NITROGEN EXCHANGE FLUX OF SEDIMENT-WATER INTERFACE IN LITOPENAEUS VANNAMEI SALT ALKALI POND
-
摘要:
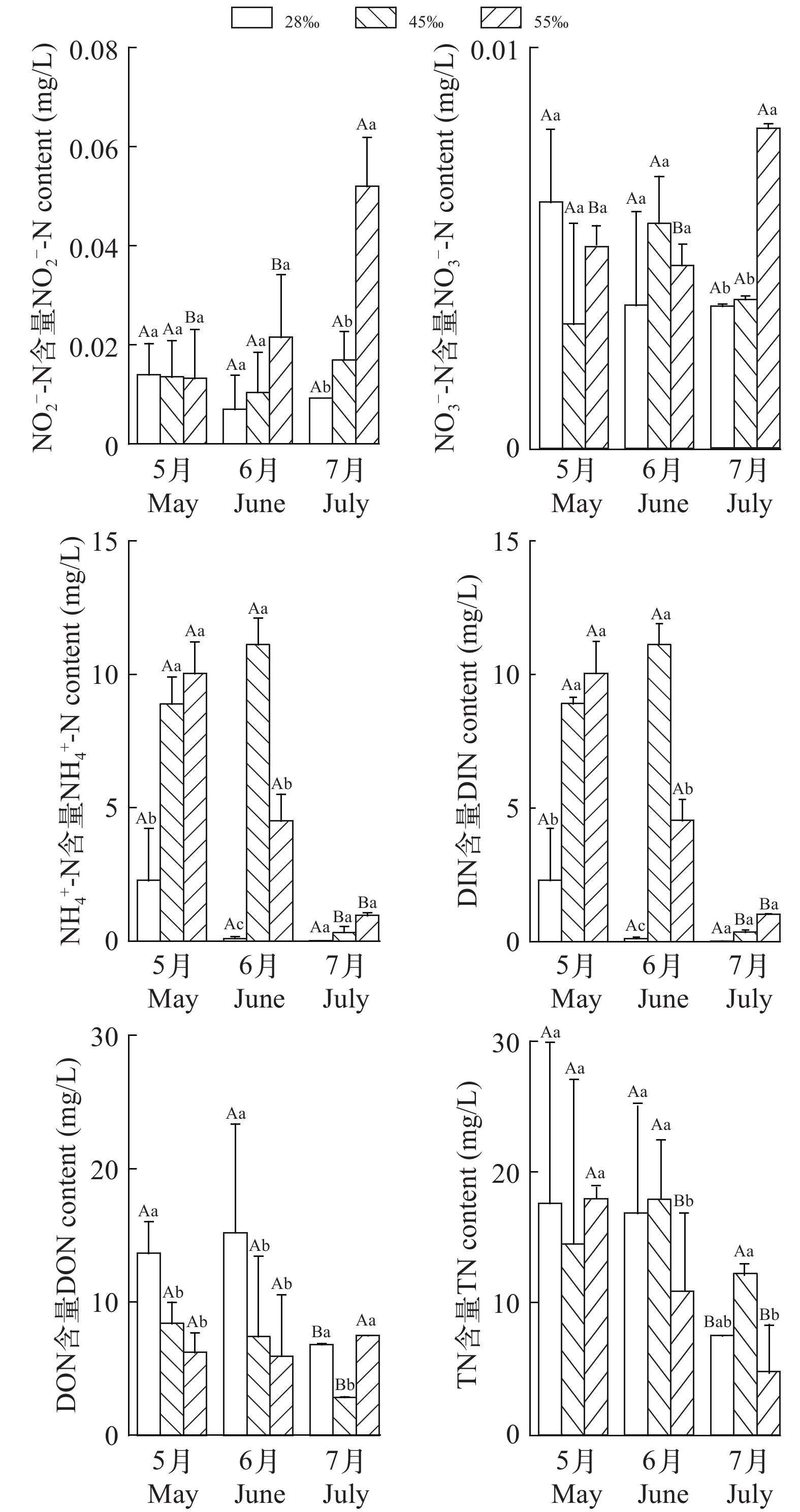
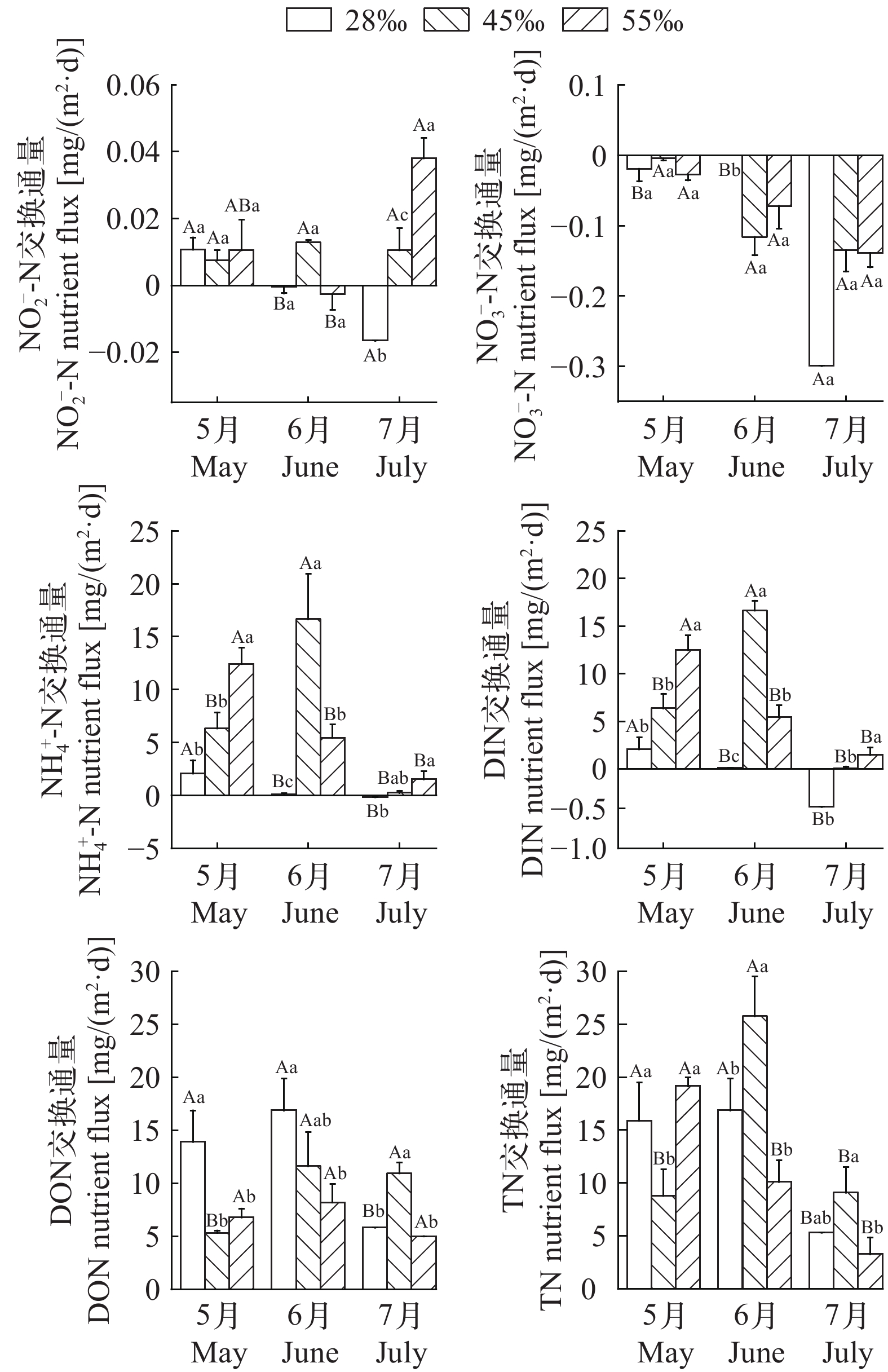
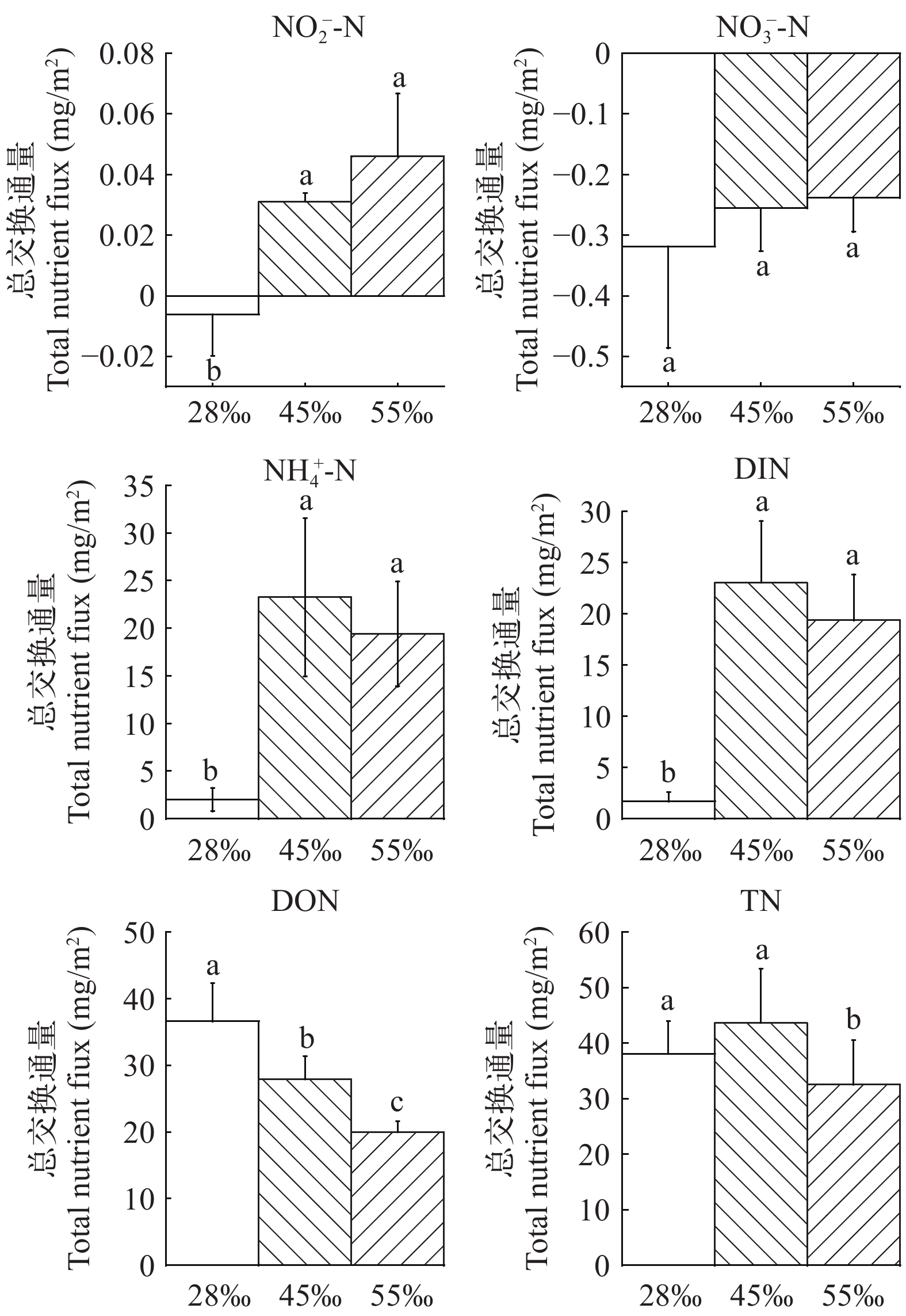
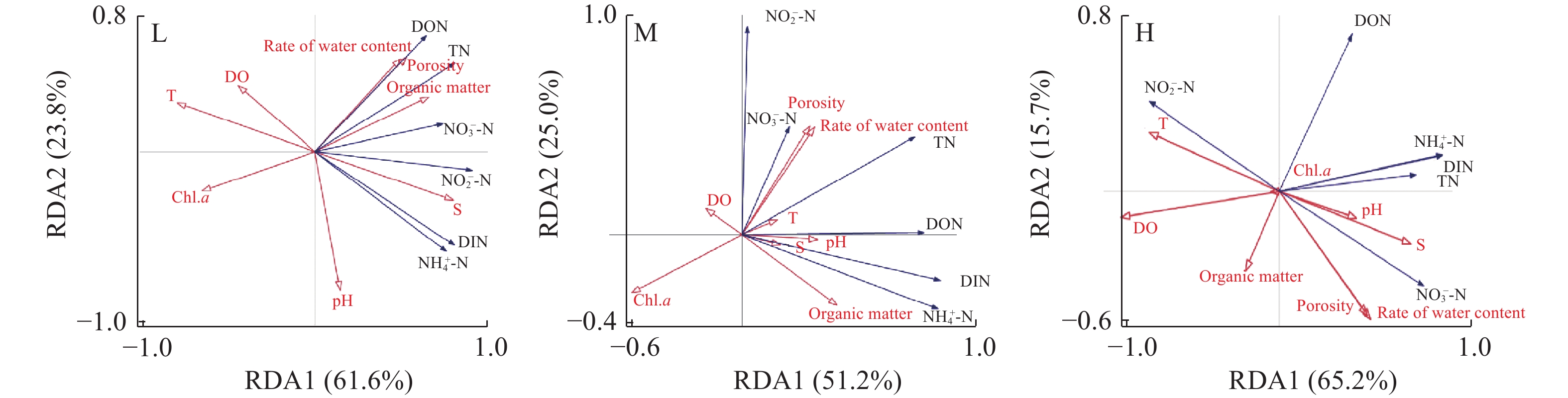
为探究凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)盐碱水养殖池塘沉积物-水界面中氮元素的转化规律, 于2019年5—7月测定了山东省滨州市3个不同盐度(28、45和55)的池塘上覆水和沉积物间隙水中各种形态氮的含量。利用Fick第一定律估算了池塘沉积物-水界面氮元素交换通量, 分析了环境因素与交换通量的相关性。结果表明: (1)总体来讲, DIN、DON、TN由沉积物向水体扩散, 即沉积物为DIN、DON和TN的源; ${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N由水体向沉积物扩散, 沉积物为$ {\rm{NO}}^-_3$-N的汇。在养殖期间, 盐度28、45和55组, DIN总交换通量分别为 1.69、23.07和19.36 mg/m2, DON总交换通量分别为36.60、27.90和19.98 mg/m2, TN总交换通量分别为38.09、43.66和32.56 mg/m2。(2)从季节变化来看, DIN、DON、TN在养殖初期(5月)的交换通量显著高于养殖末期(7月); 从盐度组来看, 在5月, 盐度28、45和55组, DIN平均交换通量分别为2.08、6.37和12.47 mg/(m2·d), 7月分别为–0.48、0.06和1.47 mg/(m2·d), 盐度55组显著大于其他两组(P<0.05); DON交换通量5月分别为13.91、5.32和6.79 mg/(m2·d), 盐度28组显著大于其他两组(P<0.05), 7月分别为5.82、10.94和5 mg/(m2·d), 盐度45组显著大于其他两组(P<0.05); 5月TN平均交换通量分别为15.9、8.79和19.16 mg/(m2·d), 盐度45组显著小于其他两组(P<0.05), 7月分别为5.31、9.1和3.28 mg/(m2·d), 盐度45组显著大于盐度55组(P<0.05)。(3)冗余分析结果显示, 盐度与${\rm{NO}}^-_2 $-N、${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N、${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N交换通量显著正相关; 有机质与${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N、TN通量显著正相关; 温度与${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N交换通量显著负相关; 含水率、孔隙度与${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N、DON交换通量显著正相关。综上所述, 沉积物是氮的潜在污染源, 此污染潜力在养殖末期显著小于养殖初期; 高盐度组有利于释放DIN, 中低盐度组有利于释放DON。研究结果将有助于认识盐碱水养殖池塘的氮交换通量, 为该种养殖模式的科学管理提供数据支撑。
Abstract:Coastal saline-alkali land aquaculture is increasingly rising, with the nutrient exchange at the sediment-water interface playing an important role in the ecosystem. It serves as an indicator of endogenous pollution levels in pond sediments. In order to explore the nitrogen transformation dynamics at the sediment-water interface in Litopenaeus vannamei culture ponds. Measurements were taken from May to July 2019, analyzing various nitrogen forms in overlying water and sediment interstitial water across three ponds in Binzhou City, Shandong Province, with different salinity (28, 45, 55). Using Fick’s first law, nitrogen exchange fluxes at the sediment-water interface were estimated, and correlations between environmental factors and exchange fluxes were examined. The results show that, (1) Nitrogen forms, including DIN, DON, and TN, predominantly diffuse from sediment to water, indicating sediment as the source. Conversely, ${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N moves from water to sediment, with sediment acting as the sink. During the breeding period, total exchange fluxes of DIN were 1.69, 23.07, and 19.36 mg/m2, DON were 36.60, 27.90, and 19.98 mg/m2, and TN were 38.09, 43.66, and 32.56 mg/m2, respectively, for salinity levels of 28, 45, and 55. (2) Seasonally, exchange fluxes of DIN, DON, and TN were significantly higher in May compared to July. For instance, the average DIN exchange fluxes for salinity levels 28, 45, and 55 were 2.08, 6.37, and 12.47 mg/(m2·d) in May respectively, decreasing to –0.48, 0.06, and 1.47 mg/(m2·d) in July respectively. Notably, the DIN exchange flux in salinity 55 group was significantly higher than that in the other two groups (P<0.05). In May, the DON exchange fluxes were 13.91, 5.32, and 6.79 mg/(m2·d), respectively. Salinity 28 group exhibited significantly higher values compared to the other two groups (P<0.05). Conversely, in July, the fluxes were 5.82, 10.94, and 5 mg/(m2·d), respectively, with the salinity 45 group significantly surpassing the others (P<0.05). Additionally, in May, the average TN exchange fluxes were 15.9, 8.79, and 19.16 mg/(m2·d) respectively. Significantly, the salinity 45 group exhibited lower fluxes than that in the other two groups (P<0.05). However, in July, the fluxes were 5.31, 9.1, and 3.28 mg/(m2·d) respectively, with the salinity 45 group significantly surpassing the salinity 55 group (P<0.05). (3) Redundancy analysis showed positively correlations between salinity and exchange fluxes of ${\rm{NO}}^-_2 $-N, ${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N, and ${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N. Organic matter exhibited positive correlations with ${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N and TN fluxes. There was a significant negative correlation between temperature and ${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $-N exchange flux, moreover, water content and porosity demonstrated positive correlations with ${\rm{NO}}^-_3 $-N and DON exchange fluxes. In conclusion, sediments act as potential sources of nitrogen, with pollution potential significantly reduced towards the end of aquaculture compared to the early stage. The salinity 55 group facilitates DIN release, while the salinity 28 and 45 groups facilitates promote DON release. The results enhance understanding of nitrogen exchange fluxes in large surface aquaculture ponds and provide valuable data to support the scientific management of this aquaculture model.
-
Keywords:
- Salt alkali pond /
- Sediment-water interface /
- Nitrogen /
- Litopenaeus vannamei
-
-
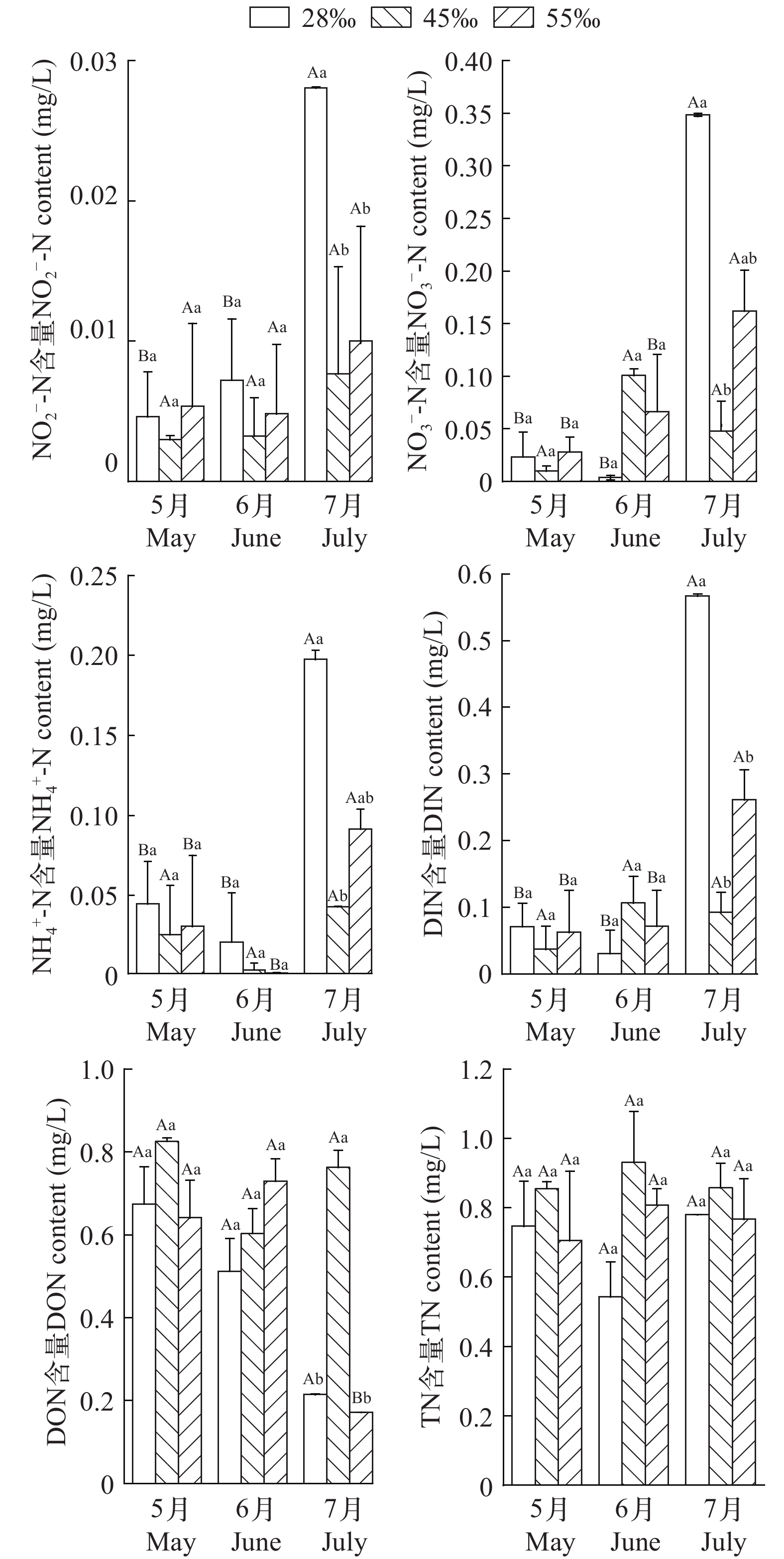
图 2 池塘上覆水中不同形态氮的含量
不同大写字母表示月份之间差异显著, 不同小写字母表示盐度组之间差异显著(P<0.05); 下同
Figure 2. The concentration of nutrient in the overlying water of pond
Different capital letters indicate significant differences in months, and different lower case letters indicate significant differences in salinity groups (P<0.05). The same applies below
表 1 养殖期间对虾池塘水质参数
Table 1 Water quality parameters of shrimp ponds during breeding period
时间
Time处理组
Group盐度
Salinity (‰)水温
Temperature (℃)溶解氧
Dissloved oxygen (mg/L)pH 叶绿素a
Chl.a (µg/L)5月May 盐度28组Salinity 28 group 33.30±0.28Ac 23.70±0.64Bb 7.66±0.17Aa 8.92±0.35Aa 31.65±1.03Ba 盐度45组Salinity 45 group 43.33±3.31Ab 22.13±0.42Bc 7.65±0.68Aa 8.96±0.21Aa 22.46±4.44Ba 盐度55组Salinity 55 group 59.88±0.37Aa 25.18±0.22Ba 7.23±0.25Ab 8.90±0.13Aa 28.51±2Ba 6月June 盐度28组Salinity 28 group 20.77±0.30Bc 25.28±0.04Ab 8.06±0.41Aa 8.69±0.11Aa 29.49±3.42Bb 盐度45组Salinity 45 group 44.84±0.09Ab 25.44±0.04Aa 6.66±0.52Ab 8.71±0.06Aa 23.03±5.75Bb 盐度55组Salinity 55 group 58.74±0.10Aa 25.24±0.01Bb 7.71±0.59Aa 8.84±0Aa 41.02±2.27Aa 7月July 盐度28组Salinity 28 group 29.90±1.14Ac 26.87±0.27Ab 8.57±0.75Aa 8.76±0.97Aa 44.27±8.9Aa 盐度45组Salinity 45 group 44.74±5.07Ab 25.64±0.36Ac 6.53±0.63Ab 8.53±0.10Ab 54.18±11.02Aa 盐度55组Salinity 55 group 49.07±0.17Ba 29.98±0.26Aa 8.90±0.55Aa 8.48±0.03Ab 26.78±2.86Bb 注: 不同大写字母表示月份之间差异显著, 不同小写字母表示盐度组之间差异显著(P<0.05); 下同Note: Different capital letters indicate significant differences in months, and different lower case letters indicate significant differences in salinity groups (P<0.05). The same applies below 表 2 养殖期间对虾池塘沉积物的理化性质
Table 2 Sediment physicochemical properties of shrimp ponds during breeding period
时间Time 处理组Group 含水率Rate of water content (%) 孔隙度Porosity 有机质Organic matter (%) 5月May 盐度28组Low salt group 35.46±2ab 0.57±0.13a 3.67±0.49a 盐度45组Medium salt group 25.59±2b 0.46±0.04a 2.82±0.3b 盐度55组High salt group 38.8±2.93a 0.61±0.03a 4.02±0.7a 6月June 盐度28组Low salt group 35.78±4a 0.58±0.09a 2.84±0.3a 盐度45组Medium salt group 29.97±4.5a 0.57±0.13a 3.45±0.61a 盐度55组High salt group 32.46±0.3a 0.55±0a 4.24±0.2a 7月July 盐度28组Low salt group 29.94±1a 0.52±0a 2.57±0.21a 盐度45组Medium salt group 33.47±5a 0.56±0.05a 2.58±0.31a 盐度55组High salt group 32.92±7.88a 0.54±0.09a 3.41±0.3a -
[1] 余云军, 于会国. 世界对虾养殖业的发展现状与发展趋势 [J]. 世界农业, 2007(5): 44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4433.2007.05.014 Yu Y J, Yu H G. Development status and trend of prawn farming industry in the world [J]. World Agriculture, 2007(5): 44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4433.2007.05.014
[2] 王丹, 吴反修. 《中国渔业统计年鉴》编辑委员会 [M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2023: 22-24. Wang D, Wu F X. chief editor. Editorial Committee of China Fishery Statistical Yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2023: 22-24.
[3] Kim S H, Lee J S, Kim K T, et al. Aquaculture farming effect on benthic respiration and nutrient flux in semi-enclosed coastal waters of Korea [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 554. doi: 10.3390/jmse9050554
[4] 李晓, 王晓璐, 王颖, 等. 盐度对养殖凡纳滨对虾肌肉营养成分的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 130-137. Li X, Wang X L, Wang Y, et al. Effects of different salinities on nutritional composition in muscle of Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 130-137.
[5] 刘振鲁, 高兆明. 陆源盐碱地池塘养殖南美白对虾高产试验 [J]. 渔业致富指南, 2021(14): 27-29. Liu Z L, Gao Z M. Experiment on high yield of Penaeus vannamei cultured in saline-alkali pond in terrigenous area [J]. Fishery Guide to Be Rich, 2021(14): 27-29.
[6] Selvin P S R R. Shrimp disease management for sustainable aquaculture: innovations from nanotechnology and biotechnology [J]. Aquaculture International, 2021(1): 30.
[7] Rakhfid A, Mauga U. Growth and survival rate vannamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in various doses of fertilizer and density [J]. Akuatikisle:Jurnal Akuakultur,Pesisir Dan Pulau-Pulau Kecil, 2018, 2(2): 53-60. doi: 10.29239/j.akuatikisle.2.2.53-59
[8] Sajana T K, Ghangrekar M M, Mitra A. Application of sediment microbial fuel cell for in situ reclamation of aquaculture pond water quality [J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2013(57): 101-107. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaeng.2013.09.002
[9] 刘振鲁, 高兆明, 赵玉静, 等. 探索滨州对虾产业绿色高效发展的路径 [J]. 中国水产, 2022(6): 69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6681.2022.6.zhongguosc202206024 Liu Z L, Gao Z M, Zhao Y J, et al. Explore the path of green and efficient development of Binzhou shrimp industry [J]. China Fisheries, 2022(6): 69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6681.2022.6.zhongguosc202206024
[10] 黄艳青, 杨絮, 王怡菊, 等. 西北硫酸盐型盐碱水与低盐度海水养殖凡纳滨对虾营养成分及品质评价 [J]. 渔业信息与战略, 2023, 38(1): 60-66. Huang Y Q, Yang X, Wang Y J, et al. Analysis and quality evaluation of nutrient components in muscle of Litopenaeus vannamei of two saline-alkali aquaculture and mariculture [J]. Fishery Information & Strategy, 2023, 38(1): 60-66.
[11] Saraswathy R, Muralidhar M, Sanjoy D, et al. Changes in soil and water quality at sediment–water interface of Penaeus vannamei culture pond at varying salinities [J]. Aquaculture Research, 2019, 50(4):1096-1106.
[12] 熊莹槐, 王芳, 钟大森. 不同盐度下凡纳滨对虾扰动作用对沉积物-水界面营养盐通量的影响 [J]. 河北渔业, 2015(7): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2015.07.001 Xiong Y H, Wang F, Zhong D S. Impact of Litopenaeus vannamei bioturbation on benthic fluxes at the sediment-water interface in different salinities [J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2015(7): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2015.07.001
[13] 鲁耀鹏, 钱坤, 汪蕾, 等. 养殖盐度对凡纳滨对虾抗氧化酶及免疫相关酶活力的影响 [J]. 河北渔业, 2019(12): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2019.12.001 Lu Y P, Qian K, Wang L, et al. Effect of salinities on activities of antioxidant enzymes and immune-related enzymes of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2019(12): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2019.12.001
[14] 孙启元, 李家兵, 赖月婷, 等. 不同盐度对闽江河口沉积物硝化作用的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(4): 1313-1320. Sun Q Y, Li J B, Lai Y T, et al. Effects of different salinity levels on nitrification processes in sediments of Minjiang River Estuary, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(4): 1313-1320.
[15] Gardner W S, Seitzinger S P, Malczyk J M. The effects of sea salts on the forms of nitrogen released from estuarine and freshwater sediments: does ion pairing affect ammonium flux [J]? Estuaries, 1991, 14(2): 157-166. doi: 10.2307/1351689
[16] 李明爽. 发展盐碱水养殖 向盐碱水土要食物 [J]. 中国水产, 2023(11): 35-36. Li M S. Developing saline-alkali aquaculture and demanding food from saline-alkali soil [J]. China Fisheries, 2023(11): 35-36.
[17] 李峰. 巢湖十五里河沉积物氮磷污染特征及间隙水营养盐浓度模拟 [D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2012. Li F. Contamination characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments and simulation of its profile concentration in pore water from Shiwuli River in Chaohu Lake [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2012.
[18] 孙珊, 刘素美, 任景玲, 等. 桑沟湾养殖海域营养盐和沉积物-水界面扩散通量研究 [J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(6): 108-117. Sun S, Liu S M, Ren J L, et al. Distribution features of nutrients and flux across the sediment-water interface in the Sanggou Bay [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(6): 108-117.
[19] Mu D, Yuan D, Feng H, et al. Nutrient fluxes across sediment-water interface in Bohai Bay coastal zone, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(2): 705-714. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.056
[20] 左强, 吴训, 石建初, 等. 黄河三角洲滨海盐碱地可持续利用的水土资源约束与均衡配置策略 [J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(4): 169-179. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.07.028 Zuo Q, Wu X, Shi J C, et al. Constraints and coordinated allocation strategies of water and land resources for sustainable use of coastal saline-alkali land in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(4): 169-179. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.07.028
[21] 刘存歧, 王军霞, 张亚娟, 等. 盐碱地渗水盐度与钠钾比对凡纳滨对虾生长的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(6): 1337-1342. Liu C Q, Wang J X, Zhang Y J, et al. Effects of salinity and Na+/K+ in percolating water from saline-alkali soil on the growth of Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(6): 1337-1342.
[22] 刘慧玲, 陈荣, 王成桂, 等. 不同盐度条件下氨氮和亚硝酸盐对墨吉明对虾的急性毒性试验 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(1): 155-158. Liu H L, Chen R, Wang C G, et al. Acute toxicity test of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite for Fenneropenaeus merguiensis at different salinity levels [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(1): 155-158.
[23] 刘超毅, 何凌茜, 黄庄, 等. 模拟盐度脉冲耦合潮汐过程对闽江河口湿地土壤孔隙水中无机氮组分的影响 [J]. 湿地科学, 2023, 21(3): 483-492. Liu C Y, He L X, Huang Z, et al. Effects of simulated salinity pulse coupled tidal process on soil inorganic nitrogen components in Minjiang River estuarine wetland [J]. Wetland Science, 2023, 21(3): 483-492.
[24] 王东启, 陈振楼, 钱嫦萍, 等. 盐度对崇明东滩沉积物—水界面NH4+交换行为的影响 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2002, 21(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2002.03.002 Wang D Q, Chen Z L, Qian C P, et al. Effect of salinity on NH4+ exchange behavior at the sediment-water interface in East Chongming tidal flat [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2002, 21(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2002.03.002
[25] Liu M, Huang X H, Li C L, et al. Study on the uptake of dissolved nitrogen by Oocystis borgei in prawn (Litopenaeus vannamei) aquaculture ponds and establishment of uptake model [J]. Aquaculture International, 2020, 28(4): 1445-1458. doi: 10.1007/s10499-020-00534-z
[26] 胡利华, 施巍, 刘广绪, 等. 不同家系凡纳滨对虾对低盐度的适应能力及其适应机理 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2021, 45(2): 275-283. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.265 Hu L H, Shi W, Liu G X, et al. Mechanisms of salinity adaptability of Litopenaeus vannamei under different salinity conditions [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2021, 45(2): 275-283. doi: 10.7541/2021.2019.265
[27] 谢毅梁, 崔保山, 谢湉, 等. 2021年冬季珠江三角洲河网浮游动植物的分布和咸潮入侵的影响 [J]. 湿地科学, 2022, 20(5): 666-680. Xie Y L, Cui B S, Xie T, et al. Distribution of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the Pearl River Delta River network in winter of 2021 and effects of salt tide [J]. Wetland Science, 2022, 20(5): 666-680.
[28] Niu L, Luo X, Hu S, et al. Impact of anthropogenic forcing on the environmental controls of phytoplankton dynamics between 1974 and 2017 in the Pearl River Estuary, China [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020(116): 106484. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106484
[29] Weissman D, Ouyang T, Tully K L. Saltwater intrusion affects nitrogen, phosphorus and iron transformations under oxic and anoxic conditions: an incubation experiment [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2021, 154(3): 451-469. doi: 10.1007/s10533-021-00796-6
[30] 刘培芳, 陈振楼, 刘杰. 盐度和pH对崇明东滩沉积物中${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $释放的影响研究 [J]. 上海环境科学, 2002, 21(5): 271-273. Liu P F, Chen Z L, Liu J. Study on effects of salinity and pH on ${\rm{NH}}^+_4 $ release in east Chongming tidal flat sediment [J]. Shanghai Environmental Sciences, 2002, 21(5): 271-273.
[31] 常杰, 田相利, 董双林, 等. 对虾、青蛤和江蓠混养系统氮磷收支的实验研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 36(S1): 33-39. Chang J, Tian X L, Dong S L, et al. An experimental study on nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in polyculture of shrimp, bivalve and seaweed [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(S1): 33-39.
[32] 董佳, 田相利, 董双林, 等. 三疣梭子蟹和凡纳滨对虾混养系统的氮磷收支的研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(12): 16-24. Dong J, Tian X L, Dong S L, et al. Study on nitrogen and phosphorus budget in polyculture systems of Litopenaeus vannamei and Portunus trituberculatus [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(12): 16-24.
[33] Chang W Y B. Integrated lake farming for fish and environmental management in large shallow Chinese Lakes: a review [J]. Aquaculture Research, 2010, 20(4): 441-452.
[34] 雷兆霖, 党子乔, 张东升, 等. 3种水质调控方式下参池沉积物—水界面N、P通量的研究 [J]. 水产科学, 2021, 40(3): 354-360. Lei Z L, Dang Z Q, Zhang D S, et al. N and P fluxes in sediment-water interface of sea cucumber ponds exposed to three water quality control methods [J]. Fisheries Science, 2021, 40(3): 354-360.
[35] 邓延慧, 丁润楠. 湖泊沉积物氮矿化及其影响因素研究进展 [J]. 环境生态学, 2020, 2(11): 91-95. Deng Y H, Ding R N. Research on nitrogen mineralization of lake sediments and its influencing factors [J]. Environmental Ecology, 2020, 2(11): 91-95.
[36] 闫兴成, 王明玥, 许晓光, 等. 富营养化湖泊沉积物有机质矿化过程中碳、氮、磷的迁移特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(2): 306-313. doi: 10.18307/2018.0203 Yan X C, Wang M Y, Xu X G, et al. Migration of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus during organic matter mineralization in eutrophic lake sediments [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(2): 306-313. doi: 10.18307/2018.0203
[37] 高美云. 不同环境因子对池塘生物脱氮作用及脱氮菌菌群的影响 [D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018. Gao M Y. Effects of different environmental factors on biological nitrogen removal and bacteria population in pond [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018.
[38] 张翰林, 赵峥, 陆贻通, 等. 稻田土壤溶液中溶解性有机氮、碳的空间分布及其微生物降解特性 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(10): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.10.002 Zhang H L, Zhao Z, Lu Y T, et al. Spatial distribution and microbial degradation characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in paddy soil solution [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2014, 36(10): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.10.002
[39] 雷沛, 张洪, 王超, 等. 沉积物水界面污染物迁移扩散的研究进展 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(6): 1489-1508. doi: 10.18307/2018.0602 Lei P, Zhang H, Wang C, et al. Migration and diffusion for pollutants across the sediment-water interface in lakes: a review [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(6): 1489-1508. doi: 10.18307/2018.0602
[40] 袁轶君, 何鹏程, 刘娜娜, 等. 温度与扰动对鄱阳湖沉积物氮释放的影响 [J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(5): 495-500. Yuan Y J, He P C, Liu N N, et al. Effects of temperature and disturbance on nitrogen release from sediment of Poyang Lake [J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(5): 495-500.
[41] 高天赐, 高学鲁, 邢前国, 等. 秋季牟平海洋牧场及其邻近海域沉积物-水界面营养盐交换通量 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(3): 387-392. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200310 Gao T C, Gao X L, Xing Q G, et al. Exchange fluxes of nutrients across sediment-water interface in the Muping Marine Ranch and its adjacent waters in autumn [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(3): 387-392. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20200310
[42] 钱思萌. 渤海中部低氧现象的数值模拟研究 [D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. Qian S M. Simulation on formation of summer low oxygen zone in the Bohai Sea [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018.
[43] 张华, 李艳芳, 唐诚, 等. 渤海底层低氧区的空间特征与形成机制 [J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(14): 1612-1620. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00915 Zhang H, Li Y F, Tang C, et al. Spatial characteristics and formation mechanisms of bottom hypoxia zone in the Bohai Sea during summer [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(14): 1612-1620. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00915
[44] 江涛, 徐勇, 刘传霞, 等. 渤海中部海域低氧区的发生记录 [J]. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(4): 1-6. Jiang T, Xu Y, Liu C X, et al. Report on the occurrence of hypoxia in the central Bohai Sea [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(4): 1-6.
[45] 黄廷林, 刘飞, 史建超. 水源水库沉积物间隙水营养盐分布特征及扩散通量 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(8): 4357-4363. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201503228 Huang T L, Liu F, Shi J C. Distribution features and diffusion fluxes of nutrient in interstitial water of a source water reservoir [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(8): 4357-4363. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201503228



 下载:
下载: