INFLUENCE OF siRNA TARGETING CYHV-2 ORF57 GENE ON REPLICATION OF CYHV-2 IN CSC CELLS
-
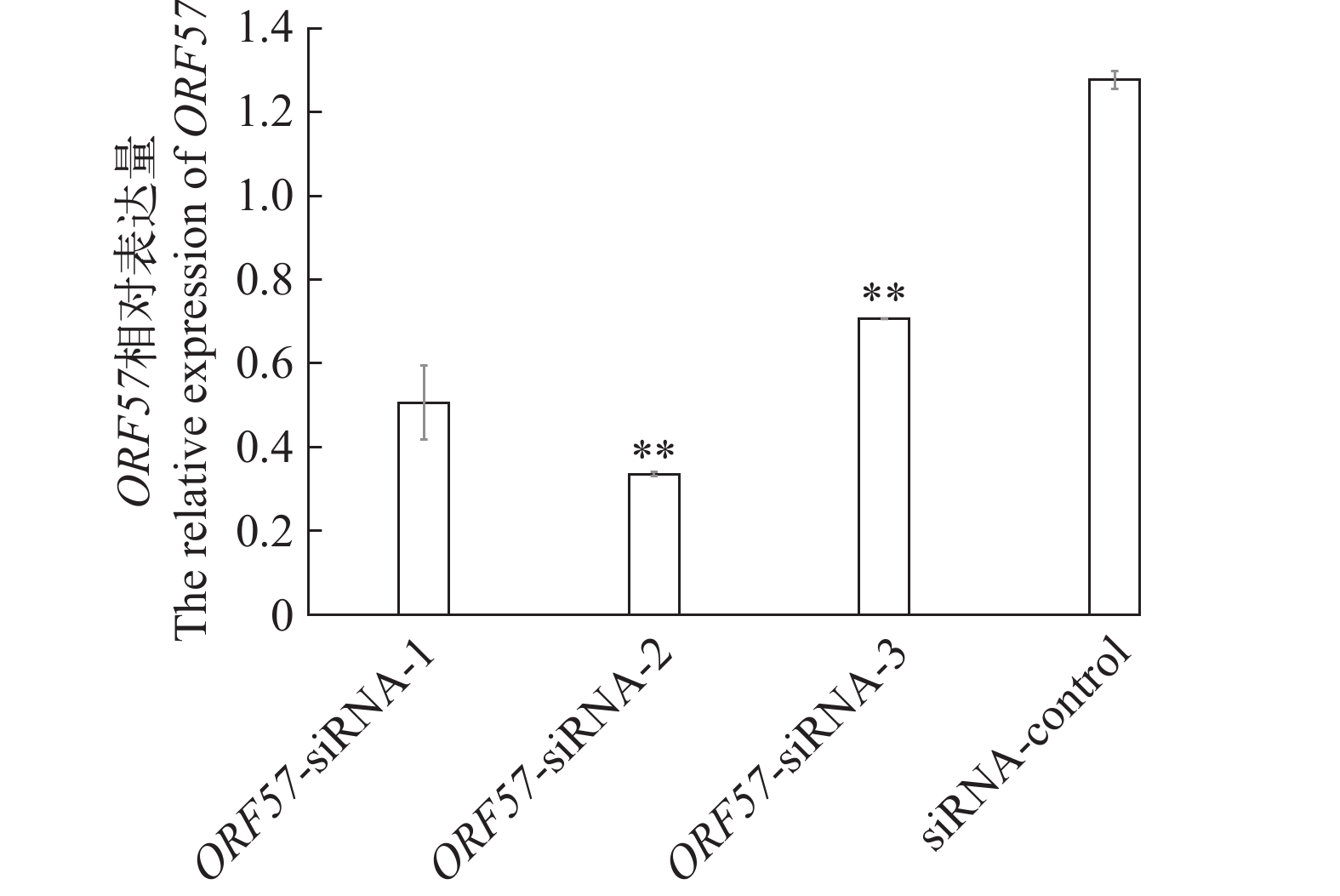
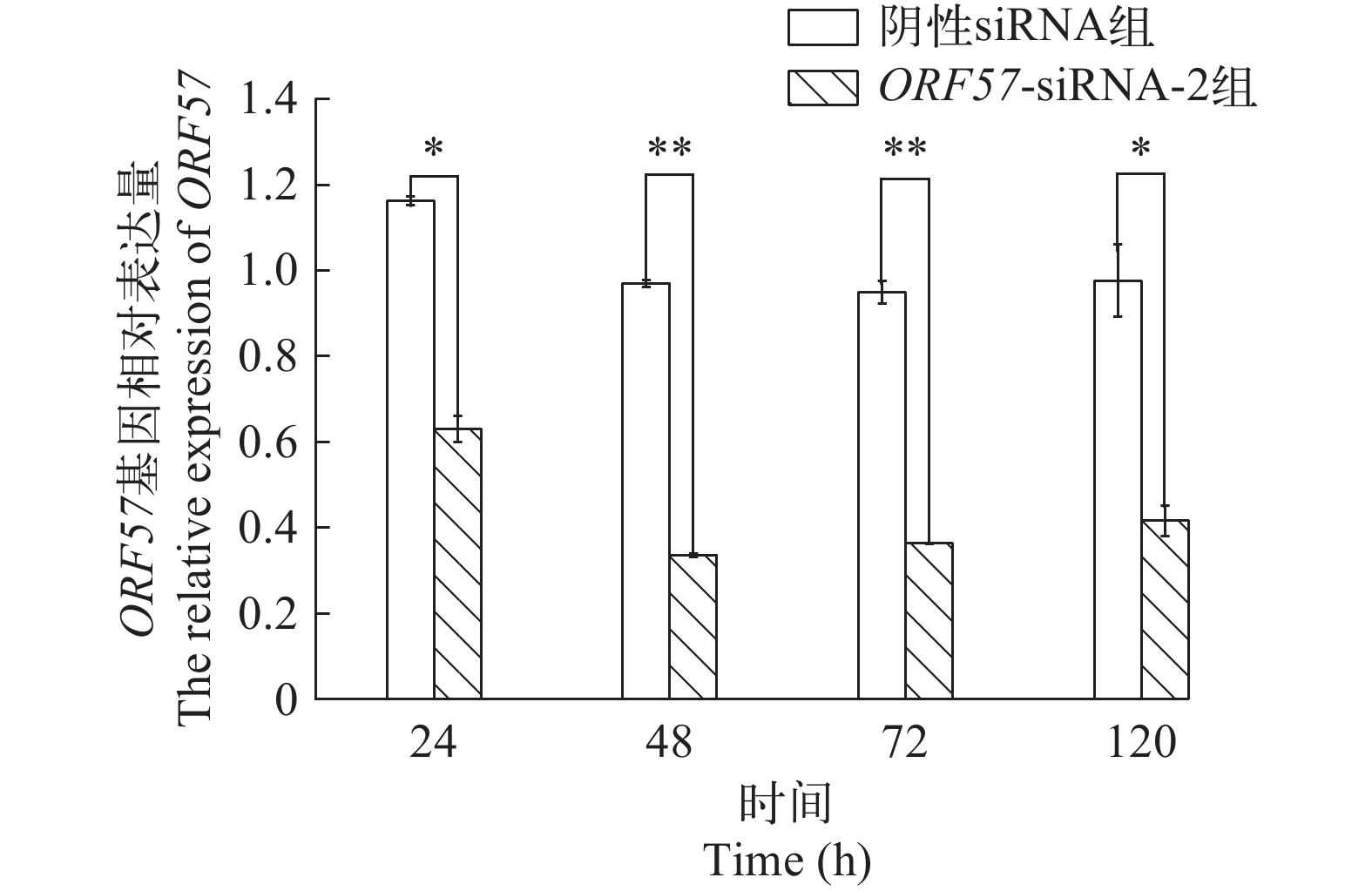
摘要: 研究通过在异育银鲫脊髓细胞系(Spinal cord tissue cell lines of Carassius auratus gibelio, CSC)中对鲤疱疹病毒Ⅱ型(Cyprinid herpesvirus 2, CyHV-2) ORF57进行RNA干扰, 以探究其对CyHV-2病毒复制的影响。首先, 以FAM标记的异育银鲫β-actin的siRNA进行CSC细胞转染条件的优化, 再将针对CyHV-2 ORF57基因设计的3条siRNA, 转染CSC细胞, 并进行病毒感染, 评估siRNA对病毒复制和致细胞病变的影响。转染条件优化结果显示, 在siRNA浓度为80 nmol/L, 转染液维持24h后更换维持液, β-actin基因表达量最低且观察到的荧光点数量最多。而ORF57-siRNAs干扰结果显示, ORF57-siRNA-2组表现出了较强的抑制效果, 在接毒48h时, ORF57-siRNA-2处理组的ORF57基因表达量降到相对于Mock组的33.55% (P<0.01), 并且各ORF57-siRNA组都表现出了延缓CyHV-2致细胞病变的时间和强度, 抑制时间可达120h。TCID50结果显示, 不同组的ORF57-siRNAs均能降低病毒滴度, 其中ORF57-siRNA-2将病毒原液TCID50 108.487/mL下降至106.776/mL。研究结果表明, 干扰ORF57的表达可大大降低CyHV-2的致细胞病变力和复制率, ORF57在CyHV-2复制与致细胞病变中起重要作用。本研究为CyHV-2基于siRNA技术的抗病毒治疗和弱毒株的改造提供了借鉴。Abstract: Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2) is the pathogen of herpesviral hematopoietic necrosis of Carassius auratus. It is a double-stranded DNA virus that can infect goldfish, crucian carp and its varieties. This study investigated the effect of CyHV-2 ORF57 on viral replication in Spinal cord tissue cell lines of Carassius auratus gibelio (CSC). Lipofectamine 2000 was used to transfect siRNA. Three pairs of siRNAs of CyHV-2-ORF57 gene were transfected into CSC cells to evaluate the effect of ORF57 on viral replication and cytopathic effect (CPE). Real-time PCR analysis revealed that ORF57-siRNA-2 had the greatest suppression of ORF57 expression with a 33.55% (P<0.01) reduction at 48h associated with the strongest inhibitory effect. All three ORF57-siRNAs delayed the time and intensity of CyHV-2 cytopathogenic effect, with the inhibition time up to 120h. The results of TCID50 showed that ORF57-siRNAs reduced the titer of the virus, and ORF57-siRNA-2 decreased the virus stock solution TCID50 108.487/mL to 106.776/mL. This study show that ORF57 can mediate the CPE and replication rate of CyHV-2. This study provides a reference for the antiviral treatment based on siRNA technology and the construction of low virulent strain of CyHV-2.
-
Keywords:
- Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 /
- RNA interference /
- ORF57 /
- siRNA /
- CSC cell line /
- TCID50
-
-
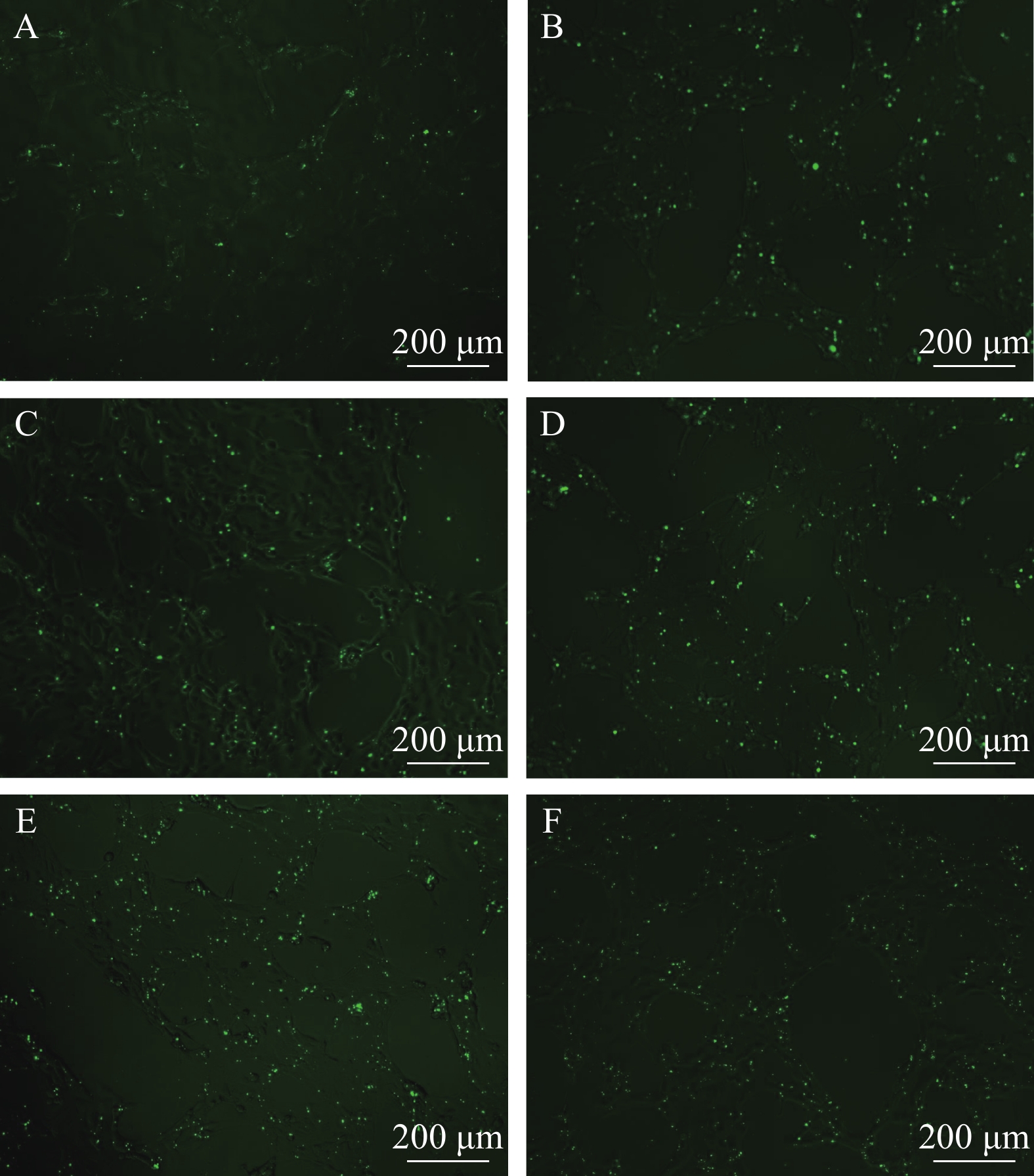
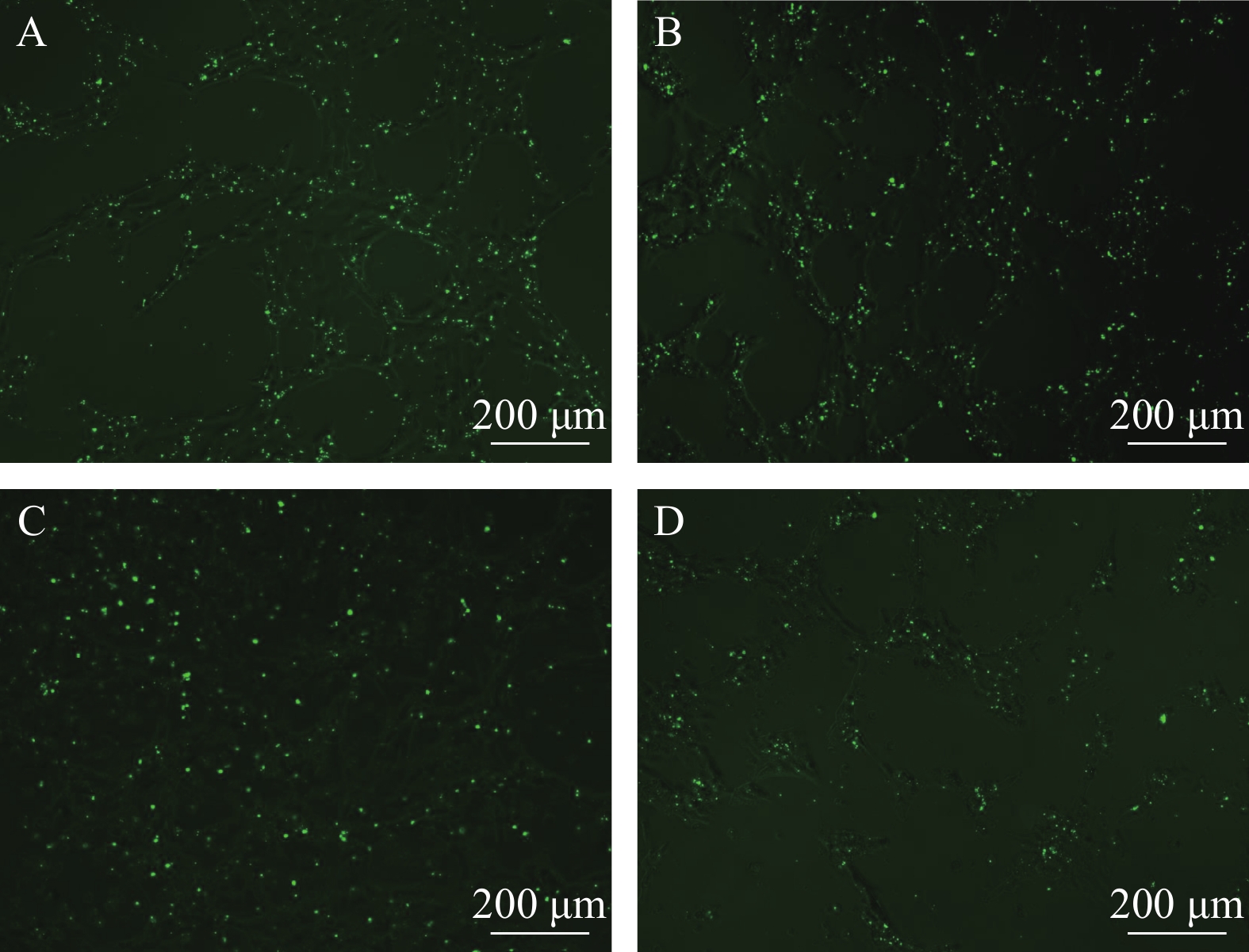
图 2 在不同条件下FAM-β-actin-siRNA转染效果
A和B转染浓度是40 nmol/L, C和D转染浓度是80 nmol/L, E和F转染浓度是120 nmol/L; A、C、E为转染6h后换液, B、D、F为转染24h后换液。标尺为200 μm
Figure 2. Effect of different concentrations of FAM-β-actin- siRNA transfection
The transfection concentrations of A and B are 40 nmol/L, C and D are 80 nmol/L, E and F are 120 nmol/L; A, C and E are 6h after transfection, the fluid changed, while B, D and F are 24h after transfection, the fluid changed. The bar in figure represent 200 μm
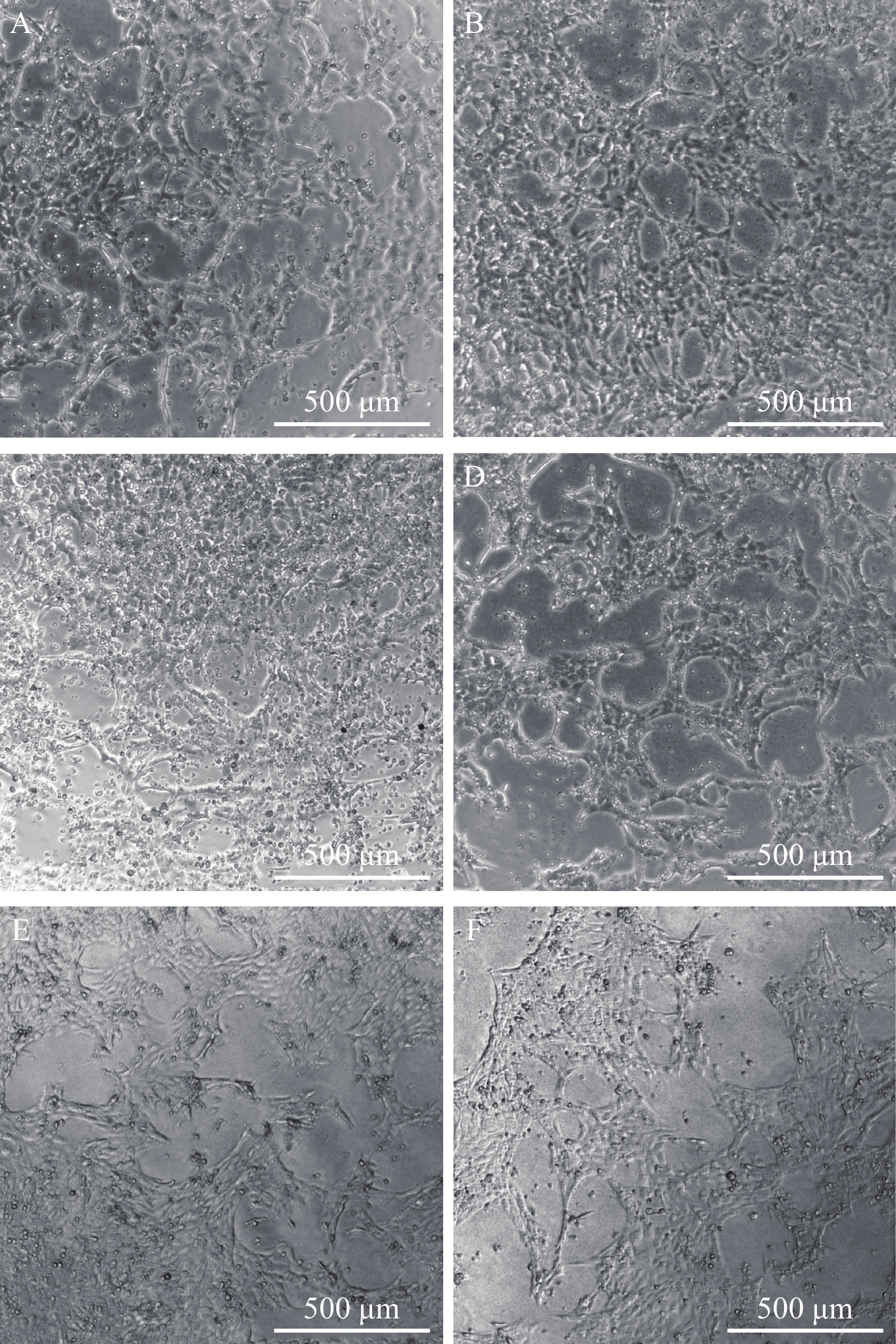
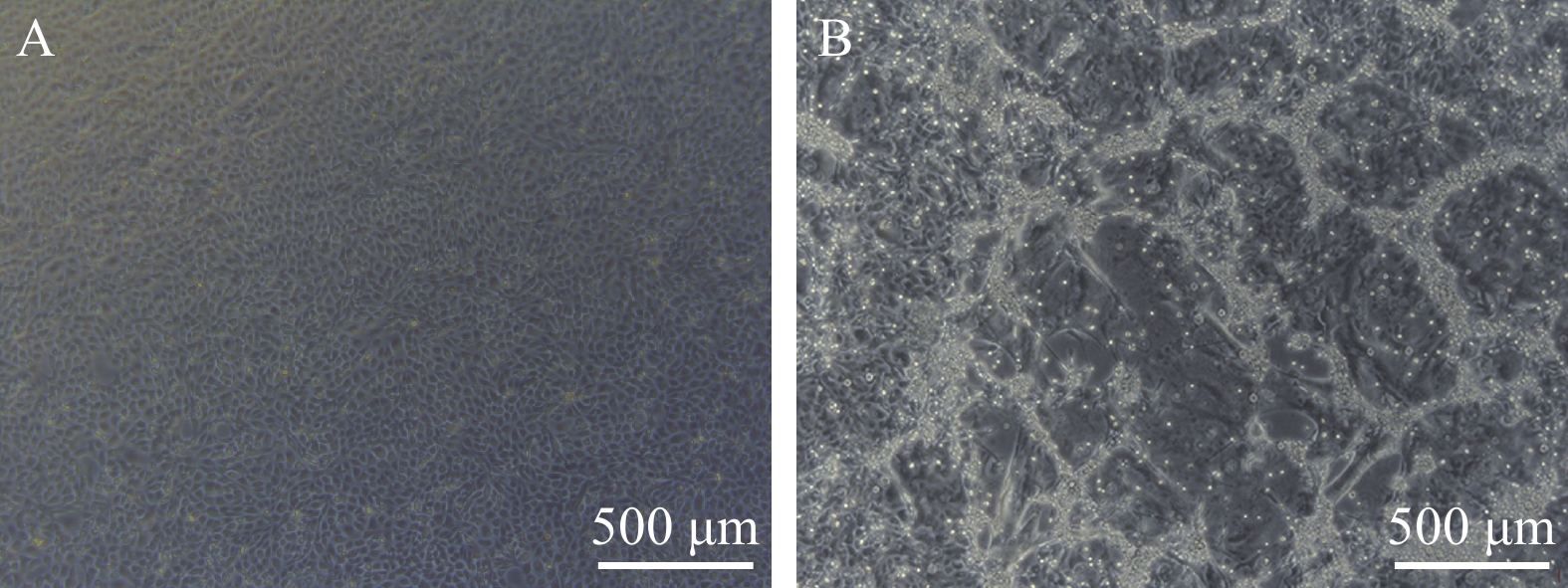
图 4 ORF57-siRNAs在120h干扰CyHV-2致CSC细胞病变效果
A. ORF57-siRNA-1组; B. ORF57-siRNA-2组; C. ORF57-siRNA-3组; D. 阴性siRNA组; E. Mock对照组; F. 空白组 (标尺500 μm)
Figure 4. Effect of ORF57-siRNAs on CyHV-2-induced CSC CPE at 120h
A.the emergence of CPE of CyHV-2-ORF57-1-siRNA group at 120h after infection; B.the emergence of CPE of CyHV-2-ORF57-2-siRNA group at 120h after infection; C.the emergence of CPE of CyHV-2-ORF57-3-siRNA group at 120h after infection; D.the emergence of CPE of Negative siRNA control group at 120h after infection; E.the emergence of CPE of Mock group at 120h after infection; F.the emergence of CPE of Blank group at 120h after infection. (the bar in figure represent 500 μm)
表 1 siRNA和PCR引物序列信息
Table 1 Sequences of siRNA and primers
组别Group 序列Sequence (5′—3′) ORF57-siRNA-1 Sense GCAAGAAGUCGUUCGAUAATT Antisense UUAUCGAACGACUUCUUGCTT ORF57-siRNA-2 Sense GGUACUUUCCAACGGCCAATT Antisense UUGGCCGUUGGAAAGUACCTT ORF57-siRNA-3 Sense GGAGCCACUGGAACAUCAATT Antisense UUGAUGUUCCAGUGGCUCCTT FAM-β-actin-siRNA Sense FAM-GGGAUGACAUGGAGAAGAUTT Antisense AUCUUCUCCAUGUCAUCCCTT siRNA-
control [11]Sense UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT Antisense ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT ORF57-1 Sense ATCATGGCAGAGTTTTTTACTGAGGAC Antisense GACGACATCGGTCTTTTTCTCTGC ORF57-2 Sense GCCCGCCGACTGGATAGAC Antisense AGGAACGCGAGGCTGTT ORF57-3 Sense AAGCCCAAGCGACTCACC Antisense TGGAGCTTTGGGTTTAGCGC β-actin Sense TCACCTCCCTTGCTCCTTCCAC Antisense CTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTG 表 2 加样配比表
Table 2 Sampling ratio table
分组
Group浓度组1
Concentration
group 1 (μL)浓度组2
Concentration
group 2 (μL)浓度组3
Concentration
group 3 (μL)阴性siRNA
对照组
siRNA-negative
control group (μL)Mock
对照
Mock control
group (μL)siRNA复合物
siRNA complexesFAM-β-actin-siRNA 1 2 3 2 0 Opti-MEMⅠ 49 48 47 48 50 Lipofectamine 复合物
Lipofectamine complexesLipofectamine 1 1 1 1 1 Opti-MEMⅠ 49 49 49 49 49 Opti-MEMⅠ 400 400 400 400 400 表 3 siRNA抑制试验分组
Table 3 Grouping of transfection inhibition test
组别
Group转染试剂Transfection reagent siRNA CyHV-2 取样时间
Sampling timeBlank group - - + / Mock group + - + 24h、48h、72h和120h Negative siRNA + + + 24h、48h、72h和120h β-actin siRNA + + + 24h、48h、72h和120h ORF57-siRNA + + + 24h、48h、72h和120h 注: +. 含; -. 不含Note: + means added; - means not added 表 4 TCID50病毒滴度测定
Table 4 Detection of TCID50 in different virus dilutions
组别
Group稀释梯度
Gradient dilution10–5 10–6 10–7 10–8 10–9 10–10 10–11 10–12 病变孔数
Number of wells with CPE7 7 6 1 1 0 0 0 未病变孔数
Number of wells without CPE1 1 2 7 7 8 8 8 表 5 Image J 统计荧光点数量
Table 5 Number of fluorescent spots counted by Image J
siRNA终浓度
Final concentration
of siRNA (nmol/L)转染后维持6h
Transfection after 6h转染后维持24h
Transfection after 24h40 618±18 700±26 80 1063±101 1366±136 120 1266±111 1031±46 表 6 在各转染方案下β-actin基因拷贝数
Table 6 Copy number of β-actin gene under each transfection scheme(copies/ng)
siRNA终浓度
Final concentration
of siRNA (nmol/L)转染后维持6h
Transfection after 6h转染后维持24h
Transfection after 24h40 8.423×104 1.258×104 80 1.147×104 3.375×103 120 4.985×104 4.685×104 表 7 转染后24h、48h、72h和120h β-actin基因表达情况
Table 7 Expression of β-actin gene at 24h, 48h, 72h and 120h after transfection (copies/ng)
转染siRNA 后时间
Times after transfection (h)β-actin基因拷贝数
Copy number of β-actin gene24 3.403×103 48 3.315×103 72 1.900×103 120 3.001×103 表 8 ORF57-siRNAs对CyHV-2 TCID50的影响
Table 8 Effect of ORF57-siRNA on CyHV-2 TCID50
组别Group TCID50 (mL) ORF57-siRNA-1 107.432 ORF57-siRNA -2 106.776 ORF57-siRNA -3 107.353 Negative siRNA 108.487 Mock 108 -
[1] Doszpoly A, Benko M, Csaba G, et al. Introduction of the family Alloherpesviridae: The first molecular detection of herpesviruses of cyprinid fish in Hungary [J]. Magyar Allatorvosok Lapja, 2011, 133(3): 174-181.
[2] 王璐. 江苏地区鲫出血病病原的分离、鉴定及检测方法研究 [D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012: 61. Wang L. The research on isolation and identification of pathogeny from the hermorrage disease of prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) in Jiangsu China and its detection method [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012: 61.
[3] 袁雪梅, 潘晓艺, 郝贵杰, 等. 一例异育银鲫(Carassius auratus gibelio)暴发性出血病病原分析 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(4): 913-920. Yuan X M, Pan X Y, Hao G J, et al. Analysis of pathogen in an explosive hemorrhage disease of Carassius auratus gibelio [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(4): 913-920.
[4] Thangaraj R S, Nithianantham S R, Dharmaratnam A, et al. Cyprinid herpesvirus-2 (CyHV-2): a comprehensive review [J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2020(13): 796-821.
[5] 张奇亚. 淡水生态系统中几种大DNA病毒研究概述 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2020, 44(5): 961-975. doi: 10.7541/2020.112 Zhang Q Y. An overview on several large DNA viruses in freshwater ecosystems [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2020, 44(5): 961-975. doi: 10.7541/2020.112
[6] Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans [J]. Plant Cell, 1990, 2(4): 279-289. doi: 10.2307/3869076
[7] Fire A. RNA-triggered gene silencing [J]. Trends in Genetics, 1999, 15(9): 358-363. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01818-1
[8] 宋华丽, 孙效迎, 孔祥会, 等. RNA干扰技术在水产动物抗病毒和抗寄生虫研究中的应用研究进展 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(2): 193-205. Song H L, Sun X Y, Kong X H, et al. Application of RNA interference technology in antiviral and antiparasitic research of aquatic animals [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(2): 193-205.
[9] 黄桂菊, 喻达辉, 柳明, 等. 石斑鱼神经坏死病毒RNA干扰的转染条件优化与效果分析 [J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2011, 32(2): 93-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-411X.2011.02.022 Huang G J, Yu D H, Liu M, et al. Preliminary study on RNA interference against red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus-optimization of transfection condition and comparison of interference effect based on FHM cell [J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2011, 32(2): 93-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-411X.2011.02.022
[10] 魏钰娟, 潘晓艺, 蔺凌云, 等. 异育银鲫(Carassius auratus gibelio)脊髓组织细胞系的建立及对CyHV-2的敏感性 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(5): 1232-1238. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200300071 Wei Y J, Pan X Y, Lin L Y, et al. Establishment of spinal cord cell line of Carassius auratus gibelio and its sensitivity to CyHV-2 [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(5): 1232-1238. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200300071
[11] Wang C, Li N, Liu X, et al. A novel endogenous human CaMKII inhibitory protein suppresses tumor growth by inducing cell cycle arrest via p27 stabilization [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(17): 11565-11574. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800436200
[12] Reed L J, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints [J]. American Journal of Epidemiology, 1938, 27(3): 493-497. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408
[13] 陈芸, 朱作言. RNA干扰在抗病毒研究中的应用 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2006, 30(3): 356-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.03.018 Chen Y, Zhu Z Y. Application of RNA interference (RNAi) in virus resistance [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2006, 30(3): 356-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2006.03.018
[14] 陈芸. 用RNA干扰(RNAi)抗草鱼出血病病毒的初步研究 [D]. 武汉: 中国科学院水生生物研究所, 2005: 106. Chen Y. Study of disease resistant on grass carp reovirus by RNA interference (RNAi) [D]. Wuhan: Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005: 106.
[15] 马杰. RNA基因干扰技术抑制草鱼呼肠孤病毒复制的研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2013: 94-95. Ma J. Study on the inhibition of replication of grass carp reovirus by RNA interference [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013: 94-95.
[16] Wu Y, Lü L, Yang L S, et al. Inhibition of white spot syndrome virus in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp by sequence-specific siRNA [J]. Aquaculture, 2007, 271(1-4): 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.06.029
[17] Fouad A M, Soliman H, Abdallah E S H, et al. In-vitro inhibition of spring viremia of carp virus replication by RNA interference targeting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene [J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2018(263): 14-19.
[18] Zenke K, Nam Y K, Kim K H. Development of siRNA expression vector utilizing rock bream β-actin promoter: a potential therapeutic tool against viral infection in fish [J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2010, 85(3): 679-690. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2177-3
[19] 牟维豪, 周燕, 耿毅, 等. RNA干扰对大鲵蛙病毒主要功能基因表达及其增殖的影响 [J]. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(4): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.04.010 Mou W H, Zhou Y, Geng Y, et al. Effect on main functional genes expression and replication of Chinese giant Salamander ranavirus (CGSRV) by RNA interference [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2017, 13(4): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.04.010
[20] van Beurden S J, Bossers A, Voorbergen-Laarman M H A, et al. Complete genome sequence and taxonomic position of anguillid herpesvirus 1 [J]. Journal of General Virology, 2010(91): 880-887.
[21] Afonso C L, Tulman E R, Delhon G, et al. Genome of crocodilepox virus [J]. Journal of Virology, 2006(80): 4978-4991.
[22] Boutier M, Gao Y, Vancsok C, et al. Identification of an essential virulence gene of cyprinid herpesvirus 3 [J]. Antiviral Research, 2017(145): 60-69.
[23] Michel B, Leroy B, Stalin Raj V, et al. The genome of cyprinid herpesvirus 3 encodes 40 proteins incorporated in mature virions [J]. Journal of General Virology, 2010(91): 452-462.
[24] Gao W, Wen H, Wang H, et al. Identification of structure proteins of cyprinid herpesvirus 2 [J]. Aquaculture, 2020(523): 735184.
[25] Tang R, Lu L, Wang B, et al. Identification of the immediate-early genes of cyprinid herpesvirus 2 [J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(9): 994. doi: 10.3390/v12090994
[26] Tseng Y C, Mozumdar S, Huang L. Lipid-based systemic delivery of siRNA [J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2009, 61(9): 721-731. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.03.003
[27] 杨光, 曹国军, 李洁, 等. siRNA抑制SARS冠状病毒感染Vero E6细胞 [J]. 医学分子生物学杂志, 2004, 1(5): 270-273. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-8009.2004.05.003 Yang G, Cao G J, Li J, et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV infection in Vero-E6 cells by siRNAs [J]. Journal of Medical Molecular Biology, 2004, 1(5): 270-273. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-8009.2004.05.003
[28] 李兵. RNA干扰抑制草鱼呼肠孤病毒复制的细胞模型 [D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2009: 26-29. Li B. Cellular model for inhibition of grass carp reovirus replication mediated by RNA interference [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2009: 26-29.



 下载:
下载: