THE EFFECT OF PGPR ON SUBMERGED MACROPHYTE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH THE SEDIMENT NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS FORMS
-
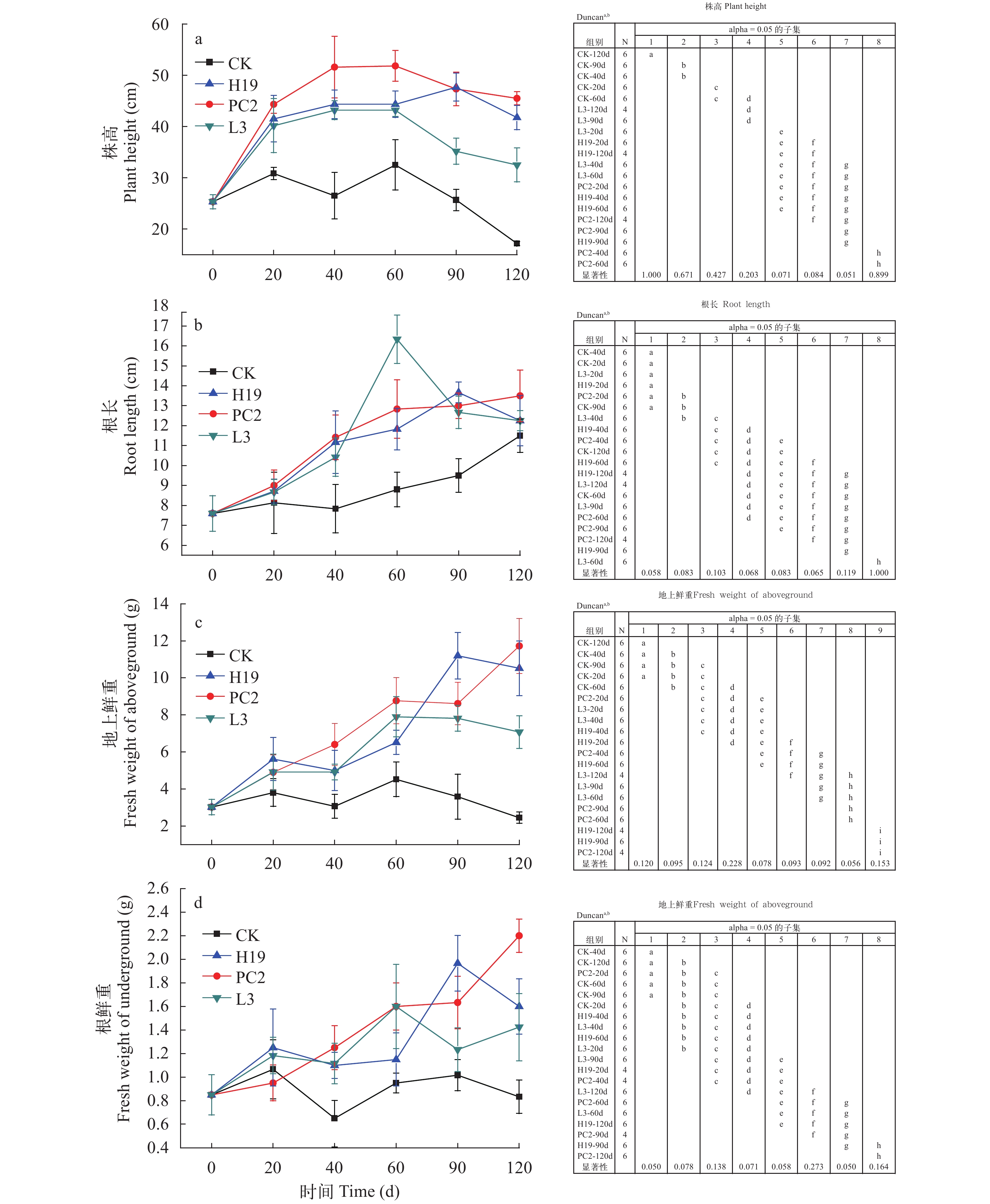
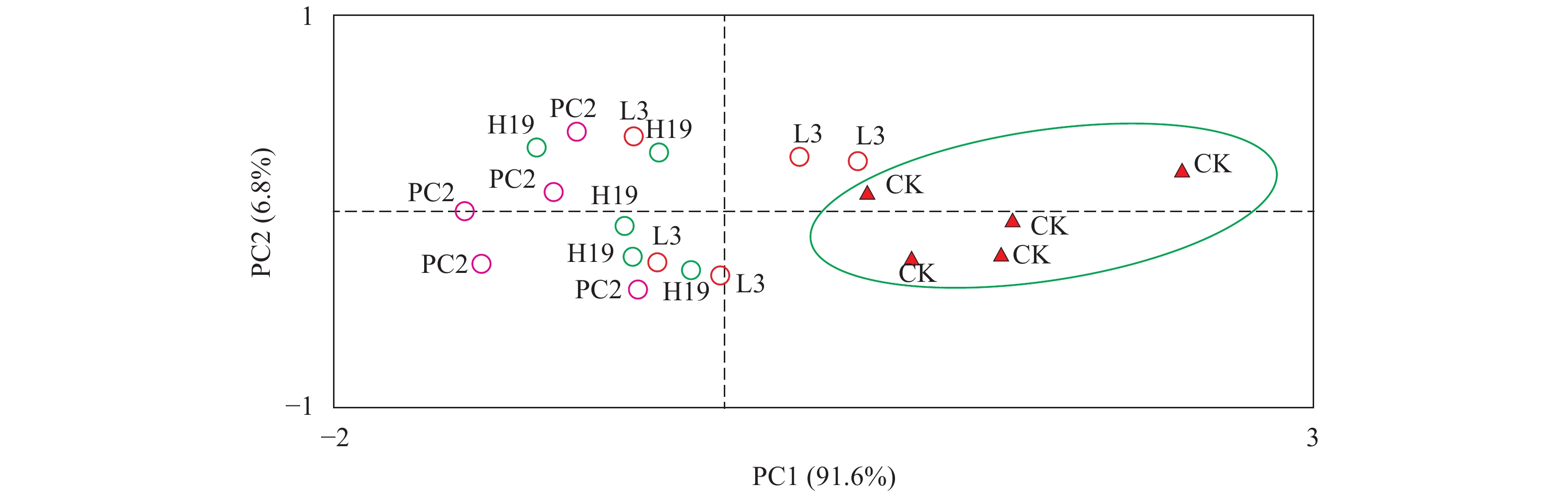
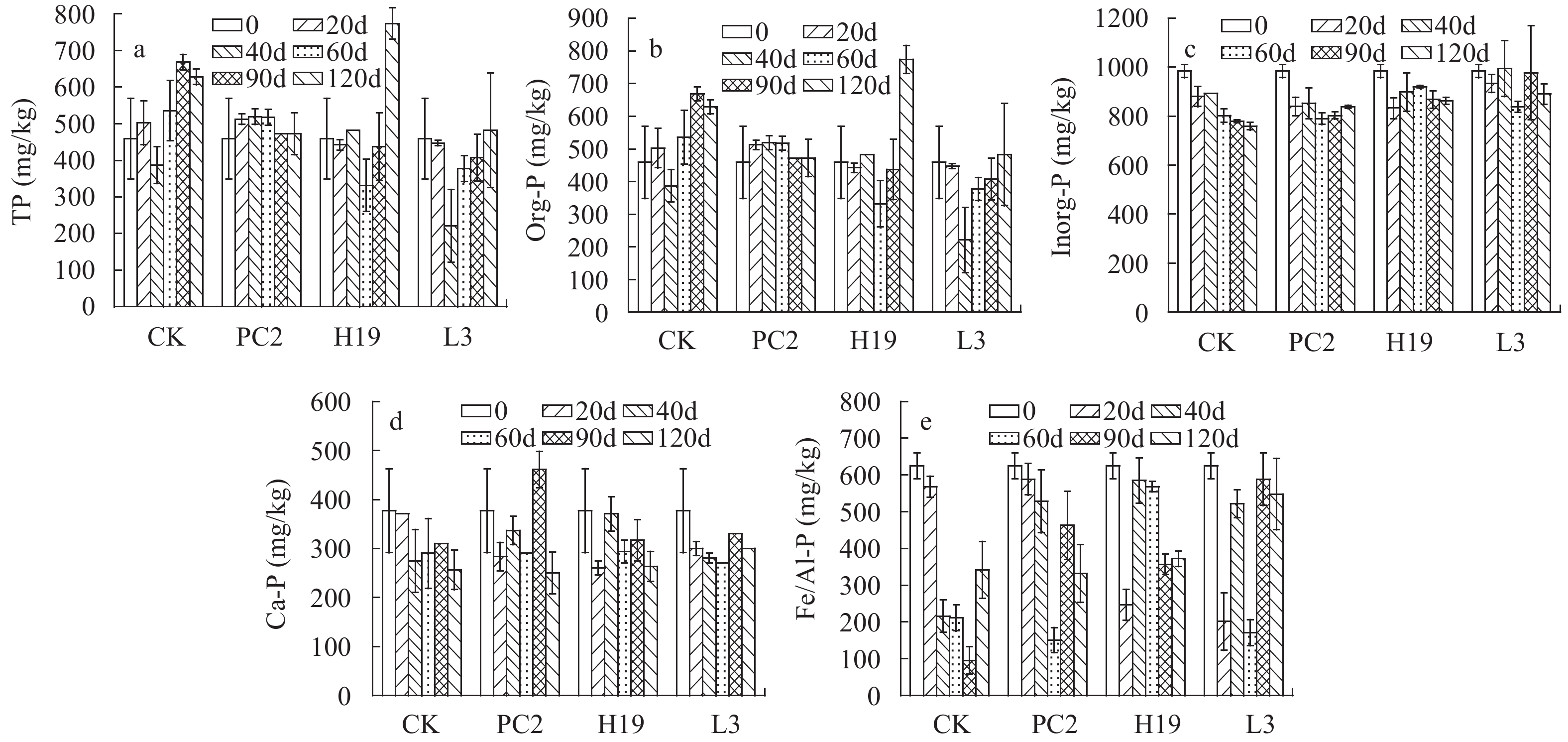
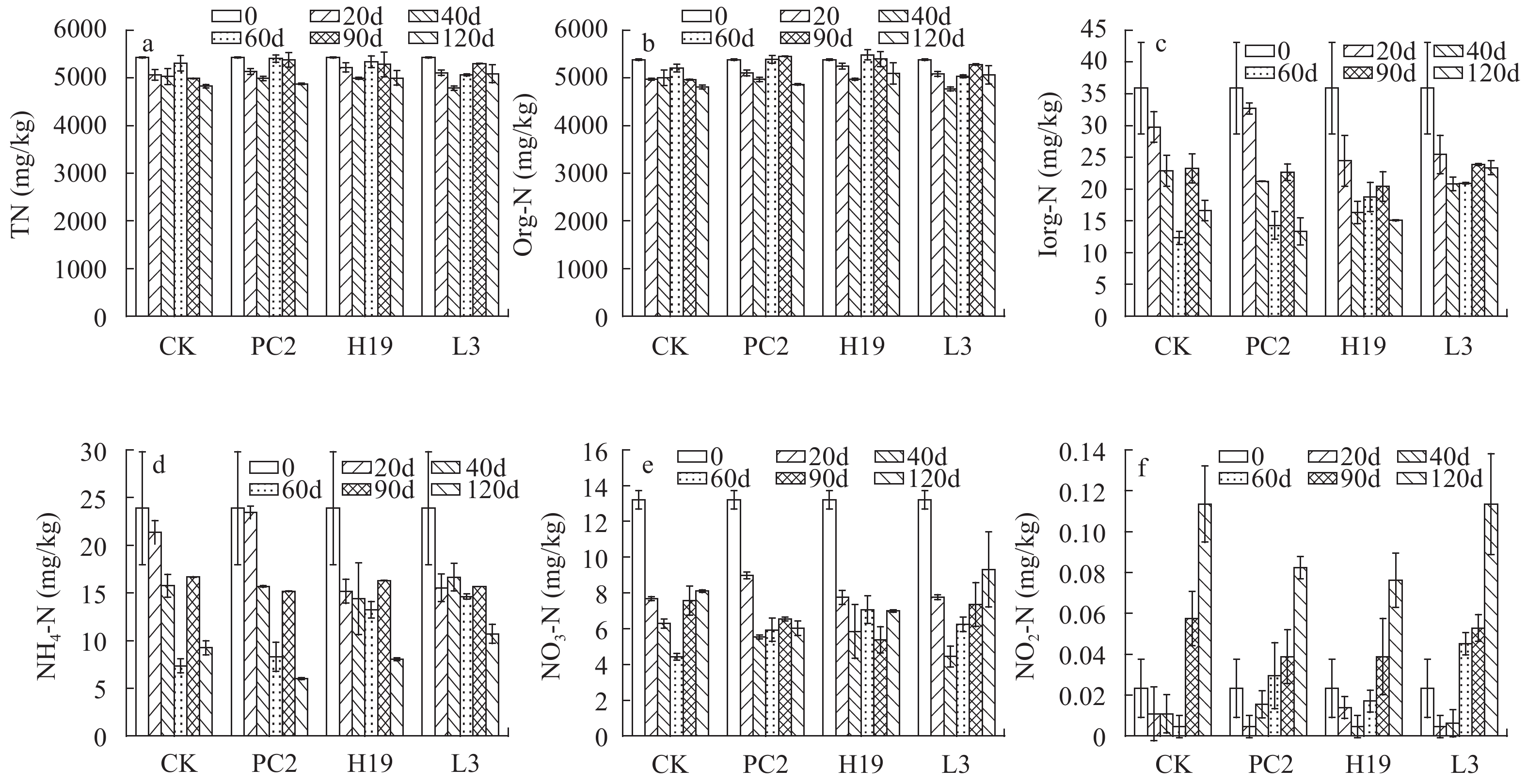
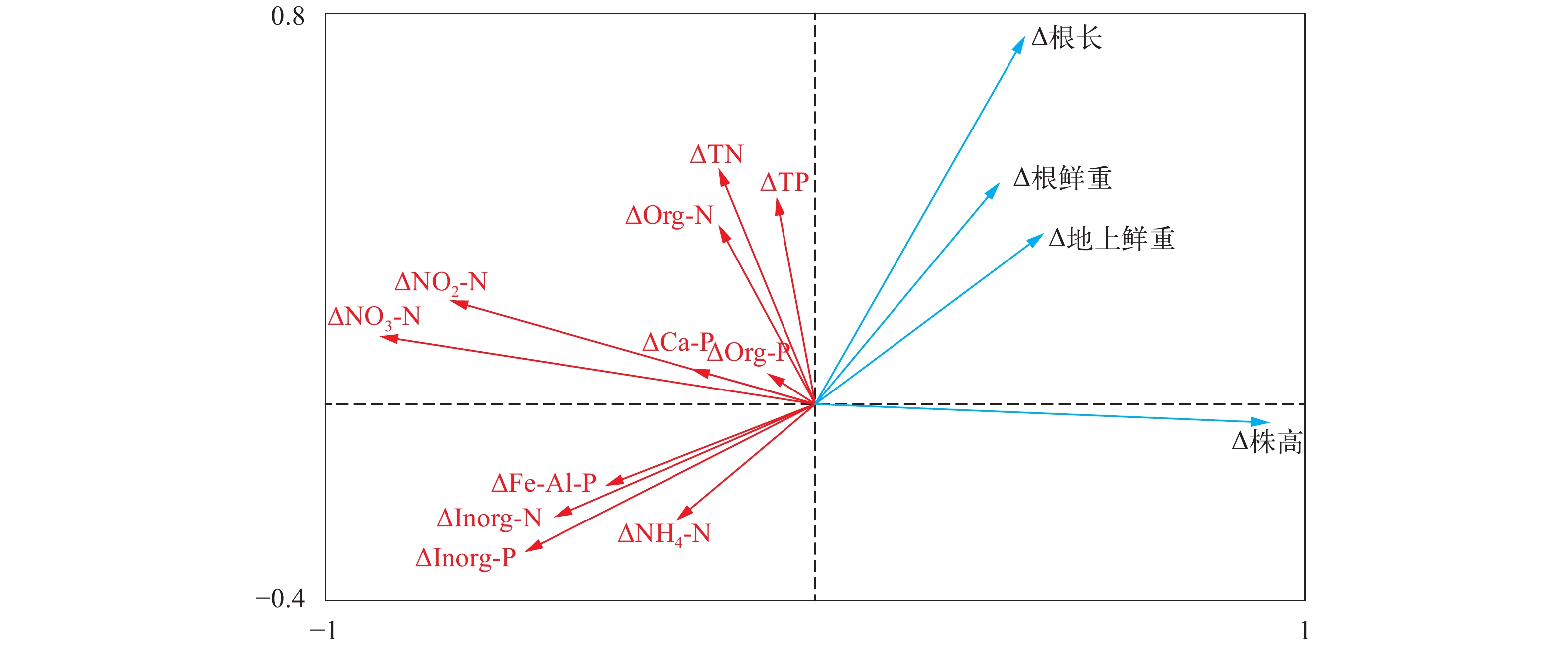
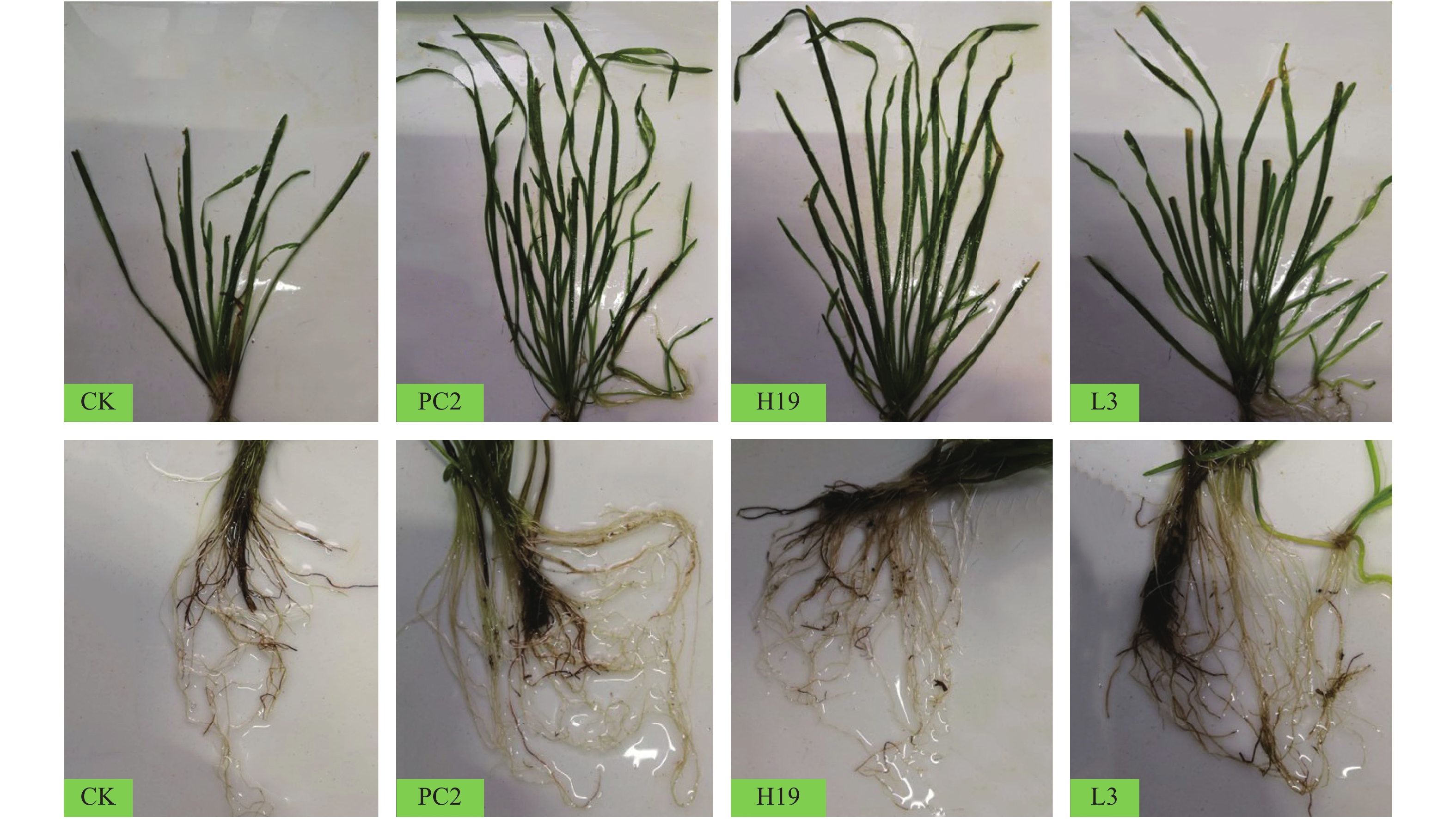
摘要: 研究在沉积物高有机质条件下, 通过接种根际促生菌(Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, PGPR) PC2(Bacillus stratosphericus)、H19(Bacillus subtilis)和L3(Bacillus cereus)的方式探讨其对苦草(Vallisneria natans)植株的促生效应及其与沉积物氮磷赋存形态的关系。结果表明, 接种组对苦草生长具有显著促进作用, 空白处理种植的苦草生长受到抑制, PGPR对苦草生长促进的综合影响为PC2>H19>L3, PC2处理组株高、根长、地上鲜重和根鲜重比空白分别增加了165.0%、17.4%、378.8%和165.1%。进一步分析不同时期苦草的各种生长指标增量与氮磷赋存形态增量的关系, 通过RDA分析及皮尔森相关分析, 苦草生长指标增量与沉积物中无机氮(Inorg-N)、亚硝态氮(NO2-N)、硝态氮(NO3-N)、无机磷(Inorg-P)和铁/铝磷(Fe/Al-P)等增量显著负相关, 表明PGPR对沉积物中无机态N、P具有一定的控制作用。因此, 接种PGPR对解决受污染湖泊沉水植物恢复及内源污染等问题具有一定潜力。Abstract: As an important primary producer, submerged macrophytes regulate the material circulation and energy flow of the ecosystem, but the recovery process of submerged macrophytes is often plagued by sediments with high organic matter load. The effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Vallisneria natans (V. natans) growth and its relationship with sediment nitrogen and phosphorus was studied by inoculating strains PC2 (Bacillus stratosphericus), H19 (Bacillus subtilis) and L3 (Bacillus cereus) under high sediment organic matter load. The results showed that PGPR inoculation significantly promoted the growth of V. natans and the comprehensive effects was PC2>H19>L3. The growth of V. natans grown in the non-inoculated treatment was inhibited. The height, root length, fresh weight of aboveground and underground tissues of V. natans in PC2 treatment group increased by 165.0%, 17.4%, 378.8% and 165.1%, respectively. Through RDA analysis and Pearson correlation analysis, the increment of plant growth index were significantly negatively correlated with the increment of Inorg-N, NO2-N, NO3-N, Inorg-P and Fe/Al-P in the sediment, indicating their potential control sediment Inorg-N and Inorg-P. Therefore, PGPR inoculation is a certain prospective way to solve the problems of submerged macrophytes recovery and internal pollution.
-
-
表 1 三株PGPR(PC2、H19、L3)基本信息情况表
Table 1 Basic information of the three strains of PGPR (PC2, H19, L3)
编号Code name 来源Source 菌种Strain 溶磷 Phosphorus solubilisation (mg/L) IAA产生IAA production (mg/L) CKs产生Cytokinins production (μg/L) ACC脱氨酶活性ACC deaminase (U/mg) PC2 菹草根际 Bacillus stratosphericus 35.9±6.6 13.9±0.4 13.3±1.7 0 H19 苦草根际 Bacillus subtilis 11.4±0.2 6.7±0.7 10.1±1.3 0.047±0.006 L3 苦草根际 Bacillus cereus 24.5±0.0 7.3±0.3 15.9±4.7 0.008±0.003 表 2 生长指标增量与环境因子增量的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between growth index increment and environmental factor increment
Pearson相关指数 ΔTN ΔNH4-N ΔNO3-N ΔNO2-N ΔInorg-N ΔOrg-N ΔTP ΔCa-P ΔFe/Al-P ΔOrg-P ΔInorg-P ∆株高 –0.204 –0.258 –0.835** –0.699** –0.491* –0.201 –0.086 –0.236 –0.391 –0.092 –0.544* Δ根长 0.253 –0.316 –0.544* –0.185 –0.515* 0.168 0.299 0.007 –0.225 –0.015 –0.473* Δ地上鲜重 0.185 –0.184 –0.327 –0.199 –0.209 0.130 0.056 –0.312 –0.565** 0.056 –0.422 Δ根鲜重 0.005 –0.104 –0.249 0.032 –0.126 –0.052 0.285 –0.184 –0.544* 0.115 –0.533* 注: *P,0.05, **P<0.01 -
[1] Zamparas M, Zacharias I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads: a review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014(496): 551-562.
[2] Xu X G, Zhou Y W, Han R M, et al. Eutrophication triggers the shift of nutrient absorption pathway of submerged macrophytes: implications for the phytoremediation of eutrophic waters [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019(239): 376-384.
[3] 叶斌, 吴蕾, 李春华, 等. 苦草不同生命阶段对水体、底泥中氮迁移转化的影响 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2015, 5(6): 485-491. Ye B, Wu L, Li C H, et al. Effect of different life stage Vallisneria natans (Lour.) hara on migration and transformation of nitrogen in water and sediment [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2015, 5(6): 485-491. [
[4] 王立志. 两种沉水植物对间隙水磷浓度的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(4): 1051-1058. Wang L Z. Influence of two submerged macrophytes on pore water phosphorus concentration [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(4): 1051-1058. [
[5] 王立志, 王国祥, 俞振飞, 等. 沉水植物生长期对沉积物和上覆水之间磷迁移的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 385-392. Wang L Z, Wang G X, Yu Z F, et al. Influence of submerged macrophytes on phosphorus transference between sediment and overlying water in the growth period [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 385-392. [
[6] 黄小龙, 郭艳敏, 张毅敏, 等. 沉水植物对湖泊沉积物氮磷内源负荷的控制及应用 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(12): 1524-1530. Huang X L, Guo Y M, Zhang Y M, et al. Controlling of internal phosphorus and nitrogen loading in lake sediment by submerged macrophytes and its application [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019, 35(12): 1524-1530. [
[7] Devereux R, Yates D F, Aukamp J, et al. Interactions of Thalassia testudinum and sediment biogeochemistry in Santa Rosa Sound, NW Florida [J]. Marine Biology Research, 2011, 7(4): 317-331. doi: 10.1080/17451000.2010.515227
[8] 吴明丽, 李叙勇. 光衰减及其相关环境因子对沉水植物生长影响研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(22): 7202-7212. doi: 10.5846/stxb201110091469 Wu M L, Li X Y. Research progress on influencing of light attenuation and the associated environmental factors on the growth of submersed aquatic vegetation [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(22): 7202-7212. [ doi: 10.5846/stxb201110091469
[9] Wu J, Cheng S, Liang W, et al. Effects of sediment anoxia and light on turion germination and early growth of Potamogeton crispus [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2009(628): 111-119.
[10] Phillips G L, Eminson D, Moss B. A mechanism to account for macrophyte decline in progressively eutrophicated freshwaters [J]. Aquatic Botany, 1978, 4(1): 103-126.
[11] Sand-Jensen K, Pedersen N L, Thorsgaard I, et al. 100 years of vegetation decline and recovery in Lake Fure, Denmark [J]. Journal of Ecology, 2008, 96(2): 260-271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2007.01339.x
[12] Arruda L, Beneduzi A, Martins A, et al. Screening of rhizobacteria isolated from maize (Zea mays L.) in Rio Grande do Sul state (South Brazil) and analysis of their potential to improve plant growth [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2013(63): 15-22.
[13] Bhattacharyya P N, Jha D K. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): emergence in agriculture [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 28(4): 1327-1350. doi: 10.1007/s11274-011-0979-9
[14] 冯维维, 武美贤, 司雨婷, 等. 中华补血草内生与根际具ACC脱氨酶活性细菌的筛选及其生物多样性 [J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(4): 719-728. Feng W W, Wu M X, Si Y T, et al. Screening and biodiversity of endophytic and rhizosphere bacteria containing ACC deaminase from halophyte Limonium sinense (Girard) Kuntze [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(4): 719-728. [
[15] 王欢, 韩丽珍. 4株茶树根际促生菌菌株的鉴定及促生作用 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(3): 548-562. Wang H, Han L Z. Identification of four plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from tea rhizosphere [J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(3): 548-562. [
[16] Qin Y, Druzhinina I S, Pan X, et al. Microbially mediated plant salt tolerance and microbiome-based solutions for saline agriculture [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(7): 1245-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.08.005
[17] Gayathri I, Smith D L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in amelioration of salinity stress: a systems biology perspective [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017(8): 1768-1781.
[18] Lasudee K, Tokuyama S, Lumyong S, et al. Actinobacteria associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal funneliformis mosseae spores, taxonomic characterization and their beneficial traits to plants: evidence obtained from mung bean (Vigna radiata) and Thai Jasmine Rice (Oryza sativa) [J]. Frontiers Microbiology, 2018(9): 1247-1264.
[19] Mudroch A, Azcue J. Manual of Aquatic Sediment Sampling [M]. Boca Raton. Florida: Lewis Publishers, 1995: 194-200.
[20] Ruban V, López-Sánchez J F, Pardo P, et al. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments-A synthesis of recent works [J]. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 370(2-3): 224-228. doi: 10.1007/s002160100753
[21] 钱君龙, 张连弟, 乐美麟. 过硫酸盐消化法测定土壤全氮全磷 [J]. 土壤, 1990(5): 258-262. Qian J L, Zhang L D, Le M L. Determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in soil by persulfate digestion [J]. Soils, 1990(5): 258-262. [
[22] 国家环境保护总局. 土壤氨氮 亚硝酸盐氮 硝酸盐氮的测定 氯化钾溶液提取-分光光度法(HJ634-2012) [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012: 1-14. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People′s Republic of China. Soil-Determination of Ammonium, Nitrite and Nitrate by Extraction with Potassium Chloride-Spectrophotometric Methods (HJ634-2012) [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2012: 1-14.
[23] Kim J K, Choi S R, Lee J, et al. Metabolic differentiation of diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella L.) resistance in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. capitata) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(46): 11222-11230. doi: 10.1021/jf403441t
[24] 赵伟进, 王孝先, 杨洋, 等. 黑青稞根际促生菌筛选及其对种子萌发的影响 [J]. 种子, 2018, 37(12): 7-11, 16. Zhao W J, Wang X Y, Yang Y, et al. Selection of rhizotrophic bacteria from rhizosphere and its effect on seed germination of black barley [J]. Seed, 2018, 37(12): 7-11, 16. [
[25] Asari S, Tarkowská D, Rolčík J, et al. Analysis of plant growth-promoting properties of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, UCMB5113 using Arabidopsis thaliana as host plant [J]. Planta, 2016, 245(1): 15-30.
[26] Bangash N, Khalid A, Mahmood T, et al. Screening rhizobacteria containing ACC-deaminase for growth promotion of wheat under water stress [J]. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2013, 45(Suppl. l): 91-96.
[27] 何志刚, 王秀娟, 董环, 等. PGPR菌肥对马铃薯产量与肥料利用率影响的初步研究 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(2): 100-103. He Z G, Wang X J, Dong H, et al. A preliminary study of the application of PGPR fertilizer on the potato [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(2): 100-103. [
[28] Singh J S, Singh D P. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): microbes in sustainable agriculture [J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2013(133): 1-88.
[29] Franco A R, Castro P M L. Inoculation of Pinus pinea seedlings with Pisolithus tinctorius and Suillus belliniipromotes plant growth in benfluralin contaminated soil [J]. Plant and Soil, 2015, 386(1-2): 113-123. doi: 10.1007/s11104-014-2247-x
[30] Castanheira Nádia L, Dourado A C, Pais I, et al. Colonization and beneficial effects on annual ryegrass by mixed inoculation with plant growth promoting bacteria [J]. Microbiological Research, 2017(198): 47-55.
[31] 郑少玲, 陈琼贤, 谭炽强, 等. 生物有机肥中磷细菌对难溶性磷的有效化研究 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2006(3): 54-56. Zheng S L, Chen Q X, Tan C Q, et al. Effects on the validity of insoluble phosphates by the phosphobacteria of bio-organic fertilizer [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2006(3): 54-56. [




 下载:
下载: