SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF ZOOPLANKTON IN THE MAIN STEM OF THE MIDDLE YANGTZE RIVER
-
摘要: 2016年10月对长江中游干流5个江段(宜昌、荆州、岳阳、武汉、湖口)开展了以轮虫、桡足类、枝角类为代表的浮游动物调查, 共检测到浮游动物23种, 隶属13科14属, 其中轮虫16种, 桡足类4种, 枝角类3种。各调查江段比较显示, 湖口江段浮游动物物种数最多, 为9种, 岳阳江段浮游动物物种数最少, 为5种, 宜昌、荆州、武汉江段物种数接近。武汉江段浮游动物密度最高, 为(10.94±5.81) ind./L, 湖口江段次之, 宜昌、岳阳和荆州段密度接近。轮虫为优势类群, 密度为(3.41±0.21) ind./L, 其中曲腿龟甲轮虫、尖尾疣毛轮虫和螺形龟甲轮虫为优势种。桡足类密度为(0.75±0.07) ind./L, 多为无节幼体。枝角类密度最低。武汉江段浮游动物生物量最高, 湖口江段次之, 其他3个江段相当。与长江干流其他江段调查结果相比, 此次调查的各江段浮游动物群落呈现较低的物种多样性。Spearman相关系数分析显示, 浮游动物生物量和多样性均与叶绿素a浓度呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。Abstract: To better understand zooplankton distribution and its relationship with the physical-chemical factors in middle Yangtze River, we collected 20 zooplankton samples from segments at Yichang, Jingzhou, Yueyang, Wuhan and Hukou in October, 2016. A total of 23 species that belong to 13 families and 14 genera were identified, among which 16 species belong to Rotifera, 4 to Copepoda and 3 to Cladocera. Among the five segments, the highest number of zooplankton species was detected at Hukou (9 species), while the lowest was at Yueyang (5 species). The average density at Wuhan (10.94±5.81) ind./L was higher than that at Hukou and the other segments. Rotifers (3.41±0.21) ind./L were dominant in the zooplanktonic community, and Keratella valga, Synchacta atylata and Keratella cochlearis were the dominant species. The average density of copepods (mainly nauplius) was (0.75±0.07) ind./L. Cladocera had the lowest average density. Similarly, the zooplankton biomass at Wuhan was also higher than that at Hukou and the other three segments. Comparing with studies at other segments of Yangtze River, we detected lower zooplankton diversity in our investigation. Spearman correlations indicated that the biomass and diversity of zooplankton were significantly and positively correlated (P<0.05) to chlorophyll a.
-
Keywords:
- Main stem of middle Yangtze River /
- Zooplankton /
- Diversity /
- Biomass
-
浮游动物是水体的重要生态类群。过去对长江水系浮游动物的调查集中在湖泊、水库、支流和河口区[1—5], 而对长江干流仅有零星报道[6—8]。我们于2016年10月对长江中游干流浮游动物开展了调查, 内容包括种类组成、现存量及其与环境因子的关系。本文报道该调查结果, 以便为长江生态研究提供基础资料。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样点设置与采样方法
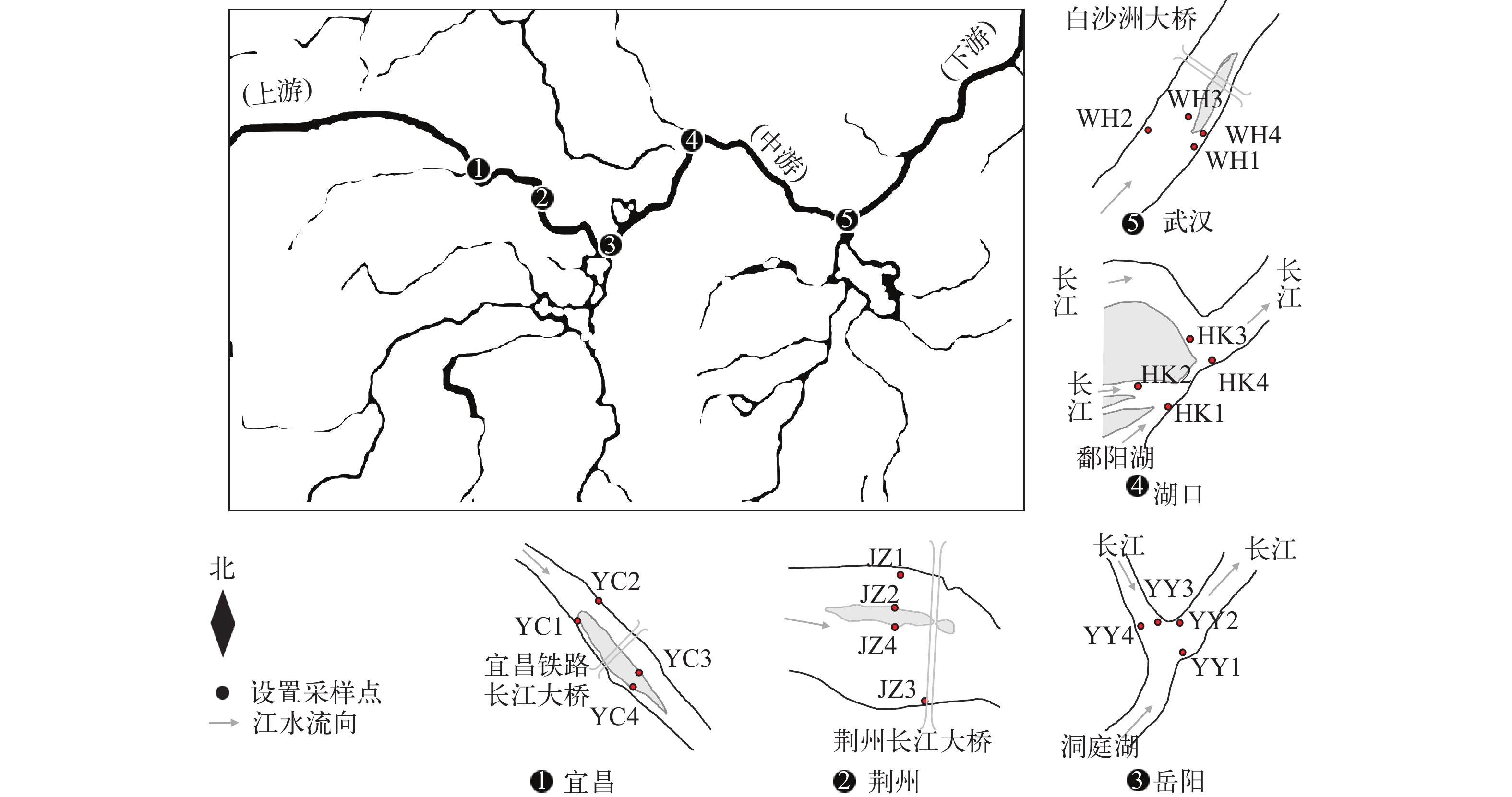
本研究于2016年10月在长江中游宜昌(YC)、荆州(JZ)、岳阳(YY)、武汉(WH)、湖口(HK)五个干流江段开展了浮游动物调查, 每个江段布设4个采样点(图 1)。现场记录各样点经纬度和河道底质类型, 透明度、盐度、水深和流速分别采用常规的透明度盘、盐度计、便携式超声波测深仪(SM-5)、多普勒流速仪(SonTek River Surveyor M9)测定, 水温、电导率、pH、溶解氧使用YSI-Pro Plus便携式多参数水质测定仪原位测定。
浮游动物样品采集使用5 L的采水器分别取上、中、下层水各10 L, 混匀后取20 L水样用25号浮游生物网(网孔径64 μm)过滤, 滤缩液加入鲁哥试液(终浓度为1%)和福尔马林(终浓度为4%)固定, 作为浮游动物定量样品。
1.2 样品处理与分析
固定后的水样静置沉淀48h后浓缩至5 mL, 取1 mL浓缩液注入1 mL浮游动物计数框中, 在10×10—10×20倍光学显微镜下计数。每个样品计数2次, 记录平均值。参照常规方法计算生物量[9]。浮游动物鉴定依据《淡水浮游生物研究方法》和《淡水浮游生物图谱》等资料[9, 10]。由于无节幼体难以鉴定到具体的种, 本文将观察到的桡足类无节幼体视为一个类群进行统计。
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
2. 结果
2.1 浮游动物群落组成与现存量
本次调查共鉴定浮游动物23种(表 1), 其中轮虫16种, 桡足类4种, 枝角类3种。各江段浮游动物丰富度均不高(表 2), 其中岳阳江段最少(5种)。5个江段均有曲腿龟甲轮虫、螺形龟甲轮虫的分布, 表明曲腿龟甲轮虫和螺形龟甲轮虫可能是长江中游干流浮游动物广布种。另外, 剑水蚤、爪趾腔轮虫、吻状异尖额溞、大肚须足轮虫和弯角腔轮虫仅在宜昌江段有分布。方形臂尾轮虫、角突臂尾轮虫仅在荆州江段有分布。裂足臂尾轮虫、小巨头轮虫仅在岳阳江段有分布。萼花臂尾轮虫、巨环旋轮虫和囊形腔轮虫仅在武汉江段有分布。广布中剑水蚤、哲水蚤、角壳网纹溞和跃进三肢轮虫仅在湖口江段有分布。
表 1 长江中游干流浮游动物组成调查结果Table 1. Species composition of zooplankton in the main stem of middle Yangtze River纲名Class name 种名Species name 桡足类Copepoda 无节幼体Nauplius 剑水蚤(属)Cyclops sp. 广布中剑水蚤Microcyclops leuckarti 哲水蚤(属)Calanus sp. 枝角类Cladocera 象鼻溞(属)Bosmina sp. 角壳网纹溞Ceriodaphnia cornigera 吻状异尖额溞Disparalona rostrata 轮虫 Rotifera 螺形龟甲轮虫Keratella cochlearis 曲腿龟甲轮虫Keratella valga 大肚须足轮虫Euchlanis dilatata 巨环旋轮虫Philodina megalotrocha 囊形腔轮虫Lecane (Monostyla) bulla 尖尾疣毛轮虫Synchacta atylata 长圆疣毛轮虫Synchaeta oblonga 方形臂尾轮虫Brachionus quadridentatus 角突臂尾轮虫Brachionus angularia 裂足臂尾轮虫Brachionus diversicornis 跃进三肢轮虫Filinia longiseta passa 小巨头轮虫Cephalodella exigna 晶囊轮(属)Asplanchna sp. 爪趾腔轮虫Lecane unguitata 弯角腔轮虫Lecane curvicornis 萼花臂尾轮虫Brachionus calyciflorus 表 2 长江中游干流浮游动物物种数、密度和生物量调查结果Table 2. Species name, density and biomass of zooplankton in the main stem of middle Yangtze River江段/类群
River segment/
Taxa物种数
Species
number密度
Density
(ind./L)生物量
Biomass
(mg/m3)宜昌YC 8 2.19±2.13 8.50±7.17 荆州JZ 7 2.19±1.20 9.06±14.14 岳阳YY 5 2.19±2.13 3.19±3.59 武汉WH 8 10.94±5.81 21.25±11.52 湖口HK 9 4.38±0.72 15.31±9.32 轮虫Rotifera 16 3.41±0.21 4.09±0.25 枝角类Cladocera 3 0.22±0.02 4.38±0.47 桡足类Copepoda 4 0.75±0.07 3.00±0.25 各调查江段浮游动物密度和生物量见表 2。浮游动物的平均密度为4.38 ind./L, 其中武汉江段密度最高, 湖口江段次之, 岳阳、宜昌和荆州段浮游动物密度接近。浮游动物平均生物量为11.46 mg/m3, 其中武汉江段生物量最高, 湖口江段次之, 宜昌和荆州江段生物量相近, 岳阳江段最低。
各类群浮游动物密度和生物量的分布见表 2。轮虫密度最高, 占77.9%。其中曲腿龟甲轮虫、尖尾疣毛轮虫和螺形龟甲轮虫的密度分别占20.0%、20.0%和13.6%, 为本次调查的优势种。桡足类(主要为无节幼体)和枝角类密度分别为17.1% 和0.05%。在生物量方面, 枝角类最高, 轮虫次之, 桡足类最低。
2.2 浮游动物分布与理化因子相关分析
分析各样点理化指标发现(表 3), 从上游至下游5个江段水温呈递减趋势, 溶解氧呈依次递增趋势, 各样点电导率和盐度相对稳定, pH在岳阳江段最高。溶解性有机碳总体呈先降低后增加的趋势, 宜昌段YY1样点(13.51 mg/m3)明显高于同一江段的其他样点。由于本次调查未能获取湖口江段溶解性有机碳数据, 该趋势有待进一步确认。硝氮、亚硝氮和氨氮3个指标中, 硝氮浓度最高且在各调查样点中相对稳定, 亚硝氮(岳阳YY1:0.13 mg/m3除外)总体呈增长趋势, 氨氮浓度在上下游各样点间分布无明显规律。溶解性反应磷总体呈先增加后降低趋势。
表 3 长江中游干流样点理化参数Table 3. Physical-chemical factors of sampling sites in the main stem of middle Yangtze River环境因子Environmental factor 宜昌YC 荆州JZ 岳阳YY 武汉WH 湖口HK 水温T (℃) 21.9±0.3 19.6±0.2 19.0±1.3 15.6±0.2 13.5±0.1 溶解氧DO (mg/m3) 7.90±0.11 8.86±0.08 8.51±0.07 9.30±0.13 9.48±0.04 电导率σ (µs/cm) 272.5±0.4 263.5±0.5 255.3±31.2 274.8±50.7 227.3±0.6 盐度S (ppt) 0.14±0.00 0.14±0.00 0.14±0.01 0.16±0.03 0.14±0.00 pH 6.57±0.11 6.76±0.08 7.05±0.11 6.77±0.05 6.97±0.06 水深D (m) 5.5±2.2 — 5.4±2.9 6.0±3.7 7.5±4.6 透明度SD (cm) 160±4 — 54±34 24±3 21±5 流速V (m/s) 0.23±0.12 0.14±0.08 0.75±0.81 0.24* — 硝氮 $ {\rm{NO}}_3^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
1.80±0.10 1.53±0.02 1.66±0.22 1.54±0.05 1.61±0.20 亚硝氮 $ {\rm{NO}}_2^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
0.00±0.00 0.02±0.01 0.04±0.06 0.05±0.01 0.06±0.02 氨氮 $ {\rm{NH}}_3^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
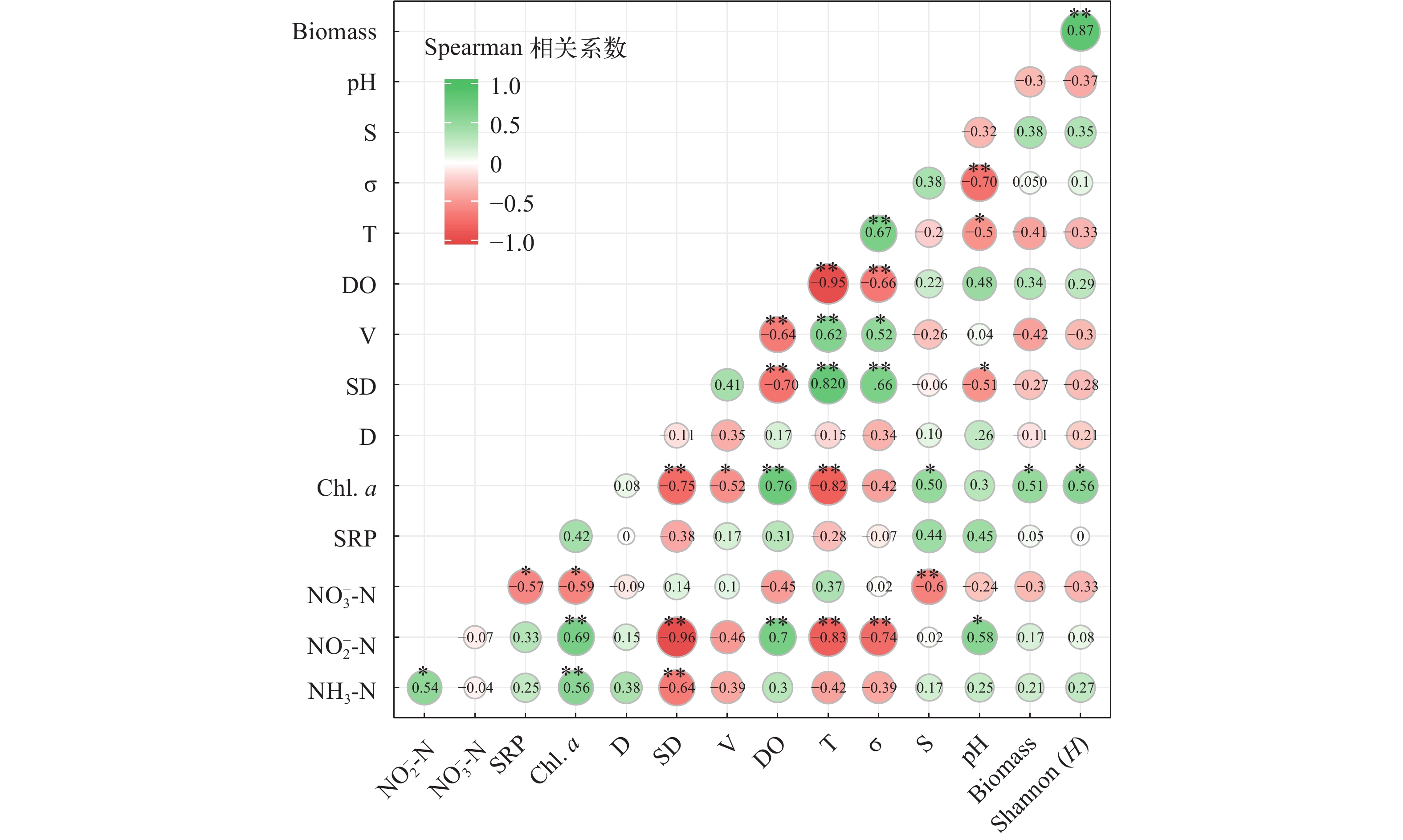
0.14±0.09 0.11±0.04 0.26±0.21 0.34±0.11 0.29±0.15 溶解性反应磷SRP (mg/m3) 0.03±0.00 0.09±0.02 0.08±0.02 0.08±0.02 0.06±0.01 叶绿素a Chl. a (mg/m3) 0.70±0.26 0.79±0.16 1.32±0.49 3.74±1.88 2.70±0.90 溶解性有机碳DOC (mg/m3) 8.63±3.29 4.11±0.60 3.22±0.65 6.90±0.82 — 注: —, 数据缺失; *, 一个样点数据Note: —, data missing; *, data from only one sampling site Spearman相关系数分析显示(图 2), 浮游生物多样性Shannon (H)和生物量与叶绿素a呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。硝氮、亚硝氮、氨氮、溶解氧以及水文环境因子透明度、流速、水温均与叶绿素a含量显著相关。此外, 各水文环境与营养盐指标间也存在显著相关性。
3. 讨论
本次调查的5个干流江段的浮游动物物种数、密度和生物量(表 4)均低于往年调查结果[8, 12]。此外, 本次调查中密度较低(不大于0.25 ind./L)的种类呈现环境异质性分布: 剑水蚤、爪趾腔轮虫等仅在宜昌江段发现, 方形臂尾轮虫、角突臂尾轮虫仅在荆州江段发现, 裂足臂尾轮虫、小巨头轮虫仅在岳阳江段发现, 萼花臂尾轮虫、巨环旋轮虫等仅在武汉江段发现, 广布中剑水蚤、哲水蚤等仅在湖口江段发现。这一结果表明各调查江段低丰度浮游动物群落之间存在较大差异。
表 4 长江中下游干流浮游动物历史数据对比Table 4. Comparison of the species number, density and biomass of zooplankton with previous investigations江段
River segment时间
Time物种数
Species number密度
Density (ind./L)生物量
Biomass (×102 mg/m3)数据来源
Data sources长江中游
Middle Yangtze River宜昌-城陵矶(8个江段) 2010 25—49 32.92—93.20 1.53—7.86 [12] 道人矶-杨林岩(3个江段) 2011—2012 81 — 0.09 [8] 昌口溪-熊家洲(9个江段) 2013—2015 34—96 66.25—509.44 0.23—11.36 [13] 宜昌-武汉(5个江段) 2016 a 23 4.38 0.01 本次调查 长江下游
Lower Yangtze River仪征-崇明(13个江段) 1988—1990 b 48—71 2.50—32.20 0.03—0.39 [14] 南京-海门(4个江段) 2004—2005 108 3.97—91.95a 0.31—4.03a [15] 青弋江-天然洲(3个江段) 2015 36—40 162.00—250.26 11.26—13.77 [16] 湖口-长江口(10个江段) 2016—2017 33—69 61.00—115.00 0.75—4.77 [17] 注: —, 数据缺失; a, 数据仅包括轮虫、枝角类、桡足类; b, 数据仅包括轮虫Note: —, data missing; a, data only includes rotifers, cladocerans and copepods; b, data only includes rotifers 本次调查结果显示长江中游宜昌至湖口江段浮游动物群落组成以轮虫为主, 这与长江其他江段的调查结果一致[13—17], 也与大多数河流浮游动物调查结果一致[18—20]。其中曲腿龟甲轮虫、螺形龟甲轮虫在长江中游5个江段均有分布, 且在长江下游芜湖段、江苏段均有分布[7, 16], 表明这两种轮虫是长江流域浮游动物广布种。然而, 与长江流域其他江段以及大多数河流的调查结果相比(表 4), 本次调查的5个干流江段浮游动物群落呈现较低的物种多样性。本次调查共发现轮虫、枝角类和桡足类浮游动物23种, 平均浮游动物密度为4.38 ind./L。长江江苏段2004—2005年发现轮虫、枝角类和桡足类共96种, 年浮游动物密度为47.96 ind./L[7]; 长江道人矶至杨林岩河河段2011—2012年分别检出轮虫、枝角类和桡足类三大类共63种[8]。研究表明流速大、含泥沙多的河流环境不利于浮游动物的生存。本次调查江段均为干流, 江水流速快且含沙量高, 因此浮游动物多样性极低很可能是因为它们本身及其饵料生物都不适应于急流和混浊的水环境[6]。
长江为大型流动水体, 流域面积广阔、环境复杂, 为探明浮游动物分布现状及其形成的原因, 我们分析发现叶绿素a是影响长江中游干流浮游动物多样性和生物量的最主要因素, 这与前人的研究结果一致[21]。研究表明浮游动物的分布与细菌及藻类等密切相关, 流速是影响流动水域叶绿素a含量的主要因素[22]。葛洲坝截流后水的流速减缓, 有利于细菌、藻类等的繁殖, 浮游动物的密度和多样性均显著增加[6]。这与本研究中浮游动物生物量和多样性与叶绿素a呈显著正相关而流动水域流速与叶绿素显著负相关的结果一致。此外, 营养、盐度和透明度等因子也与叶绿素a显著相关, 这些环境因子可能通过影响叶绿素a间接影响浮游动物, 这一结果与前人有关浮游生物与环境因子的相关性研究相吻合[2, 3]。
致谢:
感谢中国科学院水生生物研究所王洪铸研究员和冯伟松老师在样品采集、物种鉴定以及文章撰写过程中提供的指导和帮助。现场测定指标由王洪铸研究员学科组提供, 在此表示感谢。
-
表 1 长江中游干流浮游动物组成调查结果
Table 1 Species composition of zooplankton in the main stem of middle Yangtze River
纲名Class name 种名Species name 桡足类Copepoda 无节幼体Nauplius 剑水蚤(属)Cyclops sp. 广布中剑水蚤Microcyclops leuckarti 哲水蚤(属)Calanus sp. 枝角类Cladocera 象鼻溞(属)Bosmina sp. 角壳网纹溞Ceriodaphnia cornigera 吻状异尖额溞Disparalona rostrata 轮虫 Rotifera 螺形龟甲轮虫Keratella cochlearis 曲腿龟甲轮虫Keratella valga 大肚须足轮虫Euchlanis dilatata 巨环旋轮虫Philodina megalotrocha 囊形腔轮虫Lecane (Monostyla) bulla 尖尾疣毛轮虫Synchacta atylata 长圆疣毛轮虫Synchaeta oblonga 方形臂尾轮虫Brachionus quadridentatus 角突臂尾轮虫Brachionus angularia 裂足臂尾轮虫Brachionus diversicornis 跃进三肢轮虫Filinia longiseta passa 小巨头轮虫Cephalodella exigna 晶囊轮(属)Asplanchna sp. 爪趾腔轮虫Lecane unguitata 弯角腔轮虫Lecane curvicornis 萼花臂尾轮虫Brachionus calyciflorus 表 2 长江中游干流浮游动物物种数、密度和生物量调查结果
Table 2 Species name, density and biomass of zooplankton in the main stem of middle Yangtze River
江段/类群
River segment/
Taxa物种数
Species
number密度
Density
(ind./L)生物量
Biomass
(mg/m3)宜昌YC 8 2.19±2.13 8.50±7.17 荆州JZ 7 2.19±1.20 9.06±14.14 岳阳YY 5 2.19±2.13 3.19±3.59 武汉WH 8 10.94±5.81 21.25±11.52 湖口HK 9 4.38±0.72 15.31±9.32 轮虫Rotifera 16 3.41±0.21 4.09±0.25 枝角类Cladocera 3 0.22±0.02 4.38±0.47 桡足类Copepoda 4 0.75±0.07 3.00±0.25 表 3 长江中游干流样点理化参数
Table 3 Physical-chemical factors of sampling sites in the main stem of middle Yangtze River
环境因子Environmental factor 宜昌YC 荆州JZ 岳阳YY 武汉WH 湖口HK 水温T (℃) 21.9±0.3 19.6±0.2 19.0±1.3 15.6±0.2 13.5±0.1 溶解氧DO (mg/m3) 7.90±0.11 8.86±0.08 8.51±0.07 9.30±0.13 9.48±0.04 电导率σ (µs/cm) 272.5±0.4 263.5±0.5 255.3±31.2 274.8±50.7 227.3±0.6 盐度S (ppt) 0.14±0.00 0.14±0.00 0.14±0.01 0.16±0.03 0.14±0.00 pH 6.57±0.11 6.76±0.08 7.05±0.11 6.77±0.05 6.97±0.06 水深D (m) 5.5±2.2 — 5.4±2.9 6.0±3.7 7.5±4.6 透明度SD (cm) 160±4 — 54±34 24±3 21±5 流速V (m/s) 0.23±0.12 0.14±0.08 0.75±0.81 0.24* — 硝氮 $ {\rm{NO}}_3^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
1.80±0.10 1.53±0.02 1.66±0.22 1.54±0.05 1.61±0.20 亚硝氮 $ {\rm{NO}}_2^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
0.00±0.00 0.02±0.01 0.04±0.06 0.05±0.01 0.06±0.02 氨氮 $ {\rm{NH}}_3^ – {\text -} {\rm{N}}$ (mg/m3)
0.14±0.09 0.11±0.04 0.26±0.21 0.34±0.11 0.29±0.15 溶解性反应磷SRP (mg/m3) 0.03±0.00 0.09±0.02 0.08±0.02 0.08±0.02 0.06±0.01 叶绿素a Chl. a (mg/m3) 0.70±0.26 0.79±0.16 1.32±0.49 3.74±1.88 2.70±0.90 溶解性有机碳DOC (mg/m3) 8.63±3.29 4.11±0.60 3.22±0.65 6.90±0.82 — 注: —, 数据缺失; *, 一个样点数据Note: —, data missing; *, data from only one sampling site 表 4 长江中下游干流浮游动物历史数据对比
Table 4 Comparison of the species number, density and biomass of zooplankton with previous investigations
江段
River segment时间
Time物种数
Species number密度
Density (ind./L)生物量
Biomass (×102 mg/m3)数据来源
Data sources长江中游
Middle Yangtze River宜昌-城陵矶(8个江段) 2010 25—49 32.92—93.20 1.53—7.86 [12] 道人矶-杨林岩(3个江段) 2011—2012 81 — 0.09 [8] 昌口溪-熊家洲(9个江段) 2013—2015 34—96 66.25—509.44 0.23—11.36 [13] 宜昌-武汉(5个江段) 2016 a 23 4.38 0.01 本次调查 长江下游
Lower Yangtze River仪征-崇明(13个江段) 1988—1990 b 48—71 2.50—32.20 0.03—0.39 [14] 南京-海门(4个江段) 2004—2005 108 3.97—91.95a 0.31—4.03a [15] 青弋江-天然洲(3个江段) 2015 36—40 162.00—250.26 11.26—13.77 [16] 湖口-长江口(10个江段) 2016—2017 33—69 61.00—115.00 0.75—4.77 [17] 注: —, 数据缺失; a, 数据仅包括轮虫、枝角类、桡足类; b, 数据仅包括轮虫Note: —, data missing; a, data only includes rotifers, cladocerans and copepods; b, data only includes rotifers -
[1] 郭沛涌, 沈焕庭, 刘阿成, 等. 长江河口浮游动物的种类组成、群落结构及多样性. 生态学报, 2003, 23(5): 892—900 Guo P Y, Shen H T, Liu A C, et al. The species composition, community structure and diversity of zooplankton in Changjiang estuary [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(5): 892—900
[2] 纪焕红, 叶属峰. 长江口浮游动物生态分布特征及其与环境的关系. 海洋科学, 2006, 30(6): 23—30 Ji H H, Ye S F. Ecological distribution characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Yangtze River estuary [J]. Marine Sciences, 2006, 30(6): 23—30
[3] 吴利, 冯伟松, 张堂林, 等. 春、秋季武湖浮游动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系. 水生态学杂志, 2011, 32(2): 31—37 Wu L, Feng W S, Zhang T L, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community and its relation to environmental factors in Lake Wuhu in spring and autumn [J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2011, 32(2): 31—37
[4] 张晓可, 刘凯, 万安, 等. 安庆西江浮游动物群落结构及江豚生存状况评估. 水生生物学报, 2018, 42(2): 392—399 Zhang X K, Liu K, Wan A, et al. Community structure of zooplankton and its relationship with survivability of the Yangtze finless porpoise in Xijiang Oxbow, Anqing city [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2018, 42(2): 392—399
[5] 杨亮杰, 吕光汉, 竺俊全, 等. 横山水库浮游动物群落结构特征及水质评价. 水生生物学报, 2014, 38(4): 720—728 Yang L J, Lü G H, Zhu J Q, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community in hengshan reservoir and water quality assessment [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2014, 38(4): 720—728
[6] 陈受忠. 葛洲坝截流前后长江浮游动物的研究. 生态学杂志, 1985, 41(3): 1—4, 26 Chen S Z. Study on the ecology of zooplanktons before and after damming up Changjiang River [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1985, 41(3): 1—4, 26
[7] 彭刚, 边文冀, 陈校辉. 长江江苏段浮游动物群落结构调查报告. 水利渔业, 2008, 28(4): 109—111, 120 Peng G, Bian W J, Chen X H. Survey report on zooplankton community structure in Jiangsu section of Changjiang River [J]. Reservoir Fisheries, 2008, 28(4): 109—111, 120
[8] 游立新, 王珂, 祝坐满, 等. 长江中游江段水生生物资源调查及航道整治工程影响预测分析. 环境影响评价, 2017, 39(6): 43—46, 51 You L X, Wang K, Zhu Z M, et al. Aquatic biological resource survey in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and prediction analysis of the impact of navigation channel renovation [J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2017, 39(6): 43—46, 51
[9] 章宗涉, 黄祥飞. 淡水浮游生物研究方法. 北京: 科学出版社. 1991, 53—251 Zhang Z S, Huang X F. Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton [M]. Beijing: Science Press. 1991, 53—251
[10] 韩茂森. 淡水浮游生物图谱. 北京: 农业出版社. 1980, 44—107 Han M S. Maps of Freshwater Plankton [M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press. 1980, 44—107
[11] Oksanen J, Blanchet F G, Kindt R, et al. ‘vegan’: community ecology package, version 2. 3–2. (2015). https.cran.rproject.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf
[12] 李世健. 长江中游监利断面鱼类早期资源量及浮游生物群落结构特征初步研究. 硕士学位论文, 华中农业大学, 武汉. 2011 Li S J. Studies on resources of fish in early life history stages at Jianli section and characteristics of plankton community in the middle reach of Yangtze River [D]. Thesis for Master of Science. Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan. 2011
[13] 杨雪. 长江中段荆江航道整治工程对浮游生物和底栖动物群落的影响研究. 硕士学位论文, 华中师范大学, 武汉. 2016 Yang X. Responses of plankton and zoobenthos community characteristics to the Jingjiang channel regulation project in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River [D]. Thesis for Master of Science. Central China Normal University. Wuhan. 2016
[14] 韩德举, 胡菊香. 长江仪征-崇明段的轮虫调查. 动物学杂志, 1995, 30(1): 1—8 Han D J, Hu J X. A survey of the rotifers from Yizhen to Chongmin of Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 1995, 30(1): 1—8
[15] 陈校辉. 长江江苏段水生生物调查与研究. 硕士学位论文, 南京农业大学, 南京. 2007 Chen X H. Research of hydrobiology in the Yangtze River in Jiangsu province [D]. Thesis for Master of Science, Nanjing Agriculture University. Nanjing. 2007
[16] 谢满华, 任青松. 长江芜湖段水域浮游生物群落年度结构变化研究. 现代农业科技, 2016, (11): 239—241 Xie M H, Ren Q S. Annual changes of plankton community structure in Wuhu mainstream of Yangtze River [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, (11): 239—241
[17] 郭欧阳. 长江下游干流浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子相关性的研究, 上海师范大学, 上海. 2018 Guo O Y. Zooplankton community structure and its relation to environmental factors in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River [D]. Shanghai Normal University. Shanghai. 2018
[18] 姜作发, 唐富江, 董崇智, 等. 黑龙江水系主要江河浮游动物种群结构特征. 东北林业大学学报, 2006, 34(4): 64—66 Jiang Z F, Tang F J, Dong C Z, et al. Population structure of zooplankton in Heilongjiang River system [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2006, 34(4): 64—66
[19] 黎洁, 单保庆, 宋芬, 等. 永定河和滦河水系浮游动物多样性调查与分析. 华中农业大学学报, 2011, 30(6): 768—774 Li J, Shan B Q, Song F, et al. Investigation and analysis on biodiversity of zooplankton of Yongding River and Luanhe River in Haihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011, 30(6): 768—774
[20] 计勇, 张洁, 孙晓秋, 等. 赣江中下游浮游动物时空分布特征及水质综合评价. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(5): 509—513 Ji Y, Zhang J, Sun X Q, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of zooplankton and water quality assessment in middle and lower reaches of Ganjiang River [J]. Journal of Hohai University (
Natural Sciences ) , 2012, 40(5): 509—513 [21] 蔡庆华. 武汉东湖浮游生物间相互关系的多元分析. 中国科学院研究生院学报, 1995, 12(1): 97—102 Cai Q H. Multivariate analysis for the relation between zooplankton and phytoplank of lake Donghu, Wuhan [J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1995, 12(1): 97—102
[22] Pan B Z, Wang H J, Liang X M, et al. Factors influencing chlorophyll a concentration in the Yangtze-connected lakes [J]. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2009, 18(10): 1894—1900



 下载:
下载: