TAXONOMIC DISCUSSION OF GENUS EUBLEEKERIA FROM THE COASTAL WATERS OF CHINA
-
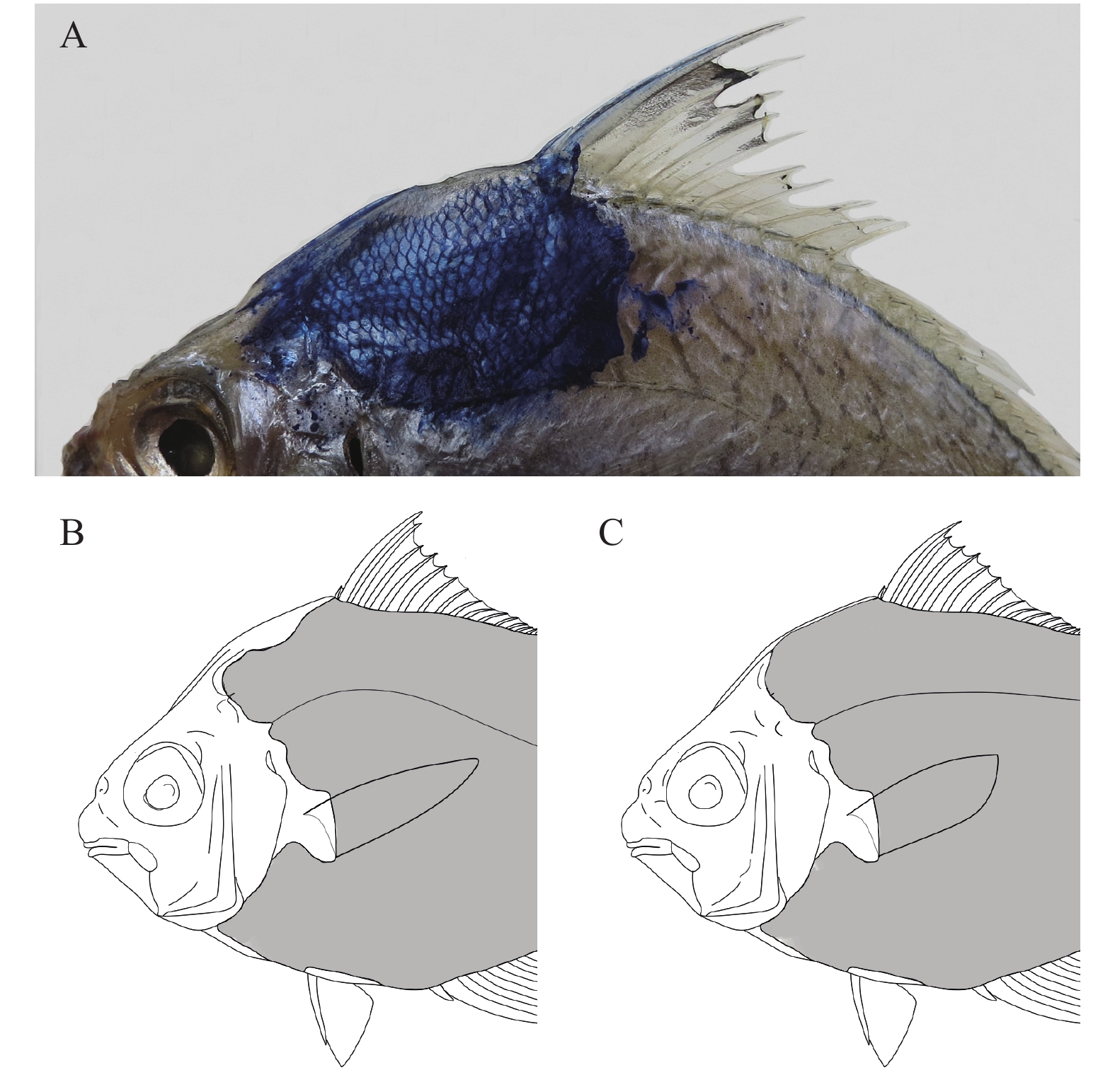
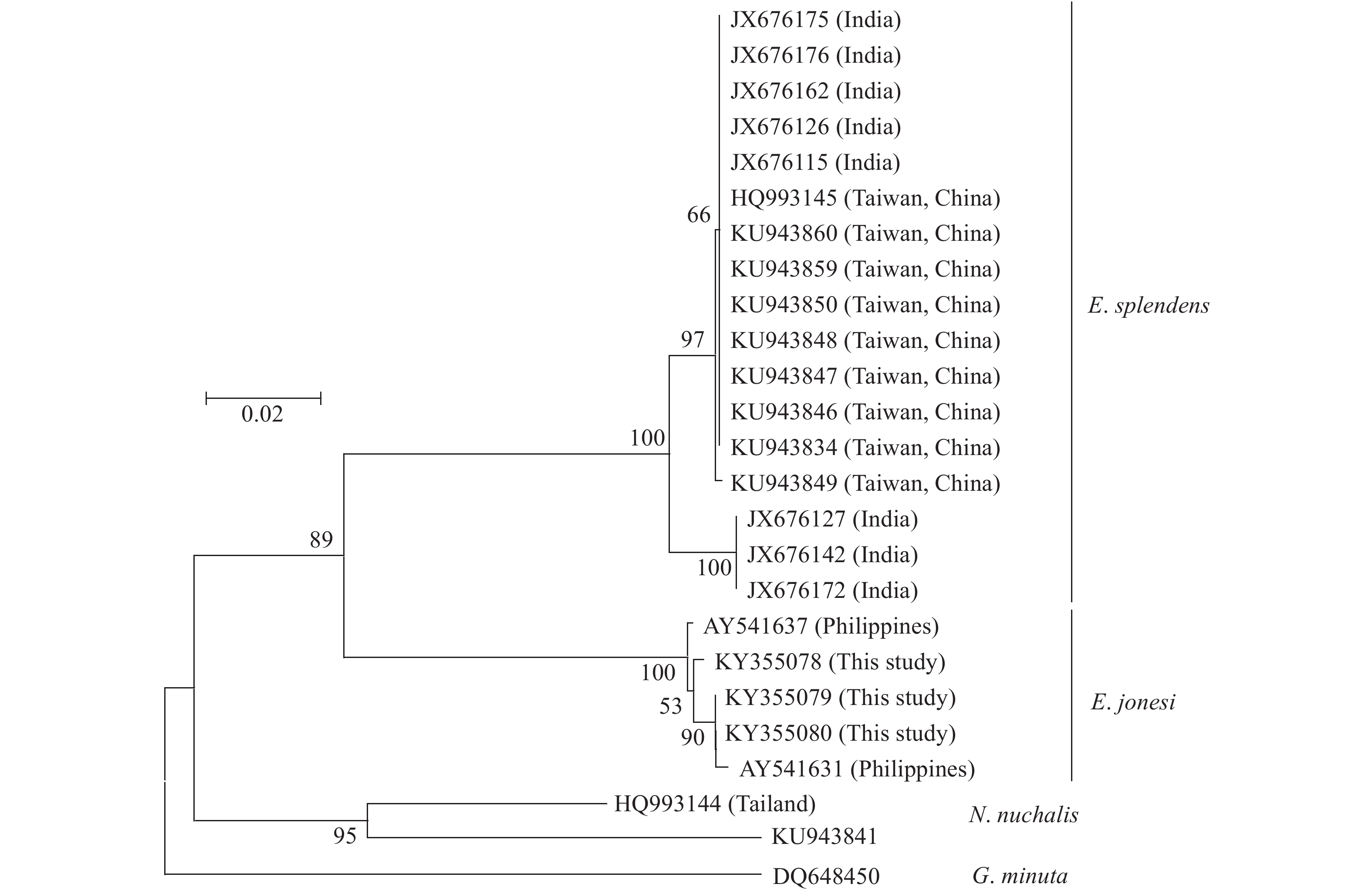
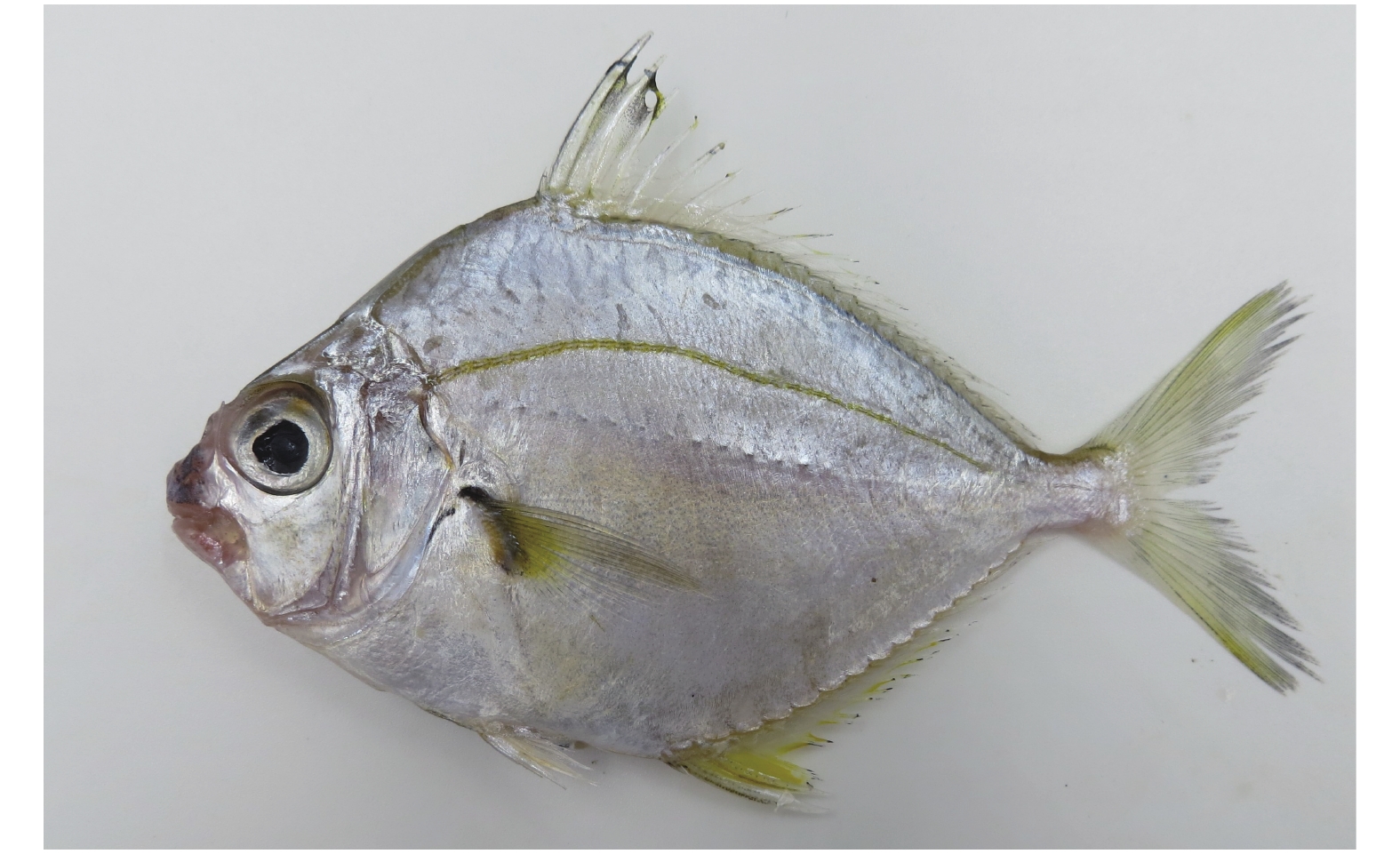
摘要: 研究旨在利用传统形态学与DNA条形码技术相结合的方法, 进一步探讨中国布氏鲾属Eubleekeria Fowler 1904鱼类的分类与鉴定问题。2014—2016年从广东湛江和广西北海、防城港和东兴近海采集了153尾鲾科鱼类样品, 经形态学鉴定为布氏鲾属种类: 琼斯氏布氏鲾Eubleekeria jonesi (James, 1971)。该种主要鉴别特征为: 眼位于口裂的水平线之上, 颊部无鳞, 两臀鳍之间区域裸露无鳞, 颈部有半圆形裸露无鳞区域, 背鳍上黑斑色淡, 略呈灰色。将其鉴别特征与相关文献记录比较, 表明之前中国大陆记录的黑边布氏鲾Eubleekeria splendens (Cuvier, 1829)可能为琼斯氏布氏鲾。基于线粒体COⅠ基因片段结合GenBank中布氏鲾属鱼类的同源序列, 采用邻接法构建的分子系统树显示, 此研究中采集自中国大陆的布氏鲾属鱼类标本与中国台湾记录的黑边布氏鲾Eubleekeria splendens (Cuvier, 1829)明显地分为两支。基于Kimura双参数模型(K2P)计算, 支系间遗传距离为0.130, 远大于支系内平均遗传距离(0.005和0.006), 支持将二者作为独立物种的观点, 与此研究传统形态学方法的结果一致。Abstract: Ponyfishes of genus Eubleekeria, order Perciformes, Leiognathidae family, are widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific. They are small edible fish. Using molecular methods and morphological analysis, the taxonomy of genus Eubleekeria in coastal waters of China was discussed. We collected 153 specimens of ponyfish from four locations (Zhanjiang, Beihai, Fangchenggang and Dongxing) of Chinese coastal waters during 2014—2015. All individuals were identified as Eubleekeria jonesi (James, 1971). The diagnosis features were as follows: when mouth is closed, the lower orbital margin above horizontal line passed through the gape; the cheeks are exposed and the interspace of pelvic keels is naked; the dark blotch on the dorsal fin are dark gray; nape with a semicircular naked area. After re-examining the taxonomy books in mainland China, we found that the species identified as Leiognathus splendens or Eubleekeria splendens (Cuvier, 1829) may be E. jonesi. We also analyzed the COI sequences of E. jonesi and related species. The mean genetic distances by Kimura-2-parameter model within E. jonesi and E. splendens were 0.005 and 0.006, respectively; and the average genetic distance between E. jonesi and E. splendens was 0.130, which supports their separate species status. The results are consistent with the morphological method in this study.
-
Keywords:
- Eubleekeria /
- Eubleekeria jonesi /
- Eubleekeria splendens /
- Identification /
- Morphology /
- DNA barcoding
-
-
表 1 琼斯氏布氏鲾的采样信息
Table 1 Sampling information of Eubleekeria jonesi
采样地点Sampling site 采样时间Sampling time 数量Number 广东湛江Zhanjiang 2014.09.25 45 2014.12.15 27 2016.01.26 24 广西北海Beihai 2015.03.06 34 广西防城港Fangchenggang 2014.10.25 11 广西东兴Dongxing 2015.09.23 12 表 2 从GenBank下载的COⅠ序列信息
Table 2 Information of cited COⅠsequences downloaded from GenBank
物种Species 采样地点Sampling site GenBank序列号GenBank accession number 琼斯氏布氏鲾
E. jonesi泰国 HQ993144 菲律宾 AY541631 黑边布氏鲾
E. splendens中国台湾 KU943860 KU943859 KU943850 KU943849 KU943848 KU943847 KU943846 KU943834 HQ993145 菲律宾 AY541637 印度 JX676176 JX676175 JX676172 JX676162 JX676142 JX676127 JX676126 JX676115 项斑鲾Nuchequula nuchalis 中国台湾 KU943841 小牙鲾Gazza minuta 菲律宾 DQ648450 表 3 琼斯氏布氏鲾和黑边布氏鲾的可数、可量性状
Table 3 Counts and measurements of E. jonesi and E. splendens
性状Character 琼斯氏布氏鲾Eubleekeria jonesi
本研究琼斯氏布氏鲾Eubleekeria jonesi James[36] 琼斯氏布氏鲾Eubleekeria jonesi Kimura等[20] 黑边布氏鲾
Eubleekeria splendens
Kimura等[20]体长 Standard length (mm) 72.7—111.6 (88.7, 32) 35—95 33—139 (78.8, 99) 38—125 (71.5, 146) 背鳍Dorsal fin ray VIII, 16 VIII, 16 VIII, 16 (99) VIII—IX, 15—17 (16.0, 146) 臀鳍Anal fin ray III, 14 III, 14 III, 14—15 (14.0, 99) III, 13—15 (14.0, 146) 胸鳍Pectoral fin ray 17—19 (17.8, 32) \ 16—19 (18.0, 99) 16—19 (17.3, 146) 侧线鳞Lateral line scale 42—53 (47.1, 32) 40—53 50—61 (54.3, 99) 50—66 (56.7, 142) 侧线上鳞Scales above lateral line 8—11 (9.9, 32) 11—13 9—14 (11.6, 71) 9—26 (13.1, 142) 侧线下鳞Scales below lateral line 21—26 (22.8, 2) 22—26 22—28 (24.8, 71) 12—33 (27.1, 141) 上鳃耙数Gill rakers on upper arch 5—7 (6.2, 32) 5—7 5—7 (5.8, 99) 4—7 (5.7, 145) 下鳃耙数Gill rakers on lower arch 18—21(19.8, 32) 21—24 19—24 (20.9, 99) 18—24 (20.6, 145) 头长/体长Head length/Standard length 29.3—32.7 (30.4, 32) 25—34 29—34 (31.4, 98) 29—35 (31.9, 145) 背鳍前长/体长Pre-dorsal length/Standard length 46.3—50.4 (48.2, 32) \ 46—51 (48.5, 99) 42—51 (46.4, 142) 背鳍基长/体长Length of dorsal fin base/Standard length 55.2—60.2 (57.3, 32) \ 54—60 (57.7, 99) 53—61 (57.6, 146) 臀鳍基长/体长Length of anal fin base/Standard length 42.7—49.4 (45.5, 32) \ 44—51 (46.4, 99) 42—50 (45.3, 146) 胸鳍起点至腹鳍起点长/体长Distance between pectoral fin and pelvic fin origins/Standard length 23.6—26.6 (24.6, 32) \ 23—26 (24.5, 99) 19—26 (22.6, 145) 腹鳍起点至臀鳍起点长/体长Distance between pelvic fin and anal fin origins/Standard length 16.1—21.2 (18.7, 32) \ 14—21 (17.8, 96) 15—22 (18.6, 135) 尾柄长/体长Length of caudal peduncle/Standard length 7.8—14.5 (10.7, 32) \ 9.1—14 (11.3, 99) 9.0—13 (10.9, 146) 体高/体长Body depth/Standard length 49.6—56.7 (53.9, 32) 51—56 51—58 (54.5, 99) 42—60 (50.5, 146) 尾柄高/体长Depth of caudal peduncle/Standard length 7.0—8.5 (7.7, 32) \ 6.6—8.7 (7.59, 99) 5.8—9.3 (7.28, 146) 吻长/头长Snout length/Head length 21.8—30.8 (27.3, 32) \ 26—36 (31.6, 98) 24—37 (28.9, 145) 眼径/头长Eye diameter/Head length 33.5—42.5 (37.0, 32) 33—44 30—40 (34.8, 98) 31—40 (35.5, 145) 上颌长/头长Upper jaw length/Head length 28.4—36.7 (31.6, 32) \ 32—44 (36.1, 98) 23—38 (33.9, 104) 眼间距/头长Interorbital width/Head length 24.3—33.4 (28.1, 32) \ 22—32 (26.2, 98) 25—36 (28.2, 145) 背鳍第二硬棘长/头长Length of the 2nd dorsal fin spine/Head length 56.7—75.4 (67.7, 22) \ 65—80 (71.9, 31) 59—80 (68.3, 108) 臀鳍第二硬棘长/头长Length of the 2nd anal fin spine/Head length 47.1—62.5 (54.1, 27) \ 50—68 (59.7, 53) 46—71 (56.8, 117) 胸鳍长/头长Length of pectoral fin/Head length 73.1—93.9 (81.2, 32) \ 74—91 (83.5, 83) 66—87 (78.4, 140) 腹鳍长/头长Length of pelvic fin/Head length 27.4—39.6 (32.0, 32) \ 30—39 (34.9, 87) 32—47 (38.2, 129) 注: 括号内为平均值和测量的标本数; 可量性状与体长、头长的比值(%)Note: The mean value and the number of specimens measured are shown in brackets; The ratios of measurable characters and standard length or head length (%) -
[1] McFall-Ngai M J, Dunlap P V. External and internal sexual dimorphism in leiognathid fishes: Morphological evidence for sex-specific bioluminescent signaling [J]. Journal of Morphology, 1984, 182(1): 71-83. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051820105
[2] Woodland D J, Premcharoen S, Cabanban A S. Leiognathidae: Slipmouths (ponyfishes) [M]//Carpenter K E, Niem V H (Eds.), Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes. The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific. Bony Fishes part 3 (Menidae to Pomacentridae). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization, 2001: 2792-2823
[3] Abraham K J, Joshi K K, Murty V S. Taxonomy of the fishes of the family Leiognathidae (Pisces, Teleostei) from the West coast of India [J]. Zootaxa, 2011(2886): 1-18.
[4] 郑文莲. 鲾科//朱元鼎, 张春霖, 成庆泰. 南海鱼类志 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1962: 438-454. Zheng W L. Family Leiognathidae [M]//Zhu Y D, Zhang C L, Cheng Q T (Eds.), Fishes of South China Sea. Beijing: Science Press, 1962: 438-454.
[5] Seigel J A. Median fin-spine locking in the ponyfishes (Perciformes: Leiognathidae) [J]. Copeia, 1982, 1982(1): 202-205. doi: 10.2307/1444296
[6] Chakrabarty P, Davis M P, Smith W L, et al. Is sexual selection driving diversification of the bioluminescent ponyfishes (Teleostei: Leiognathidae) [J]? Molecular Ecology, 2011, 20(13): 2818-2834. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05112.x
[7] Nelson J S. Fishes of the World. Third Edition [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1994: 600
[8] Chakrabarty P, Sparks J S. Diagnoses for Leiognathus Lacepede 1802, Equula Cuvier 1815, Equulites Fowler 1904, Eubleekeria Fowler 1904, and a new ponyfish genus (Teleostei: Leiognathidae) [J]. American Museum Novitates, 2008, 3623(7): 1-11.
[9] Kottelat M. The fishes of the inland waters of Southeast Asia: a catalogue and core bibliography of the fishes known to occur in freshwaters, mangroves and estuaries [J]. Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 2013(27): 663.
[10] Eschmeyer W N, Fricke R, Van der Laan R. Catalog of fishes: genera, species, references [EB/OL]. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp, accessed 2019-07-08.
[11] Froese R, Pauly D. FishBase: World Wide Web electronic publication [DB/OL]. http://www.fishbase.org, version (04/2019).
[12] 田明诚. 鲾科 [M]//成庆泰, 郑葆珊. 中国鱼类系统检索. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 324-326. Tian M C. Family Leiognathidae [M]//Cheng Q T, Zheng B S (Eds.), Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 324-326.
[13] 黄宗国, 林茂. 中国海洋生物图集第八册 [M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012: 70-71. Huang Z G, Lin M. Atlas of Marine Biota in China Volume 8 [M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2012: 70-71.
[14] 陈大刚, 张美昭. 中国海洋鱼类 [M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社. 2015: 1114-1123. Chen D G, Zhang M Z. Marine Fishes of China [M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2015: 1114-1123.
[15] 刘静, 陈咏霞, 马琳. 黄渤海鱼类图志 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2015: 176-177. Liu J, Chen Y X, Ma L. Fishes of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015: 176-177.
[16] Shao K T. The Fish Datebase of Taiwan [DB/OL]. WWW Web electronic publication. http://fishdb.sinica.edu.tw, accessed 2019-07-08.
[17] Whitley G P. Some fishes of the family Leiognathidae [J]. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum, 1932(10): 99-116.
[18] James P. Comparative Osteology of the fishes of the family Leiognathidae Part I: Osteology [J]. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 1985, 32(3): 309-358.
[19] Jones G. Revision of the Australian species of the fish family Leiognathidae [J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 1985, 36(4): 559-613. doi: 10.1071/MF9850559
[20] Kimura S, Ito T, Peristiwady T, et al. The Leiognathus splendens complex (Perciformes: Leiognathidae) with the description of a new species, Leiognathus kupanensis Kimura and Peristiwady [J]. Ichthyological Research, 2005, 52(3): 275-291. doi: 10.1007/s10228-005-0283-5
[21] Kimura S, Ikejima K, Iwatsuki Y. Eubleekeria Fowler 1904, a valid genus of Leiognathidae (Perciformes) [J]. Ichthyological Research, 2008, 55(2): 202-203. doi: 10.1007/s10228-007-0025-y
[22] 郑文莲. 鲾科 [M]//朱元鼎, 张春霖, 成庆泰. 东海鱼类志. 北京: 科学出版社, 1963: 294-299. Zheng W L. Family Leiognathidae [M]//Zhu Y D, Zhang C L, Cheng Q T (Eds.), Fishes of East China Sea. Beijing: Science Press, 1963: 294-299.
[23] 黄宗强. 鲾科 [M]//朱元鼎. 福建鱼类志. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 1985: 136-145. Huang Z Q. Family Leiognathidae [M]//Zhu Y D (Eds.), The Fishes of Fujian Province. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Publishing House, 1985: 136-145.
[24] 沈世杰. 台湾鱼类志 [M]. 中国台湾: 台湾大学动物学系出版社, 1993: 342-346. Shen S C. Fishes of Taiwan [M]. Taiwan, China: Taiwan University Zoology Department Press, 1993: 342-346.
[25] 孙典荣, 陈铮. 南海鱼类检索 [M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 2013: 539-540. Sun D Y, Chen Z. Synopsis of Fishes in the South China Sea [M]. Beijing: Ocean Press. 2013: 539-540.
[26] 赖延和, 何斌源. 广西北部湾海洋硬骨鱼类图鉴 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 192-197. Lai Y H, He B Y. Marine Osteichthyes Fishes in Guangxi Beibu Gulf of China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 192-197.
[27] 刘静, 吴仁协, 康斌, 等. 北部湾鱼类图鉴 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 158-166. Liu J, Wu R X, Kang B, et al. Fishes of Beibu Gulf [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 158-166.
[28] Hebert P D N, Penton E H, Burns J M, et al. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2004, 101(41): 14812-14817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406166101
[29] 郭爱民, 喀迪尔丁·艾尔肯, 焦丽, 等. 额尔齐斯河流域不同来源哲罗鲑形态及COⅠ基因比较研究 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2020, 40(1): 36-43. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716x Guo A M, Kadirdin Alken, Jiao L, et al. Morphology and COⅠ genes of different sources of Hucho taimen in the Irtysh river basin [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 36-43. [ doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716x
[30] Gross M. Barcoding biodiversity [J]. Current Biology, 2012, 22(3): R73-R76. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.036
[31] Pauls S U, Blahnik R J, Zhou X, et al. DNA barcode data confirm new species and reveal cryptic diversity in Chilean smicridea (Smicridea) (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) [J]. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 2010, 29(3): 1058-1074. doi: 10.1899/09-108.1
[32] Gao T X, Ji D P, Xiao Y S, et al. Description and DNA barcoding of a new sillago species, Sillago sinica (Perciformes: Sillaginidae), from coastal waters of China [J]. Zoological Studies, 2011, 50(2): 254-263.
[33] Puckridge M, Andreakis N, Appleyard S A, et al. Cryptic diversity in flathead fishes (Scorpaeniformes: Platycephalidae) across the Indo-West Pacific uncovered by DNA barcoding [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2013, 13(1): 32-42. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12022
[34] Xiao J G, Song N, Han Z Q, et al. Description and DNA barcoding of a new Sillago species, Sillago shaoi (Perciformes: Sillaginidae), in the Taiwan Strait [J]. Zoological Studies, 2016, 55(47): 55-47.
[35] Ward R D, Zemlak T S, Innes B H, et al. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1462): 1847-1857. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716
[36] James P. A new species of silver-belly, Leiognathus jonesi (Family Leiognathidae: Pisces) from the Indian Seas [J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India, 1969, 11(1&2): 316-319.
[37] Sparks J S, Dunlap P V, Smith W L. Evolution and diversification of a sexually dimorphic luminescent system in ponyfishes (Teleostei: Leiognathidae), including diagnoses for two new genera [J]. Cladistics, 2005, 21(4): 305-327. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2005.00067.x
[38] Ward R D R. DNA barcode divergence among species and genera of birds and fishes [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2010, 9(4): 1077-1085.




 下载:
下载: