_4^ {3 – } $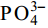
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 7 at column 23: Extra content at the end of the documentBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
${\rm{NO}}_3^ – $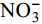
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 7 at column 23: Extra content at the end of the documentBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
${\rm{NO}}_2^ – $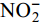
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
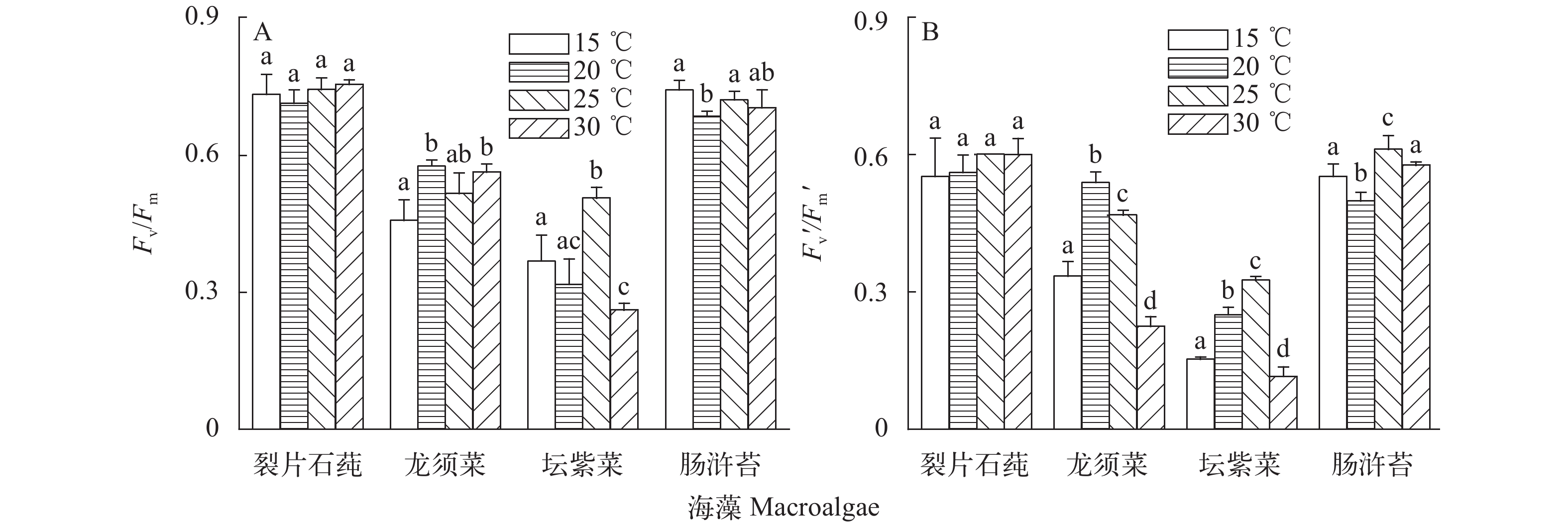
2.3 荧光参数
随着温度升高, ETRmax与Ik均呈先上升后下降的趋势, 25℃时, 裂片石莼、龙须菜、坛紫菜与肠浒苔的rETRmax显著增高, 在15℃和30℃时数值相对较低; 温度对其表观光能利用效率的影响不显著(P>0.05)(表 1)。温度对裂片石莼和肠浒苔的最大(Fv/Fm)及有效光化学效率(Fv′/Fm′)无明显影响, 说明这2种藻温度耐受范围较广。在15℃培养时, 龙须菜的Fv/Fm及Fv′/Fm′均降低; 而30℃时不影响龙须菜Fv/Fm, 但明显抑制了Fv′/Fm′。坛紫菜在25℃时Fv/Fm和Fv′/Fm′显著增高, 至30℃时Fv/Fm和Fv′/Fm′均迅速下降(图 6), 说明30℃对坛紫菜的PSII系统造成伤害。总体来讲, 肠浒苔与裂片石莼rETRmax与Ik数值较高, 与Fv/Fm与Fv′/Fm′数值表现一致。
表 1 不同温度下4种大型海藻的相对电子传递速率与光强关系的最佳拟合参数Table 1. The best fitting parameters derived from relative electron transport rate (rETR) v.s. irradiance curve of four macroalgae species under different temperatures海藻Macroalgae 指标Index 温度Temperature (℃) 15 20 25 30 裂片石莼 rETRmax 55.05±0.044b 70.549±1.072b 96.161±13.282a 60.450±8.206b α 0.273±0.036b 0.265±0.013b 0.335±0.002a 0.350±0.008a Ik 206.182±32.417bc 266.945±9.793ab 287.022±38.295a 173.525±27.587c 龙须菜 rETRmax 27.991±1.189c 53.593±4.907b 71.978±3.765a 31.264±2.261c α 0.641±0.080a 0.383±0.055bc 0.298±0.004c 0.494±0.065ab Ik 44.601±7.394c 144.531±33.455b 241.118±9.163a 63.760±3.758c 坛紫菜 rETRmax 15.205±1.838c 41.135±3.498a 38.927±0.535b 26.609±4.697c α 0.149±0.029c 0.195±0.009b 0.233±0.012a 0.174±0.054b Ik 108.603±33.407b 210.498±8.014a 167.631±6.701a 160.392±23.003ab 肠浒苔 rETRmax 88.617±2.099a 96.500±16.516a 96.236±5.633a 61.059±2.734b α 0.314±0bc 0.294±0.022c 0.356±0.032ab 0.366±0.003a Ik 282.474±6.553a 325.748±31.635a 273.729±40.145a 166.876±8.922b 注:rETRmax为最大相对电子传递速率, α为表观光能利用效率, Ik为饱和光强[μmol/( m2·s)] Note: rETRmax, the maximum rate of rETR; α, the apparent photosynthetic efficiency; Ik, the initial light saturation point [μmol/(m2·s)] 3. 讨论
3.1 温度对大型海藻营养盐吸收的影响
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
3.2 温度对藻类生长及光合作用的影响
温度是影响藻类生长发育, 也是影响植物生理成分的重要因素[28], 研究在不同温度条件下叶绿素荧光的特性, 能够指示出藻类光合系统的温度适宜和抑制范围[29]。在本研究中, 裂片石莼具有较高的适温能力, 坛紫菜对高温的耐受性相对较弱。肠浒苔的生长速率在4种藻类中最高, 且在不同温度下均维持较好的生长状况(图 1), 已有的研究发现, 在我国由浒苔(Ulva prolifera)引发的绿潮事件中, 往往混有肠浒苔, 肠浒苔作为绿潮物种之一, 在5—30℃内都可以存活, 具有旺盛的生长力[30, 31]。因此利用肠浒苔进行养殖污水处理时应注意水域封闭性, 避免造成生态污染。
龙须菜、坛紫菜、肠浒苔在20℃与25℃时生长较快, 15℃与30℃生长受抑制。这可能是由于在适宜温度范围内, 一定程度的气温升高能够加快藻类的代谢, 促进藻类的生长, 一旦超过这个范围, 就会引起藻体同化和异化作用减弱、水分和营养吸收减慢、酶活性降低, 藻类光合作用受到抑制, 进而阻碍了藻类的正常生长[32, 33]。
高温30℃对龙须菜Fv/Fm影响不显著, 但显著降低其Fv′/Fm′, 且该温度下其生长速率也明显下降(表 1、图 6), 这可能是在30℃条件下, 温度胁迫阻碍PSII的电子传递, 使光合作用器官受氧化的风险增强, 这种氧化作用导致PSII系统的慢性损伤, 导致叶绿素荧光参数改变, 但并未使PSII系统完全失活[35]。尽管龙须菜是抗高温品种, 但在30℃条件下其部分生理指数有显著降低, 证明该温度对龙须菜已经造成一定胁迫。
3.3 利用藻类进行污水处理的方案
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
值得注意的是, 裂片石莼与肠浒苔在36h内已达到净水目的, 龙须菜和坛紫菜在48h内培养基中的营养盐浓度也达到极低水平, 这说明在实际应用中应考虑到换水周期(一般情况下36—48h即可更换水体)或采用流通循环式的培养模式, 以达到既能去除N、P等营养盐, 又能促进大型海藻的生长并避免因藻体腐烂造成的二次污染的目的。当然, 不同藻类净水效果不同, 因此可根据实际情况调整净水工艺。另外, 温度胁迫将造成大型海藻生长效率与同化作用减弱, 影响净水效果, 并且大型海藻具有一定的生长季节, 在夏秋季节利用大型海藻进行养殖污水处理将存在一定的局限性。发掘抗高温藻类, 利用多种海藻轮作, 深入研究大型藻类与鱼、虾、贝类等互利机制是利用大型海藻进行海水修复的重要趋势。
-
表 1 不同温度下4种大型海藻的相对电子传递速率与光强关系的最佳拟合参数
Table 1 The best fitting parameters derived from relative electron transport rate (rETR) v.s. irradiance curve of four macroalgae species under different temperatures
海藻Macroalgae 指标Index 温度Temperature (℃) 15 20 25 30 裂片石莼 rETRmax 55.05±0.044b 70.549±1.072b 96.161±13.282a 60.450±8.206b α 0.273±0.036b 0.265±0.013b 0.335±0.002a 0.350±0.008a Ik 206.182±32.417bc 266.945±9.793ab 287.022±38.295a 173.525±27.587c 龙须菜 rETRmax 27.991±1.189c 53.593±4.907b 71.978±3.765a 31.264±2.261c α 0.641±0.080a 0.383±0.055bc 0.298±0.004c 0.494±0.065ab Ik 44.601±7.394c 144.531±33.455b 241.118±9.163a 63.760±3.758c 坛紫菜 rETRmax 15.205±1.838c 41.135±3.498a 38.927±0.535b 26.609±4.697c α 0.149±0.029c 0.195±0.009b 0.233±0.012a 0.174±0.054b Ik 108.603±33.407b 210.498±8.014a 167.631±6.701a 160.392±23.003ab 肠浒苔 rETRmax 88.617±2.099a 96.500±16.516a 96.236±5.633a 61.059±2.734b α 0.314±0bc 0.294±0.022c 0.356±0.032ab 0.366±0.003a Ik 282.474±6.553a 325.748±31.635a 273.729±40.145a 166.876±8.922b 注:rETRmax为最大相对电子传递速率, α为表观光能利用效率, Ik为饱和光强[μmol/( m2·s)] Note: rETRmax, the maximum rate of rETR; α, the apparent photosynthetic efficiency; Ik, the initial light saturation point [μmol/(m2·s)] -
[1] Villares R, Carballeira A. Seasonal variation in the concentrations of nutrients in two green macroalgae and nutrient levels in sediments in the Rfas Baixas (NW Spain) [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 58: 887—900
[2] Zheng H. Analysis on purification effect of the three typi cal seaweeds on N and P in eutrophic water [J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2016, 32(3): 222—225 [郑辉. 3种典型大型海藻对富营养化水体氮磷净化效果的分析. 科技通报, 2016, 32(3): 222—225] Zheng H. Analysis on purification effect of the three typi cal seaweeds on N and P in eutrophic water [J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2016, 32(3): 222—225 [郑辉. 3种典型大型海藻对富营养化水体氮磷净化效果的分析. 科技通报, 2016, 32(3): 222—225]
[3] McClanahan T R, Carreiro-Silva M, DiLorenzo M. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorous, and their interaction on coral reef algal succession in Glover’s Reef, Belize [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(12): 1947—1957
[4] Lin Z X, Ru S G, Yang Y, et al. Prospect for bioremedia tion of large-sized seaweed cultivation in eutrophic bays [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2006, 40(4): 128—134 [林贞贤, 汝少国, 杨宇峰, 等. 大型海藻对富营养化海湾生物修复的研究进展研究. 海洋湖沼通报, 2006, 40(4): 128—134] Lin Z X, Ru S G, Yang Y, et al. Prospect for bioremedia tion of large-sized seaweed cultivation in eutrophic bays [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2006, 40(4): 128—134 [林贞贤, 汝少国, 杨宇峰, 等. 大型海藻对富营养化海湾生物修复的研究进展研究. 海洋湖沼通报, 2006, 40(4): 128—134]
[5] Chai S Y, He P M. Trends of marine eutrophication in China and ecological restoration strategy [J]. Science, 2013, 65(4): 48—52 [柴邵阳, 何培民. 我国海洋富营养化趋势与生态修复策略. 科学, 2013, 65(4): 48—52] Chai S Y, He P M. Trends of marine eutrophication in China and ecological restoration strategy [J]. Science, 2013, 65(4): 48—52 [柴邵阳, 何培民. 我国海洋富营养化趋势与生态修复策略. 科学, 2013, 65(4): 48—52]
[6] He J, Liu Y, Zhang L Y, et al. Study on the nutrient up take kinetics of three kinds of macroalga [J]. Fishery Modernization, 2010, 37(1): 1—5 [何洁, 刘瑀, 张立勇, 等. 三种大型海藻吸收营养盐的动力学研究. 渔业现代化, 2010, 37(1): 1—5] He J, Liu Y, Zhang L Y, et al. Study on the nutrient up take kinetics of three kinds of macroalga [J]. Fishery Modernization, 2010, 37(1): 1—5 [何洁, 刘瑀, 张立勇, 等. 三种大型海藻吸收营养盐的动力学研究. 渔业现代化, 2010, 37(1): 1—5]
[7] Kraemer G P, Carmona P R, Chopin T, et al. Evaluation of the bioremediatory potential of several species of the red alga Porphyra using short-term measurements of nitrogen uptake as a rapid bioassay [J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2004, 16(6): 489—497
[8] Chen T, Li J R, Wang L, et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen release from Jialu River sediment [J]. Meteorological and Environmental Research, 2011, 2(6): 82—84
[9] Xu S N, Wen S S, Wu W X, et al. Bioremediation of caged fish aquaculture by the red alga Gracilaria verrucosa in an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 28(4): 1466—1475 [徐姗楠, 温珊珊, 吴望星, 等. 真江蓠(Gracilaria verrucosa)对网箱养殖海区的生态修复及生态养殖匹配模式. 生态学报, 2004, 28(4): 1466—1475] Xu S N, Wen S S, Wu W X, et al. Bioremediation of caged fish aquaculture by the red alga Gracilaria verrucosa in an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 28(4): 1466—1475 [徐姗楠, 温珊珊, 吴望星, 等. 真江蓠(Gracilaria verrucosa)对网箱养殖海区的生态修复及生态养殖匹配模式. 生态学报, 2004, 28(4): 1466—1475]
[10] Yang Y F, Song J M, Lin X T, et al. Seaweed cultivation and its ecological roles in coastal waters [J]. Marine Environment Science, 2005, 24(3): 77—80 [杨宇峰, 宋金明, 林小涛, 等. 大型海藻栽培及其在近海环境的生态作用. 海洋环境科学, 2005, 24(3): 77—80] Yang Y F, Song J M, Lin X T, et al. Seaweed cultivation and its ecological roles in coastal waters [J]. Marine Environment Science, 2005, 24(3): 77—80 [杨宇峰, 宋金明, 林小涛, 等. 大型海藻栽培及其在近海环境的生态作用. 海洋环境科学, 2005, 24(3): 77—80]
[11] Carmona R, Kraemer G P, Yarish C. Exploring Northeast American and Asian species of Porphyra for use in an integrated finfish-algal aquaculture system [J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 252(1): 54—65
[12] Ignacio Hernández, Abraham Pérez-Pastor, Juan J, et al. Stu dies on the biofiltration capacity of Gracilariopsis longissima: From microscale to macroscale [J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 252(1): 43—53
[13] Li H, Li M Z, Cao J, et al. Effects of temperature on nitrogen uptake and growth in several species of macroalgae [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013, 34(1): 159—165 [李恒, 李美真, 曹婧, 等. 温度对几种大型海藻硝氮吸收及其生长的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2013, 34(1): 159—165] Li H, Li M Z, Cao J, et al. Effects of temperature on nitrogen uptake and growth in several species of macroalgae [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013, 34(1): 159—165 [李恒, 李美真, 曹婧, 等. 温度对几种大型海藻硝氮吸收及其生长的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2013, 34(1): 159—165]
[14] Cheng L W, Zou D H, Zheng Q S, et al. Effects of temperature and light intensity on the nitrate uptake kinetics of nitrogen starved and replete Ulva lactuca [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(5): 939—944 [程丽巍, 邹定辉, 郑青松, 等. 光照和温度对氮饥饿及饱和营养条件下石莼(Ulva lactuca)的硝态氮吸收动力学影响. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(5): 939—944] Cheng L W, Zou D H, Zheng Q S, et al. Effects of temperature and light intensity on the nitrate uptake kinetics of nitrogen starved and replete Ulva lactuca [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(5): 939—944 [程丽巍, 邹定辉, 郑青松, 等. 光照和温度对氮饥饿及饱和营养条件下石莼(Ulva lactuca)的硝态氮吸收动力学影响. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(5): 939—944]
[15] Xu Z G, Li M Z, Sun F X, et al. Effects of temperature, irradiance level and nutritional history on the uptake of inorganic phosphorus in Hizikia fusiforme [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2013, 9(3): 8—13 [徐智广, 李美真, 孙福新, 等. 温度、光强和营养史对羊栖菜无机磷吸收的影响. 南方水产科学, 2013, 9(3): 8—13] Xu Z G, Li M Z, Sun F X, et al. Effects of temperature, irradiance level and nutritional history on the uptake of inorganic phosphorus in Hizikia fusiforme [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2013, 9(3): 8—13 [徐智广, 李美真, 孙福新, 等. 温度、光强和营养史对羊栖菜无机磷吸收的影响. 南方水产科学, 2013, 9(3): 8—13]
[16] Shao F, Fei L, Wu H L. Effect of environmental factors and algae density on the growth and nutrient uptake in Porphyra yezoensis [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(21): 6164—6171 [邵飞, 费岚, 吴海龙. 环境因子及藻体密度对条斑紫菜生长与氮磷去除效率的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(21): 6164—6171] Shao F, Fei L, Wu H L. Effect of environmental factors and algae density on the growth and nutrient uptake in Porphyra yezoensis [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(21): 6164—6171 [邵飞, 费岚, 吴海龙. 环境因子及藻体密度对条斑紫菜生长与氮磷去除效率的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(21): 6164—6171]
[17] Qian L M, Xu Y J, Jiao N Z, et al. Effects of environmental factors on uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus by Gracilaria lemaneiformis and G. 1ichevoides [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2006, 13(2): 257—262 [钱鲁闽, 徐永健, 焦念志, 等. 环境因子对龙须菜和菊花心江蓠N、P吸收速率的影响. 中国水产科学, 2006, 13(2): 257—262] Qian L M, Xu Y J, Jiao N Z, et al. Effects of environmental factors on uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus by Gracilaria lemaneiformis and G. 1ichevoides [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2006, 13(2): 257—262 [钱鲁闽, 徐永健, 焦念志, 等. 环境因子对龙须菜和菊花心江蓠N、P吸收速率的影响. 中国水产科学, 2006, 13(2): 257—262]
[18] Zhang Y Z, Wang P, Gui F K, et al. Utilization of nitrogen of Ulva lactuca, Ishige foliaceaokamurai and Grateloupia filicina [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2012, 31(3): 341—345 [张永正, 王萍, 桂福坤, 等. 石莼、铁钉菜和蜈蚣藻对氮源利用的研究. 海洋环境科学, 2012, 31(3): 341—345] Zhang Y Z, Wang P, Gui F K, et al. Utilization of nitrogen of Ulva lactuca, Ishige foliaceaokamurai and Grateloupia filicina [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2012, 31(3): 341—345 [张永正, 王萍, 桂福坤, 等. 石莼、铁钉菜和蜈蚣藻对氮源利用的研究. 海洋环境科学, 2012, 31(3): 341—345]
[19] Morel F M M, Rueter J G. Aquil: a chemically defined phytoplankton culture medium for trace metal studies [J]. Journal of Phycology, 1979, 15(2): 135—141
[20] Eilers PHC, Peeters JCH. A model for the relationship between light intensity and the rate of photosynthesis in phytoplankton [J]. Ecology Modelling, 1988, 42(3): 199—215
[21] 姚南瑜. 藻类生理学. 大连: 大连工学院出版社. 1987, 259 Yao N Y. Algal Physiology [M]. Dalian: Dalian Institute of Technology Press. 1987, 259
姚南瑜. 藻类生理学. 大连: 大连工学院出版社. 1987, 259[22] Lomas M W, Glibert P M. Interactions between
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ and${\rm{NO}}_3^ – $ uptake and assimilation: Comparison of diatoms and dinoflagellates at several growth temperatures [J]. Ma rine Biology, 1999, 133(3): 541—551[23] 潘瑞炽, 董愚得. 植物生理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社. 1995, 74—77 Pan R C, Dong Y D. Plant Physiology [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. 1995, 74—77
潘瑞炽, 董愚得. 植物生理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社. 1995, 74—77[24] Liu J W, Dong S L. Nature of ${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ uptake kinetics of Gracilaria tenuistipitata var.liui and Ulva pertusa [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(2): 95—102 [刘静雯, 董双林. 氮饥饿细基江蓠繁枝变型和孔石莼氨氮的吸收动力学特征. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2004, 26(2): 95—102]Liu J W, Dong S L. Nature of
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ uptake kinetics of Gracilaria tenuistipitata var.liui and Ulva pertusa [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(2): 95—102 [刘静雯, 董双林. 氮饥饿细基江蓠繁枝变型和孔石莼氨氮的吸收动力学特征. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2004, 26(2): 95—102][25] Wen S S, Zhang H Y, He W H, et al. Study on NH4-N removing efficiency and kinetics in Gracilaria asiatica [J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2008, 32(5): 794—803 [温珊珊, 张寒野, 何文辉, 等. 真江蓠对氨氮去除效率与吸收动力学研究. 水产学报, 2008, 32(5): 794—803] Wen S S, Zhang H Y, He W H, et al. Study on NH4-N removing efficiency and kinetics in Gracilaria asiatica [J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2008, 32(5): 794—803 [温珊珊, 张寒野, 何文辉, 等. 真江蓠对氨氮去除效率与吸收动力学研究. 水产学报, 2008, 32(5): 794—803]
[26] Jin Y L, Wu W T, Chen W Z. Effects of different tempera ture and salinity on growth and biochemical constituents of Gracilaria chouae [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2012, 8(2): 51—57 [金玉林, 吴文婷, 陈伟洲. 不同温度和盐度条件对脆江蓠生长及其生化组分的影响. 南方水产科学, 2012, 8(2): 51—57] Jin Y L, Wu W T, Chen W Z. Effects of different tempera ture and salinity on growth and biochemical constituents of Gracilaria chouae [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2012, 8(2): 51—57 [金玉林, 吴文婷, 陈伟洲. 不同温度和盐度条件对脆江蓠生长及其生化组分的影响. 南方水产科学, 2012, 8(2): 51—57]
[27] 雷衍之. 养殖水环境化学. 中国农业出版社. 2004, 116—117 Lei Y Z. Aquaculture Environmental Chemistry [M]. China Agriculture Press. 2004, 116—117
雷衍之. 养殖水环境化学. 中国农业出版社. 2004, 116—117[28] 李伟新, 朱仲嘉, 刘凤贤. 海藻学概论. 上海科学技术出版社. 1982, 224—225 Li W X, Zhu Z J, Liu F X. Introduction of Phycology [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai science and Technology Press. 1982, 224—225
李伟新, 朱仲嘉, 刘凤贤. 海藻学概论. 上海科学技术出版社. 1982, 224—225[29] Song T, Zhang M, Gao J X, et al. Fast chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics and its application in plant physiology research [J]. Journal of Biology, 2011, 28(6): 81—86 [宋婷, 张谧, 高吉喜, 等. 快速叶绿素荧光动力学及其在植物抗逆生理研究中的应用. 生物学杂志, 2011, 28(6): 81—86] Song T, Zhang M, Gao J X, et al. Fast chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics and its application in plant physiology research [J]. Journal of Biology, 2011, 28(6): 81—86 [宋婷, 张谧, 高吉喜, 等. 快速叶绿素荧光动力学及其在植物抗逆生理研究中的应用. 生物学杂志, 2011, 28(6): 81—86]
[30] Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhu Lin, et al. Comparative studies on the ecophysiological differences of two green tide macroalgae under controlled laboratory conditions [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(8): 1—16
[31] Lotze H K, Schramm W, Schories D, et al. Control of macroalgal blooms at early developmental stages: Pilayella littoralis versus Enteromorpha spp [J]. Oecologia, 1999, 119(1): 46—54
[32] Li W Q, Li Q, Liao Q B, et al. Effect of temperature on the fatty acid composition of four species of marine microalgae [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 5(1): 40—44
[33] Liu J W, Dong S L. Interactions between light and temperature on the growth and levels of chemical constituents of Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. Liui [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2001, 31(3): 332—338 [刘静雯, 董双林. 光照和温度对细枝江蓠繁枝变型的生长及生化组成影响. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2001, 31(3): 332—338] Liu J W, Dong S L. Interactions between light and temperature on the growth and levels of chemical constituents of Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. Liui [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2001, 31(3): 332—338 [刘静雯, 董双林. 光照和温度对细枝江蓠繁枝变型的生长及生化组成影响. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2001, 31(3): 332—338]
[34] Schansker G, Rensen J J S V. Performance of active photosystem II centers in photoinhibited pea leaves [J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1999, 62(2): 175—184
[35] 刘海英. 对虾工厂化养殖水质特征及高溶解氧对养殖的影响. 中国海洋大学, 山东. 2006 Liu H Y. Water quality characteristic of industrial shrimp farming and effects of higher dissolves oxygen on its farming [D]. Ocean University of China, Shandong. 2006
刘海英. 对虾工厂化养殖水质特征及高溶解氧对养殖的影响. 中国海洋大学, 山东. 2006[36] 陈东兴. 5种养殖池塘水质、污染物排放强度及氮、磷收支. 上海海洋大学, 上海. 2012 Chen D X. Water quality, discharge pollutants, nitroge and phosphorus budget in five types of aquaculture pond [D]. Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai. 2012
陈东兴. 5种养殖池塘水质、污染物排放强度及氮、磷收支. 上海海洋大学, 上海. 2012[37] Guo Y J, Luo S L, Li J W, et al. Assessment of water environmental quality of mariculture areas in Liusha Bay in 2012-2013 [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(19): 130—136 [郭永坚, 罗昭林, 李俊伟, 等. 2012-2013年流沙湾海水养殖区水环境质量评价. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(19): 130—136] Guo Y J, Luo S L, Li J W, et al. Assessment of water environmental quality of mariculture areas in Liusha Bay in 2012-2013 [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(19): 130—136 [郭永坚, 罗昭林, 李俊伟, 等. 2012-2013年流沙湾海水养殖区水环境质量评价. 广东农业科学, 2015, 42(19): 130—136]
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 曹金凤,李秋芬,黄经献,罗梓峻,张传涛,孙祥山. 温度和光照强度对强壮硬毛藻氮磷营养盐吸收效果的影响. 渔业科学进展. 2024(02): 105-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨晓龙,王晓丽,唐文海,吴振邦,王一航,田阔,李宏亮,唐峰,张秀梅. 两种生态型铜藻对不同氮源的吸收特征及生长响应. 生态学报. 2024(24): 11450-11458 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 柳林青,刘之威,何泉,杨宇峰,邹定辉. 粤港澳大湾区潮间带大型海藻多样性与生物量分布格局. 生态学杂志. 2023(03): 677-684 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈泽宇,丁雨豪,王静文,倪嘉璇,何昊林,徐加涛,蒋书英,王津果. 温度和氮营养盐对龙须菜生长与光合生理的影响. 湖北农业科学. 2023(12): 94-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 区丽华,卢家磊,吴圣哲,赵志淼,鲁仙,张饮江. 低温对大型海藻型微生物脱盐电池处理海产品暂养水的影响. 上海海洋大学学报. 2022(05): 1146-1157 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 谭清乾,王沛芳,王洵,马晶洁,胡斌. 不同光照下梅尼小环藻对昼夜温差变化的生理响应. 水资源保护. 2021(03): 127-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. Tingting ZHOU,Jing HE,Zhihua LIN,Lin HE. Treatment of Shrimp Effluent by Integrated Culture of Bivalves and Macroalgae. Asian Agricultural Research. 2021(05): 33-39 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: